The Fresnel Coefficients - The Society of Vacuum Coaters
... on the other hand, knew that somehow the vibrations had to be transverse and proposed a light ray as a transverse propagating regular continuous sinusoidal oscillation, or vibration, of luminous particles, supported in a much less dense continuous medium, in other words a progressive harmonic wave. ...
... on the other hand, knew that somehow the vibrations had to be transverse and proposed a light ray as a transverse propagating regular continuous sinusoidal oscillation, or vibration, of luminous particles, supported in a much less dense continuous medium, in other words a progressive harmonic wave. ...
de Sénarmont Bias Retardation in DIC Microscopy Introduction
... conjugate focal plane of the iris diaphragm aperture. Incident wavefronts are sheared by the prism into orthogonal polarized components separated by less than a micrometer, rendered parallel by the condenser optical system, and then utilized to illuminate the specimen. Positioned behind the objectiv ...
... conjugate focal plane of the iris diaphragm aperture. Incident wavefronts are sheared by the prism into orthogonal polarized components separated by less than a micrometer, rendered parallel by the condenser optical system, and then utilized to illuminate the specimen. Positioned behind the objectiv ...
Fraunhofer Diffraction
... • If the curvature of the optical waves must be taken into account at the aperture or image plane, then we must use Fresnel (near-field) diffraction theory. • The Huygens-Fresnel principle is used in diffraction theory, in that every point of a given wavefront of light can be considered as a source ...
... • If the curvature of the optical waves must be taken into account at the aperture or image plane, then we must use Fresnel (near-field) diffraction theory. • The Huygens-Fresnel principle is used in diffraction theory, in that every point of a given wavefront of light can be considered as a source ...
UW LaTeX Thesis Template - UWSpace
... Surface plasmon polaritons are electromagnetic surface waves coupled to electron plasma oscillation of metals at a metal-dielectric interface. At optical frequencies, these modes are of great interest because of their high confinement to a metal-dielectric interface. Due to the field enhancement at th ...
... Surface plasmon polaritons are electromagnetic surface waves coupled to electron plasma oscillation of metals at a metal-dielectric interface. At optical frequencies, these modes are of great interest because of their high confinement to a metal-dielectric interface. Due to the field enhancement at th ...
Simultaneous spatial and temporal focusing: A route towards
... axial resolution and reduced contrast due to the enlarged Rayleigh length, which also causes the excitation of fluorescent molecules upstream and downstream from the focal plane. Moreover, for various applications such as intraocular fs-laser surgery or back-side processing of glass, ultrashort lase ...
... axial resolution and reduced contrast due to the enlarged Rayleigh length, which also causes the excitation of fluorescent molecules upstream and downstream from the focal plane. Moreover, for various applications such as intraocular fs-laser surgery or back-side processing of glass, ultrashort lase ...
The proceedings of this workshop are available here.
... engineering,but it may be the nature of this rapidly progressingfield a reasonfor the fact that also results on more general,bianisotropic materials were discussed(not to mention the informal interaction sessionswhere topics like scientific ethics and turmoils in global political structures were rea ...
... engineering,but it may be the nature of this rapidly progressingfield a reasonfor the fact that also results on more general,bianisotropic materials were discussed(not to mention the informal interaction sessionswhere topics like scientific ethics and turmoils in global political structures were rea ...
Physical Optics
... optical components and physical optics systems gain knowledge about diffraction grating polarizers interference filters and, experiment 4 physical optics ucla physics astronomy experiment 4 physical optics click here for experiment 4 physical optics attachments lab hazard awareness information pdf l ...
... optical components and physical optics systems gain knowledge about diffraction grating polarizers interference filters and, experiment 4 physical optics ucla physics astronomy experiment 4 physical optics click here for experiment 4 physical optics attachments lab hazard awareness information pdf l ...
Theory of optical pulse propagation, dispersive and nonlinear effects
... and hence the pulse shape is small upon travelling a distance equal to the carrier wavelength, Eq. (IV-133) expresses that the pulse is long enough so that its electric field amplitude varies little – at any position – within the carrier oscillation period. Whereas the first approximation is to be f ...
... and hence the pulse shape is small upon travelling a distance equal to the carrier wavelength, Eq. (IV-133) expresses that the pulse is long enough so that its electric field amplitude varies little – at any position – within the carrier oscillation period. Whereas the first approximation is to be f ...
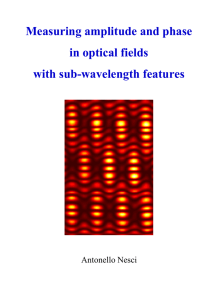
Measuring amplitude and phase in optical fields with
... fields. In scanning near-field optical microscopy, the field generated by an object, especially by sub-wavelength objects, is different from the object itself. In general, rigorous diffraction theory is needed to estimate the geometrical parameters of the object under investigation. To characterize ...
... fields. In scanning near-field optical microscopy, the field generated by an object, especially by sub-wavelength objects, is different from the object itself. In general, rigorous diffraction theory is needed to estimate the geometrical parameters of the object under investigation. To characterize ...
Full-angle Negative Reflection with An Ultrathin Acoustic
... discretized model depicted in Figure 2(b) is utilized for further analysis. In this case, one supercell is composed by M subunits and the width of each subunit is l L M . The fluid density and bulk modulus of the m-th subunit are denoted as m and Bm , which can be regarded as two constants withi ...
... discretized model depicted in Figure 2(b) is utilized for further analysis. In this case, one supercell is composed by M subunits and the width of each subunit is l L M . The fluid density and bulk modulus of the m-th subunit are denoted as m and Bm , which can be regarded as two constants withi ...
Acousto-Optic Devices and Applications
... of diffraction orders were observed. This discrepancy was later explained by the theoretical work of Raman and Nath.4 They derived a set of coupled wave equations that fully described the AO diffraction in unbounded isotropic media. The theory predicts two diffraction regimes; the Raman-Nath regime, ...
... of diffraction orders were observed. This discrepancy was later explained by the theoretical work of Raman and Nath.4 They derived a set of coupled wave equations that fully described the AO diffraction in unbounded isotropic media. The theory predicts two diffraction regimes; the Raman-Nath regime, ...
Nonlinear Optics Third Edition
... within a conventional one-semester course. For this reason, I am often asked for advice on how to structure a course based on the content of my textbook. Some of my thoughts along these lines are as follows: (1) I have endeavored as much as possible to make each part of the book self-contained. Thus ...
... within a conventional one-semester course. For this reason, I am often asked for advice on how to structure a course based on the content of my textbook. Some of my thoughts along these lines are as follows: (1) I have endeavored as much as possible to make each part of the book self-contained. Thus ...