Understanding Arc Flash Hazards
... the worker’s risk of sustaining more than a second-degree burn during an electrical arc flash incident (defined as occurring at 1.2 cal/cm2). Choosing inadequate PPE can lead to even more severe burns. Injuries occur because of flash burns from the heat generated by the electric arc and by flame bur ...
... the worker’s risk of sustaining more than a second-degree burn during an electrical arc flash incident (defined as occurring at 1.2 cal/cm2). Choosing inadequate PPE can lead to even more severe burns. Injuries occur because of flash burns from the heat generated by the electric arc and by flame bur ...
M43067982
... rectifier circuits, followed by the second stage of dcdc converter using high frequency transformer. These two stages of power conversion has the problem of power quality in terms of harmonic current at ac mains, voltage distortion, reduced power factor, high peak factor and require a large size of ...
... rectifier circuits, followed by the second stage of dcdc converter using high frequency transformer. These two stages of power conversion has the problem of power quality in terms of harmonic current at ac mains, voltage distortion, reduced power factor, high peak factor and require a large size of ...
Uninterruptible Power Supply - Mitsubishi Electric Power Products, Inc.
... bypass and control circuitry, the 9800A UPS can be utilized in Single- (SMS) or Multi-module (MMS) configurations. This allows for a highly reliable and flexible system approach. If loads on a MMS decrease, a module or modules can be removed and used elsewhere in a single module application. Likewis ...
... bypass and control circuitry, the 9800A UPS can be utilized in Single- (SMS) or Multi-module (MMS) configurations. This allows for a highly reliable and flexible system approach. If loads on a MMS decrease, a module or modules can be removed and used elsewhere in a single module application. Likewis ...
BD82022FVJ
... source line and IC. This may cause bad effects on IC operations. In order to avoid this case, connect a bypass capacitor CIN across IN terminal and GND terminal of IC. 1µF or higher is recommended. In order to decrease voltage fluctuations of power source line to IC, connect a low ESR capacitor in p ...
... source line and IC. This may cause bad effects on IC operations. In order to avoid this case, connect a bypass capacitor CIN across IN terminal and GND terminal of IC. 1µF or higher is recommended. In order to decrease voltage fluctuations of power source line to IC, connect a low ESR capacitor in p ...
Paper Title (use style: paper title)
... The boost converter is one of the most important non isolated step-up converter, however the operation with high input current and high output voltage, became impracticable the development of high performance converter, due to efficiency degradation and dynamic range limitation. Although, a dc–dc bo ...
... The boost converter is one of the most important non isolated step-up converter, however the operation with high input current and high output voltage, became impracticable the development of high performance converter, due to efficiency degradation and dynamic range limitation. Although, a dc–dc bo ...
DRAFT SOUTH AFRICAN STANDARD (DSS): PUBLIC ENQUIRY STAGE Document number
... driven generating set applications and supplements the requirements given in IEC 60034-1. It covers the use of such generators for land and marine use, but excludes generating sets used on aircraft or used to propel land vehicles and locomotives. NOTE 1 For some specific applications (e.g. essential ...
... driven generating set applications and supplements the requirements given in IEC 60034-1. It covers the use of such generators for land and marine use, but excludes generating sets used on aircraft or used to propel land vehicles and locomotives. NOTE 1 For some specific applications (e.g. essential ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQS) Chapter 2: Thyristor
... 2.23 The average on-state current for an SCR is 20 A for a resistive load. If an inductance of 5 mH is included in the load, then average on-state current would be (a) more than 20 A (b) less than 20 A (c) 15 A (d) 20 A 2.24 In a thyristor, anode current is made up of (a) electrons only (b) electron ...
... 2.23 The average on-state current for an SCR is 20 A for a resistive load. If an inductance of 5 mH is included in the load, then average on-state current would be (a) more than 20 A (b) less than 20 A (c) 15 A (d) 20 A 2.24 In a thyristor, anode current is made up of (a) electrons only (b) electron ...
Fault Finding in Thyristor Equipment
... change in operational conditions has been made or after a routine maintenance check, etc, Always study the recent history; it may be a clue to the fault and it may even be the change which has caused the fault to occur. For example, a change in the load process may result in additional current loadi ...
... change in operational conditions has been made or after a routine maintenance check, etc, Always study the recent history; it may be a clue to the fault and it may even be the change which has caused the fault to occur. For example, a change in the load process may result in additional current loadi ...
Introduction to Power Electronics
... concerned of electrical power processing using electronic devices the key component of which is a switching power converter. Power electronics has found an important place in modern technology being a core of power and energy control. Almost all the new electrical and electromechanical equipment con ...
... concerned of electrical power processing using electronic devices the key component of which is a switching power converter. Power electronics has found an important place in modern technology being a core of power and energy control. Almost all the new electrical and electromechanical equipment con ...
Amplificador de potência cmos em 2.4 ghz com potência de saída
... TABLE 2 – Gate widths of power cascodes and designation of operating modes. From [20]. ... 45 TABLE 3 – Example of width impact in a power amplifier design. The first row shows the obtained results for a 150 µm gate width transistor, the second column for a 175 µm transistor and the third for a 200 ...
... TABLE 2 – Gate widths of power cascodes and designation of operating modes. From [20]. ... 45 TABLE 3 – Example of width impact in a power amplifier design. The first row shows the obtained results for a 150 µm gate width transistor, the second column for a 175 µm transistor and the third for a 200 ...
Advanced Current-Mode Active Clamp PWM
... This is a direct input to the PWM and current limit comparators of the UCC2897 controller. The CS pin should never be connected directly across the current sense resistor (RCS) of the power converter. A small, customary R−C filter between the current sense resistor and the CS pin is necessary to acc ...
... This is a direct input to the PWM and current limit comparators of the UCC2897 controller. The CS pin should never be connected directly across the current sense resistor (RCS) of the power converter. A small, customary R−C filter between the current sense resistor and the CS pin is necessary to acc ...
LC05111CMT
... of CHG_SW FET. If CS pin voltage will get higher than discharging over-current detection current 2 (Ioc2) over the delay time of discharging over-current 2 (Toc2), discharging will be shut off, because internal power FETs as DCHG_SW is turned off.(short-circuit detection mode) After detecting short- ...
... of CHG_SW FET. If CS pin voltage will get higher than discharging over-current detection current 2 (Ioc2) over the delay time of discharging over-current 2 (Toc2), discharging will be shut off, because internal power FETs as DCHG_SW is turned off.(short-circuit detection mode) After detecting short- ...
LinAire Test Panels LTS-525/A TEST SET FOR THE
... 2.10 This Test Panel measures 7” high, 19” wide and 5 3/4” deep. It is compatible with all standard relay racks and cabinets or may be used as a stand alone unit. 2.20 Power Requirements: 115VAC 400HZ Terminal ID: AC HI, AC LO, Frame GND 2.30 It is recommended that a minimum size of 18 gauge wire be ...
... 2.10 This Test Panel measures 7” high, 19” wide and 5 3/4” deep. It is compatible with all standard relay racks and cabinets or may be used as a stand alone unit. 2.20 Power Requirements: 115VAC 400HZ Terminal ID: AC HI, AC LO, Frame GND 2.30 It is recommended that a minimum size of 18 gauge wire be ...
Loading Considerations when Paralleling Transformers
... of these applications. Their main objectives are reliability and power quality along with keeping consumers on-line. Utility power engineers understand very well the operation of paralleling transformers when it comes to load sharing between transformers and when circulating currents exist. Many tim ...
... of these applications. Their main objectives are reliability and power quality along with keeping consumers on-line. Utility power engineers understand very well the operation of paralleling transformers when it comes to load sharing between transformers and when circulating currents exist. Many tim ...
Rast 5 Power Relay 419 EA
... pole 16A, 2 form A ( 2 NO) contacts mains insulation n Quick connect terminals 6.3x0.8mm n Contact gap >3mm n 4kV/8mm coil-contact n Snap or screw mounting n Product in accordance to IEC 60335-1 n Safety ...
... pole 16A, 2 form A ( 2 NO) contacts mains insulation n Quick connect terminals 6.3x0.8mm n Contact gap >3mm n 4kV/8mm coil-contact n Snap or screw mounting n Product in accordance to IEC 60335-1 n Safety ...
TDA8920C 2 x 110 W class-D power amplifier
... external resistor, ROSC, connected between pins OSC and VSSA. The optimal carrier frequency setting is between 250 kHz and 450 kHz. The carrier frequency is set to 345 kHz by connecting an external 30 kΩ resistor between pins OSC and VSSA. See Table 9 on page 14 for more details. If two or more clas ...
... external resistor, ROSC, connected between pins OSC and VSSA. The optimal carrier frequency setting is between 250 kHz and 450 kHz. The carrier frequency is set to 345 kHz by connecting an external 30 kΩ resistor between pins OSC and VSSA. See Table 9 on page 14 for more details. If two or more clas ...
NCP1060 - High-Voltage Switcher for Low Power Offline SMPS
... reduces further, it enters into a skip mode to reduce the standby consumption down to a no load condition. Protection features include: a timer to detect an overload or a short−circuit event, Overvoltage Protection with auto−recovery and AC input line voltage detection (A version). The ON proprietar ...
... reduces further, it enters into a skip mode to reduce the standby consumption down to a no load condition. Protection features include: a timer to detect an overload or a short−circuit event, Overvoltage Protection with auto−recovery and AC input line voltage detection (A version). The ON proprietar ...
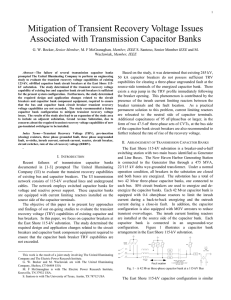
Mitigation of Transient Recovery Voltage Issues Associated with
... symmetrical three-phase ungrounded fault at or near the breaker terminals during which the system voltage is at maximum. Since the resulting prospective system TRV is greatly influenced by the design of the circuit breaker, an idealized circuit breaker is used. Therefore, when the breaker conducts, ...
... symmetrical three-phase ungrounded fault at or near the breaker terminals during which the system voltage is at maximum. Since the resulting prospective system TRV is greatly influenced by the design of the circuit breaker, an idealized circuit breaker is used. Therefore, when the breaker conducts, ...
Aalborg Universitet Selective harmonic control for power converters
... Obviously, the above stability criteria for the SHC system can be derived from that for the parallel structure RC system [16]-[18], and is compatible to those for other RC systems [10], [13], [14]. For the larger cluster of harmonic frequencies, larger control gains will be assigned to the correspon ...
... Obviously, the above stability criteria for the SHC system can be derived from that for the parallel structure RC system [16]-[18], and is compatible to those for other RC systems [10], [13], [14]. For the larger cluster of harmonic frequencies, larger control gains will be assigned to the correspon ...
Power engineering

Power engineering, also called power systems engineering, is a subfield of energy engineering that deals with the generation, transmission, distribution and utilization of electric power and the electrical devices connected to such systems including generators, motors and transformers. Although much of the field is concerned with the problems of three-phase AC power – the standard for large-scale power transmission and distribution across the modern world – a significant fraction of the field is concerned with the conversion between AC and DC power and the development of specialized power systems such as those used in aircraft or for electric railway networks. It was a subfield of electrical engineering before the emergence of energy engineering.Electricity became a subject of scientific interest in the late 17th century with the work of William Gilbert. Over the next two centuries a number of important discoveries were made including the incandescent light bulb and the voltaic pile. Probably the greatest discovery with respect to power engineering came from Michael Faraday who in 1831 discovered that a change in magnetic flux induces an electromotive force in a loop of wire—a principle known as electromagnetic induction that helps explain how generators and transformers work.In 1881 two electricians built the world's first power station at Godalming in England. The station employed two waterwheels to produce an alternating current that was used to supply seven Siemens arc lamps at 250 volts and thirty-four incandescent lamps at 40 volts. However supply was intermittent and in 1882 Thomas Edison and his company, The Edison Electric Light Company, developed the first steam-powered electric power station on Pearl Street in New York City. The Pearl Street Station consisted of several generators and initially powered around 3,000 lamps for 59 customers. The power station used direct current and operated at a single voltage. Since the direct current power could not be easily transformed to the higher voltages necessary to minimise power loss during transmission, the possible distance between the generators and load was limited to around half-a-mile (800 m).That same year in London Lucien Gaulard and John Dixon Gibbs demonstrated the first transformer suitable for use in a real power system. The practical value of Gaulard and Gibbs' transformer was demonstrated in 1884 at Turin where the transformer was used to light up forty kilometres (25 miles) of railway from a single alternating current generator. Despite the success of the system, the pair made some fundamental mistakes. Perhaps the most serious was connecting the primaries of the transformers in series so that switching one lamp on or off would affect other lamps further down the line. Following the demonstration George Westinghouse, an American entrepreneur, imported a number of the transformers along with a Siemens generator and set his engineers to experimenting with them in the hopes of improving them for use in a commercial power system.One of Westinghouse's engineers, William Stanley, recognised the problem with connecting transformers in series as opposed to parallel and also realised that making the iron core of a transformer a fully enclosed loop would improve the voltage regulation of the secondary winding. Using this knowledge he built a much improved alternating current power system at Great Barrington, Massachusetts in 1886. In 1885 the Italian physicist and electrical engineer Galileo Ferraris demonstrated an induction motor and in 1887 and 1888 the Serbian-American engineer Nikola Tesla filed a range of patents related to power systems including one for a practical two-phase induction motor which Westinghouse licensed for his AC system.By 1890 the power industry had flourished and power companies had built thousands of power systems (both direct and alternating current) in the United States and Europe – these networks were effectively dedicated to providing electric lighting. During this time a fierce rivalry in the US known as the ""War of Currents"" emerged between Edison and Westinghouse over which form of transmission (direct or alternating current) was superior. In 1891, Westinghouse installed the first major power system that was designed to drive an electric motor and not just provide electric lighting. The installation powered a 100 horsepower (75 kW) synchronous motor at Telluride, Colorado with the motor being started by a Tesla induction motor. On the other side of the Atlantic, Oskar von Miller built a 20 kV 176 km three-phase transmission line from Lauffen am Neckar to Frankfurt am Main for the Electrical Engineering Exhibition in Frankfurt. In 1895, after a protracted decision-making process, the Adams No. 1 generating station at Niagara Falls began transmitting three-phase alternating current power to Buffalo at 11 kV. Following completion of the Niagara Falls project, new power systems increasingly chose alternating current as opposed to direct current for electrical transmission.Although the 1880s and 1890s were seminal decades in the field, developments in power engineering continued throughout the 20th and 21st century. In 1936 the first commercial high-voltage direct current (HVDC) line using mercury-arc valves was built between Schenectady and Mechanicville, New York. HVDC had previously been achieved by installing direct current generators in series (a system known as the Thury system) although this suffered from serious reliability issues. In 1957 Siemens demonstrated the first solid-state rectifier (solid-state rectifiers are now the standard for HVDC systems) however it was not until the early 1970s that this technology was used in commercial power systems. In 1959 Westinghouse demonstrated the first circuit breaker that used SF6 as the interrupting medium. SF6 is a far superior dielectric to air and, in recent times, its use has been extended to produce far more compact switching equipment (known as switchgear) and transformers. Many important developments also came from extending innovations in the ICT field to the power engineering field. For example, the development of computers meant load flow studies could be run more efficiently allowing for much better planning of power systems. Advances in information technology and telecommunication also allowed for much better remote control of the power system's switchgear and generators.