Introduction to Philosophy Study Guide: Logic and Critical Thinking
... What logic deals with. [It deals with the relation between the premises and the conclusion. Generally, logic cannot tell you whether the premises are in fact true or not–that is known either by common knowledge or consulting someone who has expert knowledge.] The difference between a real and an app ...
... What logic deals with. [It deals with the relation between the premises and the conclusion. Generally, logic cannot tell you whether the premises are in fact true or not–that is known either by common knowledge or consulting someone who has expert knowledge.] The difference between a real and an app ...
Full Text
... is questionable whether they serve any purpose, and if they do have a function, the ultimate purpose or function will be survival. “But then it is unlikely that they have the production of true beliefs as a function. So the probability or our faculties' being reliable, given naturalistic evolution, ...
... is questionable whether they serve any purpose, and if they do have a function, the ultimate purpose or function will be survival. “But then it is unlikely that they have the production of true beliefs as a function. So the probability or our faculties' being reliable, given naturalistic evolution, ...
Philosophy of Religion Induction Day
... If it’s premises are true, then its conclusion could still be false. The premises provide some but not absolute support for the conclusion. How would you use inductive reasoning to demonstrate all geese are white If you see one goose, you might think, geese are white, but you don't have a large enou ...
... If it’s premises are true, then its conclusion could still be false. The premises provide some but not absolute support for the conclusion. How would you use inductive reasoning to demonstrate all geese are white If you see one goose, you might think, geese are white, but you don't have a large enou ...
Ethical Naturalism and the Naturalistic Fallacy
... verifiable to have meaning eg David Cameron is the PM of UK. • Ethical Naturalism – Ethics and morality/good and bad can be empirically verified ...
... verifiable to have meaning eg David Cameron is the PM of UK. • Ethical Naturalism – Ethics and morality/good and bad can be empirically verified ...
HW #3 Solutions
... the evidence needs to establish is that the probability that the defendant is guilty is greater than 1/2! The “beyond a reasonable doubt” standard, on the other hand, is far more strict. In a criminal trial, it is not enough for the evidence to merely support (to some degree) the defendant’s guilt. ...
... the evidence needs to establish is that the probability that the defendant is guilty is greater than 1/2! The “beyond a reasonable doubt” standard, on the other hand, is far more strict. In a criminal trial, it is not enough for the evidence to merely support (to some degree) the defendant’s guilt. ...
Nature of Argument PPT
... is uncertain of the outcome if a conclusion is certain, inescapable, there is no need to argue ...
... is uncertain of the outcome if a conclusion is certain, inescapable, there is no need to argue ...
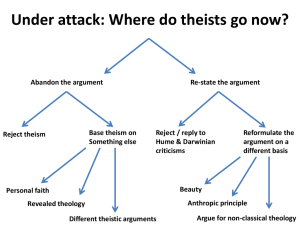
Nature of Argument
... is uncertain of the outcome if a conclusion is certain, inescapable, there is no need to argue ...
... is uncertain of the outcome if a conclusion is certain, inescapable, there is no need to argue ...
Swinburne and Tennant
... can be set out by relatively simple formulae which men can understand and by means of which they can successfully predict the future. The orderliness of the universe to which I draw attention here is its conformity to formula, to simple, formutable, scientific laws. The orderliness of the universe i ...
... can be set out by relatively simple formulae which men can understand and by means of which they can successfully predict the future. The orderliness of the universe to which I draw attention here is its conformity to formula, to simple, formutable, scientific laws. The orderliness of the universe i ...
Anthropic Principle File
... universe as we find it? • Swinburne claims that scientists are able to define laws, say how they work, and discover new ones. However, what scientists may never do is find a basis for the most fundamental laws in the first place. • In other words, the scientific method cannot explain why there is de ...
... universe as we find it? • Swinburne claims that scientists are able to define laws, say how they work, and discover new ones. However, what scientists may never do is find a basis for the most fundamental laws in the first place. • In other words, the scientific method cannot explain why there is de ...
PHIL/RS 335
... Is it intuitively true? Does reason presuppose it? If an explanation seems possible, does that mean there is one (Yandells 76c1)? ...
... Is it intuitively true? Does reason presuppose it? If an explanation seems possible, does that mean there is one (Yandells 76c1)? ...
Quiz1 - Ryerson University
... what we claim to know was: (a) To reject everything that we believed beforehand. (b) To reject everything that Aristotle had to say. (c) To reject every belief for which there was even the slightest doubt. (d) None of the above. ...
... what we claim to know was: (a) To reject everything that we believed beforehand. (b) To reject everything that Aristotle had to say. (c) To reject every belief for which there was even the slightest doubt. (d) None of the above. ...
Evolution and Theology
... philosophy that is not supported by the evidence • Evolutionary theory can be understood within a Christian theological framework • Theology becomes the metaphysics that helps to inform science and answers certain questions ...
... philosophy that is not supported by the evidence • Evolutionary theory can be understood within a Christian theological framework • Theology becomes the metaphysics that helps to inform science and answers certain questions ...