New polyanion-based cathode materials for alkali
... Inorganic Chemistry; Paper IV (pages 92—125) has been published in the journal, Chemistry of Materials; Paper V (Pages 126—150) has been accepted for publication in the journal, Chemistry of Materials. The associated supporting information (SI) for each publication is provided in the appendices in t ...
... Inorganic Chemistry; Paper IV (pages 92—125) has been published in the journal, Chemistry of Materials; Paper V (Pages 126—150) has been accepted for publication in the journal, Chemistry of Materials. The associated supporting information (SI) for each publication is provided in the appendices in t ...
CHAPtER 4 Electrolysis
... enable a prediction to be made of the overall minimum voltage required for an electrolytic reaction to occur, the actual observed voltage may vary by as much as 1 volt, owing to a phenomenon known as ‘overpotential’. Note (ii): A full analysis of this situation would also involve the possibility tha ...
... enable a prediction to be made of the overall minimum voltage required for an electrolytic reaction to occur, the actual observed voltage may vary by as much as 1 volt, owing to a phenomenon known as ‘overpotential’. Note (ii): A full analysis of this situation would also involve the possibility tha ...
electrochemistry
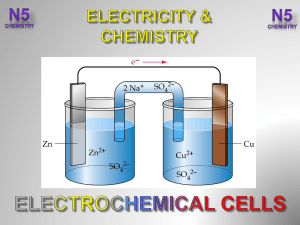
... exothermic reaction is normally lost as heat. However, it can be trapped and converted into electrical energy if the reactants involved are not in direct contact with each other. In galvanic cells redox reactions is split into two halfreactions, each occurring in two separate compartments, called ha ...
... exothermic reaction is normally lost as heat. However, it can be trapped and converted into electrical energy if the reactants involved are not in direct contact with each other. In galvanic cells redox reactions is split into two halfreactions, each occurring in two separate compartments, called ha ...
industry: applying chemical reactions
... of these jobs would be in only one company. What will happen if there’s a decline in the market for ammonia or lithium-ion batteries? Wouldn’t it be more prudent to distribute those 200 jobs among several different companies? Let’s learn from our recent experience with the city’s former main employe ...
... of these jobs would be in only one company. What will happen if there’s a decline in the market for ammonia or lithium-ion batteries? Wouldn’t it be more prudent to distribute those 200 jobs among several different companies? Let’s learn from our recent experience with the city’s former main employe ...
Mnemonic Devices - Free WonderKids-e
... - is another weak oxidizing agent. Its mode of action is to decompose into water and atomic oxygen (O). Atomic oxygen normally combines to form molecular . However, in the brief time that is available, atomic oxygen acts as a very good oxidizing agent if it encounters a suitable reactant. Hydrogen p ...
... - is another weak oxidizing agent. Its mode of action is to decompose into water and atomic oxygen (O). Atomic oxygen normally combines to form molecular . However, in the brief time that is available, atomic oxygen acts as a very good oxidizing agent if it encounters a suitable reactant. Hydrogen p ...
CHAPTER 8: ENERGY FROM ELECTRON TRANSFER
... electron transfer. Chemical reaction, such as those that take place in galvanic cells, batteries and fuel cells, produce electrons that can do work because the anode and cathode are physically separated in space. The transfer of electrons also may be initiated when light strikes a photovoltaic cell. ...
... electron transfer. Chemical reaction, such as those that take place in galvanic cells, batteries and fuel cells, produce electrons that can do work because the anode and cathode are physically separated in space. The transfer of electrons also may be initiated when light strikes a photovoltaic cell. ...
Ink and paper
... 1- the cathode, which is the positive terminal a 2-node, which is the negative terminal, 3- the electrolyte, in the centre of the battery. ...
... 1- the cathode, which is the positive terminal a 2-node, which is the negative terminal, 3- the electrolyte, in the centre of the battery. ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... The electrified interface between the Colloidal particle and the medium causes a potential difference in the interface, which interacts with the externally applied electric field lies the basis for coating of metals. Is the friction between two solids in presence of liquid film an Electrified in ...
... The electrified interface between the Colloidal particle and the medium causes a potential difference in the interface, which interacts with the externally applied electric field lies the basis for coating of metals. Is the friction between two solids in presence of liquid film an Electrified in ...
Answers for Review Questions Exam 3
... 13. Corrosion is the loss of metals to a solution of some form. The process that occurs is the oxidation of the metal and the reduction of water, followed by the formation of a metal hydroxide. 14. Because not all metals are easily oxidized by water. H2O and O2 are the two main substances. Keep the ...
... 13. Corrosion is the loss of metals to a solution of some form. The process that occurs is the oxidation of the metal and the reduction of water, followed by the formation of a metal hydroxide. 14. Because not all metals are easily oxidized by water. H2O and O2 are the two main substances. Keep the ...
Nickel–cadmium battery

The nickel–cadmium battery (NiCd battery or NiCad battery) is a type of rechargeable battery using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes. The abbreviation Ni-Cd is derived from the chemical symbols of nickel (Ni) and cadmium (Cd): the abbreviation NiCad is a registered trademark of SAFT Corporation, although this brand name is commonly used to describe all Ni–Cd batteries.Wet-cell nickel-cadmium batteries were invented in 1898. Among rechargeable battery technologies, NiCd rapidly lost market share in the 1990s, to NiMH and Li-ion batteries; market share dropped by 80%. A Ni-Cd battery has a terminal voltage during discharge of around 1.2 volts which decreases little until nearly the end of discharge. Ni-Cd batteries are made in a wide range of sizes and capacities, from portable sealed types interchangeable with carbon-zinc dry cells, to large ventilated cells used for standby power and motive power. Compared with other types of rechargeable cells they offer good cycle life and performance at low temperatures with a fair capacity but its significant advantage is the ability to deliver practically its full rated capacity at high discharge rates (discharging in one hour or less). However, the materials are more costly than that of the lead acid battery, and the cells have high self-discharge rates. Sealed Ni-Cd cells were at one time widely used in portable power tools, photography equipment, flashlights, emergency lighting, hobby R/C, and portable electronic devices. The superior capacity of the Nickel-metal hydride batteries, and more recently their lower cost, has largely supplanted their use. Further, the environmental impact of the disposal of the toxic metal cadmium has contributed considerably to the reduction in their use. Within the European Union, Ni-Cd batteries can now only be supplied for replacement purposes or for certain types of new equipment such as medical devices.Larger ventilated wet cell NiCd batteries are used in emergency lighting, standby power, and uninterruptible power supplies and other applications.