CHAPTER 5
... determine what is “known.” • Neural networks: system is “guessing” based upon examples and patterns found in the data set- trying to figure out what category something fits in. ...
... determine what is “known.” • Neural networks: system is “guessing” based upon examples and patterns found in the data set- trying to figure out what category something fits in. ...
LINKS BETWEEN LTP AND LEARNING AND MEMORY
... Water maze task is complex and requires animals to learn the general task requirement as well as the specific location of the hidden platform Non-spatial pretraining can separate the two kinds of learning Rats first made familiar with the general task requirements and subsequently trained after rece ...
... Water maze task is complex and requires animals to learn the general task requirement as well as the specific location of the hidden platform Non-spatial pretraining can separate the two kinds of learning Rats first made familiar with the general task requirements and subsequently trained after rece ...
Introduction to Algorithms
... T(n) =1 [first step] + (n) [for loop] + (n-1) [if condition] + (n-1) [the assignment in then] = 3n - 1 ...
... T(n) =1 [first step] + (n) [for loop] + (n-1) [if condition] + (n-1) [the assignment in then] = 3n - 1 ...
Tutorial Syllabus for AAAI-17 conference Title: "Rulelog: Deep KRR
... many of the requirements of cognitive computing. It combines deep logical/probabilistic reasoning tightly with natural language processing, and complements machine learning. Rulelog interoperates and composes well with graph databases, relational databases, spreadsheets, XML, and expressively simple ...
... many of the requirements of cognitive computing. It combines deep logical/probabilistic reasoning tightly with natural language processing, and complements machine learning. Rulelog interoperates and composes well with graph databases, relational databases, spreadsheets, XML, and expressively simple ...
Breaking the Neural Code
... • Let be the observable output at time t • probability: • forward component of belief propagation: ...
... • Let be the observable output at time t • probability: • forward component of belief propagation: ...
Artificial Intelligence
... something to an intelligent agent. Precise mathematical tools have been developed that analyze how dynamic decision networks, game theory and mechanism design. 5.2 Search and optimization They may begin with a population of organisms and then allow them to mutate and recombine, selecting only the fi ...
... something to an intelligent agent. Precise mathematical tools have been developed that analyze how dynamic decision networks, game theory and mechanism design. 5.2 Search and optimization They may begin with a population of organisms and then allow them to mutate and recombine, selecting only the fi ...
A biologically constrained learning mechanism in networks of formal
... guaranteeing the perfect memorization and retrieval of orthogonal prototype patterns of information (up to a maximal storage capacity). Starting from an initial synaptic matrix with random elements (synaptic strengths), which produces a very large number of stable memorized states (called prereprese ...
... guaranteeing the perfect memorization and retrieval of orthogonal prototype patterns of information (up to a maximal storage capacity). Starting from an initial synaptic matrix with random elements (synaptic strengths), which produces a very large number of stable memorized states (called prereprese ...
Call For Papers - Department of Computing Science
... knowledge acquisition and explanation generation in complex domains. The aim of the SARA series is to provide a forum for interaction among researchers in all areas of Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science with an interest in the different aspects of ARA techniques. The diverse backgrounds of ...
... knowledge acquisition and explanation generation in complex domains. The aim of the SARA series is to provide a forum for interaction among researchers in all areas of Artificial Intelligence and Computer Science with an interest in the different aspects of ARA techniques. The diverse backgrounds of ...
Partial Position Transfer in Categorical Perceptual Learning Alexander Gerganov ()
... for participation in the study. 24 participants finished successfully the training phase and were tested for translation invariance of learning. One outlier was excluded from the analysis because of a very low score (55%) in the control position. All other participants scored above 85% in the contro ...
... for participation in the study. 24 participants finished successfully the training phase and were tested for translation invariance of learning. One outlier was excluded from the analysis because of a very low score (55%) in the control position. All other participants scored above 85% in the contro ...
Evolving Spiking Neural Networks for Spatio- and - kedri
... process both data and knowledge in a supervised and/or unsupervised way [5]. ECOS learn local models from data through clustering of the data and associating a local output function for each cluster represented in a connectionist structure. They can learn incrementally single data items or chunks of ...
... process both data and knowledge in a supervised and/or unsupervised way [5]. ECOS learn local models from data through clustering of the data and associating a local output function for each cluster represented in a connectionist structure. They can learn incrementally single data items or chunks of ...
b. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
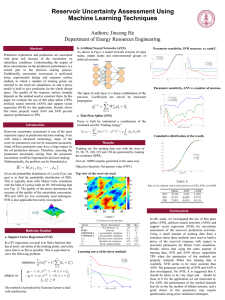
... Petroleum exploration and production are associated with great risk because of the uncertainty on subsurface conditions. Understanding the impact of those uncertainties on the production performance is a crucial part in the decision making process. Traditionally, uncertainty assessment is performed ...
... Petroleum exploration and production are associated with great risk because of the uncertainty on subsurface conditions. Understanding the impact of those uncertainties on the production performance is a crucial part in the decision making process. Traditionally, uncertainty assessment is performed ...
Michael Arbib and Laurent Itti: CS564
... Associative Search Unit: The associative search rule, based on Klopf's (1982) self-interested neuron - the unit's output is a random variable depending on the activation level: 1 with probabilit y p(t) a(t) = 0with probabilit y 1 - p(t) where p(t), between 0 and 1, is an increasing function of ...
... Associative Search Unit: The associative search rule, based on Klopf's (1982) self-interested neuron - the unit's output is a random variable depending on the activation level: 1 with probabilit y p(t) a(t) = 0with probabilit y 1 - p(t) where p(t), between 0 and 1, is an increasing function of ...
Paper
... a goal-has been a mainstay of artificial intelligence (AI) research for many years. Traditionally, the decision-making models that have been studied admit no uncertainty: every aspect of the world that is relevant to the generation and execution of a plan is known in advance. In contrast, work in op ...
... a goal-has been a mainstay of artificial intelligence (AI) research for many years. Traditionally, the decision-making models that have been studied admit no uncertainty: every aspect of the world that is relevant to the generation and execution of a plan is known in advance. In contrast, work in op ...
graphpartitioning
... • Suppose we are looking for linear separator. We believe should exist one with large separation. Transductive SVM [Joachims]: ...
... • Suppose we are looking for linear separator. We believe should exist one with large separation. Transductive SVM [Joachims]: ...
Multi-Layer Feed-Forward - Teaching-WIKI
... often provides better estimates of generalization error at the cost of even more computing time. • No matter which method is applied, the estimate of the generalization error of the best network will be optimistic. • If several networks are trained using one data set, and a second (validation set) i ...
... often provides better estimates of generalization error at the cost of even more computing time. • No matter which method is applied, the estimate of the generalization error of the best network will be optimistic. • If several networks are trained using one data set, and a second (validation set) i ...
File
... 9. Define joint probability distribution. Joint probability distribution completely specifies an agent's probability assignments to all propositions in the domain. The joint probability distribution p(x1,x2,-------xn) assigns probabilities to all possible atomic events; where x1,x2------xn=variables ...
... 9. Define joint probability distribution. Joint probability distribution completely specifies an agent's probability assignments to all propositions in the domain. The joint probability distribution p(x1,x2,-------xn) assigns probabilities to all possible atomic events; where x1,x2------xn=variables ...
Learning
... • Reinforcers increase the desire to repeat the behavior. • Punishers decrease the desire to repeat the behavior. • Law of Effect – reinforcement will lead to repeated performance, punishment will ...
... • Reinforcers increase the desire to repeat the behavior. • Punishers decrease the desire to repeat the behavior. • Law of Effect – reinforcement will lead to repeated performance, punishment will ...
marked - Kansas State University
... CIS732 Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition http://www.kddresearch.org/Courses/Fall-2005/CIS732 CIS830 Advanced Topics in Artificial Intelligence http://www.kddresearch.org/Courses/Spring-2005/CIS830 CIS690 Implementation of High-Performance Data Mining Systems http://ringil.cis.ksu.edu/Co ...
... CIS732 Machine Learning and Pattern Recognition http://www.kddresearch.org/Courses/Fall-2005/CIS732 CIS830 Advanced Topics in Artificial Intelligence http://www.kddresearch.org/Courses/Spring-2005/CIS830 CIS690 Implementation of High-Performance Data Mining Systems http://ringil.cis.ksu.edu/Co ...
Machine learning

Machine learning is a subfield of computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence. Machine learning explores the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. Such algorithms operate by building a model from example inputs in order to make data-driven predictions or decisions, rather than following strictly static program instructions.Machine learning is closely related to and often overlaps with computational statistics; a discipline that also specializes in prediction-making. It has strong ties to mathematical optimization, which delivers methods, theory and application domains to the field. Machine learning is employed in a range of computing tasks where designing and programming explicit algorithms is infeasible. Example applications include spam filtering, optical character recognition (OCR), search engines and computer vision. Machine learning is sometimes conflated with data mining, although that focuses more on exploratory data analysis. Machine learning and pattern recognition ""can be viewed as two facets ofthe same field.""When employed in industrial contexts, machine learning methods may be referred to as predictive analytics or predictive modelling.