Slide 1
... 26.3 Overview: The vertebrate endocrine system consists of more than a dozen major glands Some endocrine glands (such as the thyroid) primarily secrete hormones into the blood. Other glands (such as the pancreas) have – endocrine and – nonendocrine functions. ...
... 26.3 Overview: The vertebrate endocrine system consists of more than a dozen major glands Some endocrine glands (such as the thyroid) primarily secrete hormones into the blood. Other glands (such as the pancreas) have – endocrine and – nonendocrine functions. ...
Physiology Lecture 2
... ● The axons of the neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus extend into the posterior lobe of the pituitary. ● Oxytocin and ADH are transported through these axons into the posterior pituitary, where they are stored for eventual release into the bloodstream. ● Blood vessels connects the hypothalamus ...
... ● The axons of the neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus extend into the posterior lobe of the pituitary. ● Oxytocin and ADH are transported through these axons into the posterior pituitary, where they are stored for eventual release into the bloodstream. ● Blood vessels connects the hypothalamus ...
The Hypothalamus
... produce oxytocin and vassopressin (ADH) Transported via axonal transport systems (hypothalamohypophysial tract) to neurohypophysis Released in circulation Damage to supraoptic n. diabetes insipidus ...
... produce oxytocin and vassopressin (ADH) Transported via axonal transport systems (hypothalamohypophysial tract) to neurohypophysis Released in circulation Damage to supraoptic n. diabetes insipidus ...
Ovaries
... secreted into the bloodstream • Function: – Regulate metabolic rate of all cells – Regulate cell growth – Regulate tissue differentiation ...
... secreted into the bloodstream • Function: – Regulate metabolic rate of all cells – Regulate cell growth – Regulate tissue differentiation ...
Background Information for the Teacher`s Guide
... the pancreas secretes the hormone glucagon. This signals the liver to break down glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the blood stream. So, homeostasis can be thought of as a dynamic equilibrium where feedback mechanisms are constantly being made so that levels are staying at or near t ...
... the pancreas secretes the hormone glucagon. This signals the liver to break down glycogen into glucose, which is then released into the blood stream. So, homeostasis can be thought of as a dynamic equilibrium where feedback mechanisms are constantly being made so that levels are staying at or near t ...
Endocrine System
... • Most common, 90% of all cases of diabetes • Typically found in obese people over age 35 • Can be controlled through diet, exercise and weight loss – Can be temporary ...
... • Most common, 90% of all cases of diabetes • Typically found in obese people over age 35 • Can be controlled through diet, exercise and weight loss – Can be temporary ...
The Encorine System and Homeostasis
... system. The nervous system acts on specific muscles and glands. The influences of the endocrine system are broader and regulate virtually all types of body cells. A hormone is a mediator molecule that is released in one part of the body but regulates the activity of cells in other parts of the body. ...
... system. The nervous system acts on specific muscles and glands. The influences of the endocrine system are broader and regulate virtually all types of body cells. A hormone is a mediator molecule that is released in one part of the body but regulates the activity of cells in other parts of the body. ...
endocrine system - Sakshieducation.com
... Endocrine glands release their hormones, into blood, circulate in the whole body and regulate metabolism, growth, secretion, homeostasis, gastrointestinal mobility and digestion, blood pressure and heart beat, kidney function, lactation, reproduction etc. Endocrine system includes certain glands, ca ...
... Endocrine glands release their hormones, into blood, circulate in the whole body and regulate metabolism, growth, secretion, homeostasis, gastrointestinal mobility and digestion, blood pressure and heart beat, kidney function, lactation, reproduction etc. Endocrine system includes certain glands, ca ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
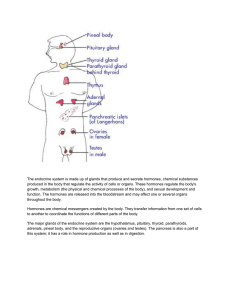
... the bloodstream are called endocrine glands – They are one of two major types of glands in the body, the other being exocrine glands (which secrete their products into ducts ) ...
... the bloodstream are called endocrine glands – They are one of two major types of glands in the body, the other being exocrine glands (which secrete their products into ducts ) ...
Chapter 18
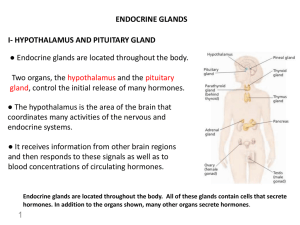
... Both are master endocrine glands since their hormones control other endocrine glands Hypothalamus is a section of brain above where pituitary gland is suspended from stalk Hypothalamus receives input from cortex, thalamus, ...
... Both are master endocrine glands since their hormones control other endocrine glands Hypothalamus is a section of brain above where pituitary gland is suspended from stalk Hypothalamus receives input from cortex, thalamus, ...
The Endocrine System
... the brain. The pineal gland produces two hormones; cortisol and melatonin. The production of these hormones follows a daily 24 hour cycle which is referred to as a circadian rhythm. Cortisol hormone production is greatest at night and peaks just before a person wakes. The level of the hormine de ...
... the brain. The pineal gland produces two hormones; cortisol and melatonin. The production of these hormones follows a daily 24 hour cycle which is referred to as a circadian rhythm. Cortisol hormone production is greatest at night and peaks just before a person wakes. The level of the hormine de ...
Assessment and Management of Patients with Endocrine Disorders
... Each type of thyroiditis is characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, or lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland. Characterized by autoimmune damage to the thyroid. May cause thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, or both ...
... Each type of thyroiditis is characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, or lymphocytic infiltration of the thyroid gland. Characterized by autoimmune damage to the thyroid. May cause thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, or both ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Steroid Hormones ~ from cholesterol Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized resp ...
... Steroid Hormones ~ from cholesterol Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized resp ...
Endocrine System
... The hypothalamus is part of the brain that lies just above the pituitary gland. It releases hormones that start and stop the release of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls hormone production in the pituitary gland through several "releasing" hormones. Some of these are growth hormone-rele ...
... The hypothalamus is part of the brain that lies just above the pituitary gland. It releases hormones that start and stop the release of pituitary hormones. The hypothalamus controls hormone production in the pituitary gland through several "releasing" hormones. Some of these are growth hormone-rele ...
Chapter 18
... Its complexity makes it possible to stimulate more than one tissue and organs simultaneously. The effect is relatively short lived. ...
... Its complexity makes it possible to stimulate more than one tissue and organs simultaneously. The effect is relatively short lived. ...
MD0807 6-1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Review of the
... The parathyroid glands are usually four in number. They are embedded in the posterior portion of the thyroid. Their principal action is the production of parathormone. a. Parathormone. Parathormone is a hormone that works in conjunction with another hormone, calcitonin, to regulate the calcium and p ...
... The parathyroid glands are usually four in number. They are embedded in the posterior portion of the thyroid. Their principal action is the production of parathormone. a. Parathormone. Parathormone is a hormone that works in conjunction with another hormone, calcitonin, to regulate the calcium and p ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine
... i. Name the two hormones secreted from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. What chemical element is essential for the production of these hormones? What condition arises in an adult from the lack of this element? ii. What is the storage form of these hormones called? Where is this substance s ...
... i. Name the two hormones secreted from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. What chemical element is essential for the production of these hormones? What condition arises in an adult from the lack of this element? ii. What is the storage form of these hormones called? Where is this substance s ...
Pituitary Gland
... Endocrine glands secrete chemicals (hormones) into the blood Hormones perform general functions of communication and control; it is a slower, longerlasting type of control than that provided by nerve impulses Cells acted on by hormones are called target organ cells ...
... Endocrine glands secrete chemicals (hormones) into the blood Hormones perform general functions of communication and control; it is a slower, longerlasting type of control than that provided by nerve impulses Cells acted on by hormones are called target organ cells ...
Endocrine System Endocrine glands - secrete chemical
... ovarian estrogen production. Produced by gonadotrophs. In the male it stimulates the testes to produce sperm. luteinizing hormone: (LH) in the female, along with FSH it stimulates ovulation and thus indirectly the production of progesterone. Produced by gonadotrophs. In the male it is called interst ...
... ovarian estrogen production. Produced by gonadotrophs. In the male it stimulates the testes to produce sperm. luteinizing hormone: (LH) in the female, along with FSH it stimulates ovulation and thus indirectly the production of progesterone. Produced by gonadotrophs. In the male it is called interst ...
Chapter 15 - Los Angeles City College
... Varying hormone concentration within normal, physiological range can affect the responsiveness of target cells. Priming effects (upregulation) Increase number of receptors formed on target cells. Greater response by the target cell. ...
... Varying hormone concentration within normal, physiological range can affect the responsiveness of target cells. Priming effects (upregulation) Increase number of receptors formed on target cells. Greater response by the target cell. ...
Endocrine Virtual Lab! AP Biology
... greater area) and affects more than one person or organ. Although the hormone travels through the body via the blood, it can only affect those cells with receptors for that specific hormone. Hormones are a slower method of communication, but their effects last longer. The command center for the endo ...
... greater area) and affects more than one person or organ. Although the hormone travels through the body via the blood, it can only affect those cells with receptors for that specific hormone. Hormones are a slower method of communication, but their effects last longer. The command center for the endo ...
hormones
... The sex and the form of a developing fetus are affected by events that take place in the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetically, the proper hormones must be available for the fetus to develop the appropriate sex organs. Its gonads are fairly inactive at birth, but gradual ...
... The sex and the form of a developing fetus are affected by events that take place in the woman's womb. Even though a fetus's sex is determined genetically, the proper hormones must be available for the fetus to develop the appropriate sex organs. Its gonads are fairly inactive at birth, but gradual ...
Chapter 45 Worksheet Sy Ha Hormones and the Endocrine System
... conditions. For example, the control of blood glucose is controlled by insulin and glucagon. Insulin triggers uptake of glucose from blood decreasing glucose levels in blood when it is high and glucagon triggers release of glucose into blood increasing glucose levels when they are low. Another examp ...
... conditions. For example, the control of blood glucose is controlled by insulin and glucagon. Insulin triggers uptake of glucose from blood decreasing glucose levels in blood when it is high and glucagon triggers release of glucose into blood increasing glucose levels when they are low. Another examp ...
Hormones and Young Living Essential Oils
... • Hormones literally control every aspect of our lives; just about every single function of the body is affected by hormones? • If one of the glands in our body is not functioning properly and production of hormones is impaired, the entire endocrine system is compromised and hormonal imbalance resul ...
... • Hormones literally control every aspect of our lives; just about every single function of the body is affected by hormones? • If one of the glands in our body is not functioning properly and production of hormones is impaired, the entire endocrine system is compromised and hormonal imbalance resul ...
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs
... A) a hormone-receptor complex that interacts directly with the cell's DNA B) extracellular receptors with a specificity for only a single amino acid sequence on the hormone C) second-messenger systems D) an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cyclic AMP ...
... A) a hormone-receptor complex that interacts directly with the cell's DNA B) extracellular receptors with a specificity for only a single amino acid sequence on the hormone C) second-messenger systems D) an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of cyclic AMP ...
Endocrine disruptor

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that, at certain doses, can interfere with the endocrine (or hormone) system in mammals. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Any system in the body controlled by hormones can be derailed by hormone disruptors. Specifically, endocrine disruptors may be associated with the development of learning disabilities, severe attention deficit disorder, cognitive and brain development problems; deformations of the body (including limbs); breast cancer, prostate cancer, thyroid and other cancers; sexual development problems such as feminizing of males or masculinizing effects on females, etc. The critical period of development for most organisms is between the transition from a fertilized egg into a fully formed infant. As the cells begin to grow and differentiate, there are critical balances of hormones and protein changes that must occur. Therefore, a dose of disrupting chemicals may do substantial damage to a developing fetus. The same dose may not significantly affect adult mothers.There has been controversy over endocrine disruptors, with some groups calling for swift action by regulators to remove them from the market, and regulators and other scientists calling for further study. Some endocrine disruptors have been identified and removed from the market (for example, a drug called diethylstilbestrol), but it is uncertain whether some endocrine disruptors on the market actually harm humans and wildlife at the doses to which wildlife and humans are exposed. Additionally, a key scientific paper, published in the journal Science, which helped launch the movement of those opposed to endocrine disruptors, was retracted and its author found to have committed scientific misconduct.Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors are substances that ""interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis (normal cell metabolism)."" They are sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs).Studies in cells and laboratory animals have shown that EDs can cause adverse biological effects in animals, and low-level exposures may also cause similar effects in human beings.The term endocrine disruptor is often used as synonym for xenohormone although the latter can mean any naturally occurring or artificially produced compound showing hormone-like properties (usually binding to certain hormonal receptors). EDCs in the environment may also be related to reproductive and infertility problems in wildlife and bans and restrictions on their use has been associated with a reduction in health problems and the recovery of some wildlife populations.