OUTLINE for the Algebra Midterm FRIDAY, JANUARY 11, 2013
... OUTLINE for the Algebra Midterm FRIDAY, JANUARY 11, 2013 ...
... OUTLINE for the Algebra Midterm FRIDAY, JANUARY 11, 2013 ...
1.5 Linear Equations and Inequalities
... Recall: x-intercept is the zero of the linear function. ...
... Recall: x-intercept is the zero of the linear function. ...
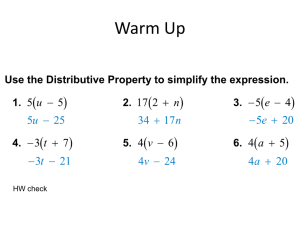
MATH 120 chapter 3 online quiz
... first car travels at 60 m.p.h. while the second travels at 70 m.p.h. In how many hours will they be 600 miles apart? a) d - 600 = 60t and d+600 =70t b) d = 60 t + 70 and d=600 - 70t c) d =60t and 600 - d = 70t * d) d = t +10 and 10d =60 7. Which of the following systems could be used to solve the f ...
... first car travels at 60 m.p.h. while the second travels at 70 m.p.h. In how many hours will they be 600 miles apart? a) d - 600 = 60t and d+600 =70t b) d = 60 t + 70 and d=600 - 70t c) d =60t and 600 - d = 70t * d) d = t +10 and 10d =60 7. Which of the following systems could be used to solve the f ...