Lecture 4 1 Unitary Operators and Quantum Gates
... have been sent well before Alice had decided what message she wanted to send. Perhaps only much later did she decide on her message and send over the second qubit. One can show that it is not possible to do any better. Two qubits are necessary to send two classical bits. Superdense coding allows hal ...
... have been sent well before Alice had decided what message she wanted to send. Perhaps only much later did she decide on her message and send over the second qubit. One can show that it is not possible to do any better. Two qubits are necessary to send two classical bits. Superdense coding allows hal ...
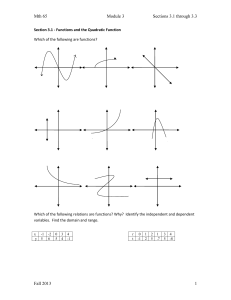
Mth 65 Module 3 Sections 3.1 through 3.3 Section 3.1
... The function above is called a _______________________________function. The shape of the graph is called a ___________________________. Each parabola has a _______________(maximum or minimum) and an axis of symmetry (always a ______________________ line which passes through the vertex). State the ve ...
... The function above is called a _______________________________function. The shape of the graph is called a ___________________________. Each parabola has a _______________(maximum or minimum) and an axis of symmetry (always a ______________________ line which passes through the vertex). State the ve ...
GALOIS DESCENT 1. Introduction Let L/K be a field extension. A K
... a K-basis {ei } of W turns into an L-basis {1 ⊗ ei } of L ⊗K W . Passing from W to L ⊗K W is called ascent. In the other direction, if we are given an L-vector space V 6= 0, we may ask how to describe the K-subspaces W ⊂ V such that a K-basis of W is an L-basis of V . Definition 1.1. For an L-vector ...
... a K-basis {ei } of W turns into an L-basis {1 ⊗ ei } of L ⊗K W . Passing from W to L ⊗K W is called ascent. In the other direction, if we are given an L-vector space V 6= 0, we may ask how to describe the K-subspaces W ⊂ V such that a K-basis of W is an L-basis of V . Definition 1.1. For an L-vector ...
Sage Quick Reference - Sage Wiki
... CC^4 4-dimensional, 53-bit precision complexes Y = VectorSpace(GF(7), 4) finite Y.list() has 74 = 2401 vectors Vector Space Properties V.dimension() V.basis() V.echelonized_basis() V.has_user_basis() with non-canonical basis? V.is_subspace(W) True if W is a subspace of V V.is_full() rank equals degr ...
... CC^4 4-dimensional, 53-bit precision complexes Y = VectorSpace(GF(7), 4) finite Y.list() has 74 = 2401 vectors Vector Space Properties V.dimension() V.basis() V.echelonized_basis() V.has_user_basis() with non-canonical basis? V.is_subspace(W) True if W is a subspace of V V.is_full() rank equals degr ...
Lecture07
... In principle, could be used to solve any dynamics problem, But, often, they are very difficult to apply, especially to very complicated systems. So, alternate formulations have been developed. Often easier to apply. ...
... In principle, could be used to solve any dynamics problem, But, often, they are very difficult to apply, especially to very complicated systems. So, alternate formulations have been developed. Often easier to apply. ...























