Histological Characteristics of Submandibular Gland after Induction
... body functions.4, 5 Thyroid hormones are known to regulate the rate of metabolism also affecting the growth and rate of function of many other systems of the body such as neuromuscular, gastrointestinal and cardiovascular system.1 Impaired thyroid hormone production causes serious intellectual and b ...
... body functions.4, 5 Thyroid hormones are known to regulate the rate of metabolism also affecting the growth and rate of function of many other systems of the body such as neuromuscular, gastrointestinal and cardiovascular system.1 Impaired thyroid hormone production causes serious intellectual and b ...
S10 Clinicalbiochem2 DrNansy Hypothalamus And Pituitary
... now routinely measured in the diagnosis and especially monitoring of treated acromegaly, with an elevated level suggestive of active disease. Treatment 1. Surgery. Its success depends on the size of the tumor. 2. Radiation. This is usually reserved for patients whose disease remains active despite s ...
... now routinely measured in the diagnosis and especially monitoring of treated acromegaly, with an elevated level suggestive of active disease. Treatment 1. Surgery. Its success depends on the size of the tumor. 2. Radiation. This is usually reserved for patients whose disease remains active despite s ...
MD0807 6-1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Review of the
... involving the thyroid gland. (1) Goiter. Goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland producing a distinct swelling at the base of the neck just below the larynx (“Adam’s Apple”). Simple goiters result from a dietary lack of iodine. This occurs most commonly in areas in which the soil is r ...
... involving the thyroid gland. (1) Goiter. Goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland producing a distinct swelling at the base of the neck just below the larynx (“Adam’s Apple”). Simple goiters result from a dietary lack of iodine. This occurs most commonly in areas in which the soil is r ...
in the cell
... Control of Hormone Secretion (Release) • Following a particular stimulus, the gland can increase or decrease the rate of secretion • Circulating (blood) levels of hormones are not permitted to get too high because they are controlled by 2 separate negative feedback loops – activity of the target re ...
... Control of Hormone Secretion (Release) • Following a particular stimulus, the gland can increase or decrease the rate of secretion • Circulating (blood) levels of hormones are not permitted to get too high because they are controlled by 2 separate negative feedback loops – activity of the target re ...
Lecture Notes
... 1. When a neurotransmitter is released it acts on specific cell right next to it. Whereas when a hormone is released it ca travel to another nearby cell or it can act on another part of the body. 2. Neurotransmitters have their effects within milliseconds. Hormones take minutes or days to have their ...
... 1. When a neurotransmitter is released it acts on specific cell right next to it. Whereas when a hormone is released it ca travel to another nearby cell or it can act on another part of the body. 2. Neurotransmitters have their effects within milliseconds. Hormones take minutes or days to have their ...
Stress, Thyroid Hormone Secretion and Vestibular
... following intervention.11 The impact of cold mild stress will reduce the T3 and T4 levels, these altered thyroid function in turn alter the immunity.12 During stress Corticotrophin-releasing hormone suppress the thyroid function by inhibiting the secretion of thyroid releasing hormone and thyroid st ...
... following intervention.11 The impact of cold mild stress will reduce the T3 and T4 levels, these altered thyroid function in turn alter the immunity.12 During stress Corticotrophin-releasing hormone suppress the thyroid function by inhibiting the secretion of thyroid releasing hormone and thyroid st ...
Virilism and Ectopic Expression of HSD17B5 in Mature Cystic
... Mature cystic teratoma (MCT) is rarely involved in the overproduction of steroid hormones in contrast to sex cord stromal tumors. A 31-year-old woman visited our hospital with hirsutism, hoarseness, and hair loss from the scalp. Serum testosterone and free-testosterone levels were 7.3 ng/ml and 2.3 ...
... Mature cystic teratoma (MCT) is rarely involved in the overproduction of steroid hormones in contrast to sex cord stromal tumors. A 31-year-old woman visited our hospital with hirsutism, hoarseness, and hair loss from the scalp. Serum testosterone and free-testosterone levels were 7.3 ng/ml and 2.3 ...
1 Chapter 11: The Endocrine System • Exocrine glands will produce
... o Utilizes hormones secreted from endocrine glands to target precisely a specific structure. The process and communication of the endocrine system may be slower than that of the nervous system but the target is precise and the effects are longer-lasting even with a small amount of hormonal secretion ...
... o Utilizes hormones secreted from endocrine glands to target precisely a specific structure. The process and communication of the endocrine system may be slower than that of the nervous system but the target is precise and the effects are longer-lasting even with a small amount of hormonal secretion ...
can - UMBC
... If this is the way you feel, then please take note. Your health problems are not “all in your head.” Your symptoms are very real and have a physical cause. You are not being punished by God. However, you may be suffering needlessly at the hands of unsympathetic physicians who do not have the time, ...
... If this is the way you feel, then please take note. Your health problems are not “all in your head.” Your symptoms are very real and have a physical cause. You are not being punished by God. However, you may be suffering needlessly at the hands of unsympathetic physicians who do not have the time, ...
The Endocrine System - Austin Community College
... Cortisol levels also increase during exercise for protein catabolism for later gluconeogenesis. Growth Hormone mobilizes free fatty acids Thyroxine promotes glucose catabolism As intensity of exercise increases, so does the rate of catecholamine release for glycogenolysis During endurance events the ...
... Cortisol levels also increase during exercise for protein catabolism for later gluconeogenesis. Growth Hormone mobilizes free fatty acids Thyroxine promotes glucose catabolism As intensity of exercise increases, so does the rate of catecholamine release for glycogenolysis During endurance events the ...
Pituitary Adenomas in Patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
... - Prolactin secreting (40%)! - Growth hormone secreting (20%)! - Corticotropin secreting (7%)! - Gonadotropin secreting (<1%)! - Thyrotropin secreting (<1%)! - Some tumors secrete more than one hormone! - May compress normal gland and decrease other hormone production! ...
... - Prolactin secreting (40%)! - Growth hormone secreting (20%)! - Corticotropin secreting (7%)! - Gonadotropin secreting (<1%)! - Thyrotropin secreting (<1%)! - Some tumors secrete more than one hormone! - May compress normal gland and decrease other hormone production! ...
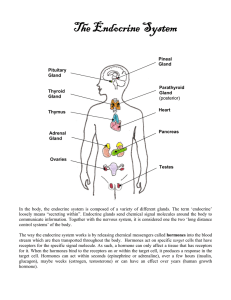
The Endocrine System
... communicate information. Together with the nervous system, it is considered one the two ‘long distance control systems’ of the body. The way the endocrine system works is by releasing chemical messengers called hormones into the blood stream which are then transported throughout the body. Hormones a ...
... communicate information. Together with the nervous system, it is considered one the two ‘long distance control systems’ of the body. The way the endocrine system works is by releasing chemical messengers called hormones into the blood stream which are then transported throughout the body. Hormones a ...
Highly Sensitive lmmunoenzymometricAssay for Human Thyrotropin
... thyrotoxic patients with Graves’ disease were less than 0.2 milli-int. unit/L, clearly different from those of normal subjects. Thyrotoxicpatients in early normal pregnancy showed TSH ...
... thyrotoxic patients with Graves’ disease were less than 0.2 milli-int. unit/L, clearly different from those of normal subjects. Thyrotoxicpatients in early normal pregnancy showed TSH ...
Endocrine - Hamzology
... animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please note: once you have used any of the animation functions (such as Play or Pause), you must first click in the white background before you advance the next slide. ...
... animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please note: once you have used any of the animation functions (such as Play or Pause), you must first click in the white background before you advance the next slide. ...
Endocrine functions of the pituitary and pineal glands 1/20
... – Insulin/Obesity: reduced receptors causes Type II diabetes – Fewer hormone receptors Less ability to remove glucose from blood! • How does receptor up/down regulation explain why a drug may work at first, but not later? • Hormone/Second Messenger Destruction: Cells can also learn to destroy hormo ...
... – Insulin/Obesity: reduced receptors causes Type II diabetes – Fewer hormone receptors Less ability to remove glucose from blood! • How does receptor up/down regulation explain why a drug may work at first, but not later? • Hormone/Second Messenger Destruction: Cells can also learn to destroy hormo ...
full text pdf
... accidents and insufficient preoperative preparation. Clinical manifestations include: (1) hyperpyrexia >40°C, which is rarely seen in the elderly; (2) hypothermia <30°C; (3) hypoglycemia; (4) hypotension; (5) overhydration; and (6) mixed type. All these types could be complicated by their correspond ...
... accidents and insufficient preoperative preparation. Clinical manifestations include: (1) hyperpyrexia >40°C, which is rarely seen in the elderly; (2) hypothermia <30°C; (3) hypoglycemia; (4) hypotension; (5) overhydration; and (6) mixed type. All these types could be complicated by their correspond ...
Endocrine System - El Camino College
... Posterior Pituitary stores and releases 2 hormones produced by hypothalamus 1. ADH 2. Oxytocin Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland: secretes Thyroxin = T4 and Triiodothyronine = T3 hormones having similar influence. These hormones have wide range of effects. Main influences include – 1 Basal Metabolic Rate ...
... Posterior Pituitary stores and releases 2 hormones produced by hypothalamus 1. ADH 2. Oxytocin Thyroid Gland Thyroid Gland: secretes Thyroxin = T4 and Triiodothyronine = T3 hormones having similar influence. These hormones have wide range of effects. Main influences include – 1 Basal Metabolic Rate ...
The Thyroid and Its Control
... by ETH- Eidgenossische Technische Hochschule Zurich - BIBLIOTHEK on 09/17/12. For personal use only. ...
... by ETH- Eidgenossische Technische Hochschule Zurich - BIBLIOTHEK on 09/17/12. For personal use only. ...
The Endocrine System
... 1. Receptors located in either the cytoplasm or nucleus of the cell. 2. Receptors that extend across the cell membrane and have a receptor site on the outer surface of the membrane. 3. Relatively small chemical signals that are soluble in lipids bind to these receptors. 4. Large, water-soluble chemi ...
... 1. Receptors located in either the cytoplasm or nucleus of the cell. 2. Receptors that extend across the cell membrane and have a receptor site on the outer surface of the membrane. 3. Relatively small chemical signals that are soluble in lipids bind to these receptors. 4. Large, water-soluble chemi ...
Endocrine System
... Introduction to the Endocrine System A. Multiple Choice Questions 1. (b) – Because target cells have specific cytoplasmic receptor proteins as binding sites, they respond quite precisely to the presence of particular hormones within the blood. 2. (a) – The effects of hormones are frequently long las ...
... Introduction to the Endocrine System A. Multiple Choice Questions 1. (b) – Because target cells have specific cytoplasmic receptor proteins as binding sites, they respond quite precisely to the presence of particular hormones within the blood. 2. (a) – The effects of hormones are frequently long las ...
chemical coordination and integration
... Deficiency of dietary iodine causes enlargement of thyroid which results swelling of neck. This disorder due to hypothyroidism is called goitre. Hypothyroidism during pregnancy causes defective development and maturation of growing baby leading to stunted growth (cretinism), mental retardation, low ...
... Deficiency of dietary iodine causes enlargement of thyroid which results swelling of neck. This disorder due to hypothyroidism is called goitre. Hypothyroidism during pregnancy causes defective development and maturation of growing baby leading to stunted growth (cretinism), mental retardation, low ...
Stereology of the Thyroid Gland in Indo-Pacific Bottlenose
... follicles are filled with homogeneous colloid. The epithelial cells vary in size and number dependant on the activity of the gland. In the hyperactive state, hyperplasia or abnormal increase of epithelial cells may occur [16]. Previous histological examination of the thyroid gland in marine mammal r ...
... follicles are filled with homogeneous colloid. The epithelial cells vary in size and number dependant on the activity of the gland. In the hyperactive state, hyperplasia or abnormal increase of epithelial cells may occur [16]. Previous histological examination of the thyroid gland in marine mammal r ...
Document
... • Iodides (I–) are actively taken into the cell, oxidized to iodine (I2), and released into the lumen • Iodine attaches to tyrosine, mediated by peroxidase enzymes, forming T1 (monoiodotyrosine, or MIT), and T2 (diiodotyrosine, or DIT) • Iodinated tyrosines link together to form T3 and T4 • Colloid ...
... • Iodides (I–) are actively taken into the cell, oxidized to iodine (I2), and released into the lumen • Iodine attaches to tyrosine, mediated by peroxidase enzymes, forming T1 (monoiodotyrosine, or MIT), and T2 (diiodotyrosine, or DIT) • Iodinated tyrosines link together to form T3 and T4 • Colloid ...
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism, also known as over active thyroid and hyperthyreosis, is the condition that occurs due to excessive production of thyroid hormone by the thyroid gland. Thyrotoxicosis is the condition that occurs due to excessive thyroid hormone of any cause and therefore includes hyperthyroidism. Some, however, use the terms interchangeably. Signs and symptoms vary between people and may include irritability, muscle weakness, sleeping problems, a fast heartbeat, poor tolerance of heat, diarrhea, enlargement of the thyroid, and weight loss. Symptoms are typically less in the old and during pregnancy. An uncommon complication is thyroid storm in which an event such as an infection results in worsening symptoms such as confusion and a high temperature and often results in death. The opposite is hypothyroidism, when the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone.Graves' disease is the cause of about 50% to 80% of case of hyperthyroidism in the United States. Other causes include multinodular goiter, toxic adenoma, inflammation of the thyroid, eating too much iodine, and too much synthetic thyroid hormone. A less common cause is a pituitary adenoma. The diagnosis may be suspected based on signs and symptoms and then confirmed with blood tests. Typically blood tests show a low thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and raised T3 or T4. Radioiodine uptake by the thyroid, thyroid scan, and TSI antibodies may help determine the cause.Treatment depends partly on the cause and severity of disease. There are three main treatment options: radioiodine therapy, medications, and thyroid surgery. Radioiodine therapy involves taking iodine-131 by mouth which is then concentrated in and destroys the thyroid over weeks to months. The resulting hypothyroidism is treated with synthetic thyroid hormone. Medications such as beta blockers may control the symptoms and anti-thyroid medications such as methimazole may temporarily help people while other treatments are having effect. Surgery to remove the thyroid is another option. This may be used in those with very large thyroids or when cancer is a concern. In the United States hyperthyroidism affects about 1.2% of the population. It occurs between two and ten times more often in women. Onset is commonly between 20 and 50 years of age. Overall the disease is more common in those over the age of 60 years.