Chapter 35.3 The Endocrine System (pages
... b. Pituitary gland i. Located at base of brain ii. “Master gland” because it regulates so many body functions iii. Regulates other glands – thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes ...
... b. Pituitary gland i. Located at base of brain ii. “Master gland” because it regulates so many body functions iii. Regulates other glands – thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes ...
Chapter 11 Quiz
... 1. Endocrine glands secrete their products into ducts. A. True *B. False 2. Those hormones that are nonpolar can pass through the plasma membrane and are called A. hydrophilic. B. hydrophobic. C. lipophilic. *D. Both hydrophobic and lipophilic are correct. 3. Responsiveness of cells to hormones is d ...
... 1. Endocrine glands secrete their products into ducts. A. True *B. False 2. Those hormones that are nonpolar can pass through the plasma membrane and are called A. hydrophilic. B. hydrophobic. C. lipophilic. *D. Both hydrophobic and lipophilic are correct. 3. Responsiveness of cells to hormones is d ...
020409 Endocrine System gl 2842KB Jan
... • ACTH – (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) stimulates growth of the adrenal cortex & release of corticosteroids • FSH – (Follicle stimulating hormone) ovarian release • LH – (Luteinzing hormone) - ovarian ...
... • ACTH – (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) stimulates growth of the adrenal cortex & release of corticosteroids • FSH – (Follicle stimulating hormone) ovarian release • LH – (Luteinzing hormone) - ovarian ...
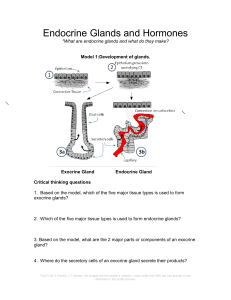
Physioactivity 1: Endocrine glands
... 10. Just looking at the structures in model 1B, do any of these hormones look similar to one another? a. Which ones look similar? b. What is the same about all of them? ...
... 10. Just looking at the structures in model 1B, do any of these hormones look similar to one another? a. Which ones look similar? b. What is the same about all of them? ...
Endocrine and Reproductive System Web Quest Vanessa Cooper
... Glands are a group of cells that produce and secrets chemicals. The chemical messengers are called hormones. They convey their messages through the blood stream, this way they can reach your entire body. This system responds to stress, dehydration, and low blood glucose. It regulates growth, mood, a ...
... Glands are a group of cells that produce and secrets chemicals. The chemical messengers are called hormones. They convey their messages through the blood stream, this way they can reach your entire body. This system responds to stress, dehydration, and low blood glucose. It regulates growth, mood, a ...
Endocrine System Study Guide Regulation
... Hormones of the Pituitary Gland 1. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone-TSH, stimulates cells of the thyroid to release thyroxin 2. Growth Hormone-GH, controls growth by causing bones to increase in size, also causes cells to reproduce at a quicker rate 3. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone- FSH - Stimulates the p ...
... Hormones of the Pituitary Gland 1. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone-TSH, stimulates cells of the thyroid to release thyroxin 2. Growth Hormone-GH, controls growth by causing bones to increase in size, also causes cells to reproduce at a quicker rate 3. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone- FSH - Stimulates the p ...
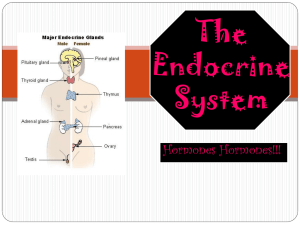
The Endocrine System Coloring Activities
... The Endocrine System Coloring Activities Question Sheet Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are________________glands that secrete ____________________ directly into body fluids. The job o ...
... The Endocrine System Coloring Activities Question Sheet Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are________________glands that secrete ____________________ directly into body fluids. The job o ...
Chapter 14
... Chapter Concepts 1. Glands can be classified structurally and functionally as endocrine or exocrine. 2. Both the nervous and endocrine systems work together through different modes of action to regulate body activities and maintain homeostasis. 3. Hormones are transported by the blood to target cell ...
... Chapter Concepts 1. Glands can be classified structurally and functionally as endocrine or exocrine. 2. Both the nervous and endocrine systems work together through different modes of action to regulate body activities and maintain homeostasis. 3. Hormones are transported by the blood to target cell ...
Notes
... Hormones produced by the endocrine system influence the activity of every organ and tissue in the body. Hormones act as chemical messengers which initiate some type of specialized biochemical processes in the target organ. Specific hormones act on specific target organs because the target organs hav ...
... Hormones produced by the endocrine system influence the activity of every organ and tissue in the body. Hormones act as chemical messengers which initiate some type of specialized biochemical processes in the target organ. Specific hormones act on specific target organs because the target organs hav ...
chapter 56: the endocrine system
... Chemical hormones are produced by ductless endocrine glands and are transported to the target organ through the blood. Their actions are broadly based and have long term effects, contrary to the localized, short-term effects of the nervous system. Receptor proteins in the target organs respond to th ...
... Chemical hormones are produced by ductless endocrine glands and are transported to the target organ through the blood. Their actions are broadly based and have long term effects, contrary to the localized, short-term effects of the nervous system. Receptor proteins in the target organs respond to th ...
Chapter 36 Integration: Endocrine Control I. The Endocrine System
... glands, have targets outside the body; they integrate social activities between animals. ...
... glands, have targets outside the body; they integrate social activities between animals. ...
A Small Dose of EDC
... male and female reproductive tract abnormalities skewed male/female sex ratios changes in hormone levels early puberty brain and behavior problems impaired immune functions various cancers A Small Dose of Toxicology ...
... male and female reproductive tract abnormalities skewed male/female sex ratios changes in hormone levels early puberty brain and behavior problems impaired immune functions various cancers A Small Dose of Toxicology ...
CSM ANATOMY ENDOCRINE SYSTEM REVIEW SHEET
... 11. Describe the major parts of the adrenal gland. Which part is neural, and which is epithelial in origin? What hormone groups come from each part? 12. What is the role of epinephrine in the body? 13. Describe the targets and effects of aldosterone, adrenal cortical androgens and estrogens, an ...
... 11. Describe the major parts of the adrenal gland. Which part is neural, and which is epithelial in origin? What hormone groups come from each part? 12. What is the role of epinephrine in the body? 13. Describe the targets and effects of aldosterone, adrenal cortical androgens and estrogens, an ...
File
... it into provitamin D. • Sun exposure changes it into Vit. D (some also comes from foods) •The liver changes, stores it, and with PTH, the kidneys can control absorbtion of Ca+2 ions from the intestine. ...
... it into provitamin D. • Sun exposure changes it into Vit. D (some also comes from foods) •The liver changes, stores it, and with PTH, the kidneys can control absorbtion of Ca+2 ions from the intestine. ...
chakra body systems
... complex ways. While each system provides a contribution to the continuous change of my body and mind, they are interdependent with one another. The emergent properties of their dynamic interactions create a structure of both support and expression. I relate to my body systems through becoming increa ...
... complex ways. While each system provides a contribution to the continuous change of my body and mind, they are interdependent with one another. The emergent properties of their dynamic interactions create a structure of both support and expression. I relate to my body systems through becoming increa ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... the middle of the brain. It secretes melatonin, a hormone that regulates when you sleep at night and wake up in the morning. ...
... the middle of the brain. It secretes melatonin, a hormone that regulates when you sleep at night and wake up in the morning. ...
Hormones
... development of male sexual characteristics § Testosterone is a steroid and has been administered to athletes in order to improve performance. This is considered to be a form of doping in most sports and is a ...
... development of male sexual characteristics § Testosterone is a steroid and has been administered to athletes in order to improve performance. This is considered to be a form of doping in most sports and is a ...
Hormone - Cloudfront.net
... body fluids (blood) communicating regulatory messages Target cells~ body cells that respond to hormones Endocrine system/glands~ hormone secreting system/glands (ductless); exocrine glands secrete chemicals (sweat, mucus, enzymes) through ducts Neurosecretory cells~ actual cells that secrete hormone ...
... body fluids (blood) communicating regulatory messages Target cells~ body cells that respond to hormones Endocrine system/glands~ hormone secreting system/glands (ductless); exocrine glands secrete chemicals (sweat, mucus, enzymes) through ducts Neurosecretory cells~ actual cells that secrete hormone ...
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
... INTERCELLULAR COMMUNICATIONS 3. Hormones released through gap junctions provide _______________ communication between cells, allowing the cells to work as a unit. ...
... INTERCELLULAR COMMUNICATIONS 3. Hormones released through gap junctions provide _______________ communication between cells, allowing the cells to work as a unit. ...
Nervous/Endocrine Notes
... •Cells of the endocrine system are arranged into specific endocrine glands. •A gland: A secretory organ. Ex. Pancreas, Pituitary gland, Adrenal gland •The specific hormones are released into the blood and transported to the specific organ called the TARGET ORGAN. •The target organ contains target ce ...
... •Cells of the endocrine system are arranged into specific endocrine glands. •A gland: A secretory organ. Ex. Pancreas, Pituitary gland, Adrenal gland •The specific hormones are released into the blood and transported to the specific organ called the TARGET ORGAN. •The target organ contains target ce ...
Endocrine System
... Regulatory System Maintains homeostasis internally Responds to environmental changes Growth and development Reproduction ...
... Regulatory System Maintains homeostasis internally Responds to environmental changes Growth and development Reproduction ...
Endocrine System and Hormones
... development of male sexual characteristics Testosterone is a steroid and has been administered to athletes in order to improve performance. This is considered to be a form of doping in most sports and is a ...
... development of male sexual characteristics Testosterone is a steroid and has been administered to athletes in order to improve performance. This is considered to be a form of doping in most sports and is a ...
Biological Bases of Behavior: 3A—Neural Processing and the
... Hormones released by endocrine glands affect other tissues, including the brain. The most influential endocrine gland, the pituitary gland, releases hormones that influence growth, and its secretions also influence the release of hormones by other glands. The nervous system directs endocrine secreti ...
... Hormones released by endocrine glands affect other tissues, including the brain. The most influential endocrine gland, the pituitary gland, releases hormones that influence growth, and its secretions also influence the release of hormones by other glands. The nervous system directs endocrine secreti ...
Endocrine disruptor

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with the endocrine (or hormone) system in mammals. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems; deformations of the body (including limbs); breast cancer, prostate cancer, thyroid and other cancers; sexual development problems such as feminizing of males or masculinizing effects on females, etc. The critical period of development for most organisms is between the transition from a fertilized egg into a fully formed infant. As the cells begin to grow and differentiate, there are critical balances of hormones and protein changes that must occur. Therefore, a dose of disrupting chemicals may do substantial damage to a developing fetus. The same dose may not significantly affect adult mothers.There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to remove them from the market, and regulators and other scientists calling for further study. Some endocrine disruptors have been identified and removed from the market (for example, a drug called diethylstilbestrol), but it is uncertain whether some endocrine disruptors on the market actually harm humans and wildlife at the doses to which wildlife and humans are exposed. Additionally, a key scientific paper, published in the journal Science, which helped launch the movement of those opposed to endocrine disruptors, was retracted and its author found to have committed scientific misconduct.Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors are substances that ""interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)."" They are sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs).Studies in cells and laboratory animals have shown that EDs can cause adverse biological effects in animals, and low-level exposures may also cause similar effects in human beings.The term endocrine disruptor is often used as synonym for xenohormone although the latter can mean any naturally occurring or artificially produced compound showing hormone-like properties (usually binding to certain hormonal receptors). EDCs in the environment may also be related to reproductive and infertility problems in wildlife and bans and restrictions on their use has been associated with a reduction in health problems and the recovery of some wildlife populations.