Nikolai G. Basov - Nobel Lecture
... (I) The creation of quantum frequency oscillators of high stability and the transition to atomic standards of time made it possible to raise the question of solving the problem of the properties of atomic time. Dicke 2 in his paper at the first conference on quantum electronics pointed out the possi ...
... (I) The creation of quantum frequency oscillators of high stability and the transition to atomic standards of time made it possible to raise the question of solving the problem of the properties of atomic time. Dicke 2 in his paper at the first conference on quantum electronics pointed out the possi ...
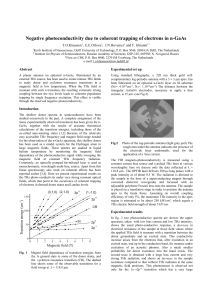
Negative photoconductivity due to coherent trapping of electrons in
... Fig. 4. Sample resistance at low bias as a function of THz intensity: saturation of the 2p+1 and the CR transition. The influence of the bias current at constant maximum THz intensity is presented in fig. 5. With increasing bias current the sample resistance in the absence of THz radiation decreases ...
... Fig. 4. Sample resistance at low bias as a function of THz intensity: saturation of the 2p+1 and the CR transition. The influence of the bias current at constant maximum THz intensity is presented in fig. 5. With increasing bias current the sample resistance in the absence of THz radiation decreases ...
Table of contents
... ◦ Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals (form -1 anions). Highly variable physical properties. Low boiling points. Gases at room temperature. ◦ Transition elements – very hard, very high melting and boiling points. Very malleable and conducts electricity since d electrons are loose. Low ionization ...
... ◦ Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals (form -1 anions). Highly variable physical properties. Low boiling points. Gases at room temperature. ◦ Transition elements – very hard, very high melting and boiling points. Very malleable and conducts electricity since d electrons are loose. Low ionization ...
The Time-Shift Technique for Measurement of Size and Velocity of
... Semidetnov (1985) [3] and is further developed in Damaschke et al (2002) and Albrecht et al (2003). It is realized by creating an illuminated volume considerably smaller than the size of the particle to be measured, usually taking a Gaussian beam shape in intensity. Under these conditions the scatte ...
... Semidetnov (1985) [3] and is further developed in Damaschke et al (2002) and Albrecht et al (2003). It is realized by creating an illuminated volume considerably smaller than the size of the particle to be measured, usually taking a Gaussian beam shape in intensity. Under these conditions the scatte ...
OPTI 511R, Spring 2015 Problem Set 8 Prof. E. M. Wright Due
... The problems of this assignment deal with optical resonators and laser light. You do not need to know the physics of how a laser works, but you need to assume the following: (i) Only a single longitudinal and transverse mode of the cavity will be occupied with light. (ii) One of the mirrors is just ...
... The problems of this assignment deal with optical resonators and laser light. You do not need to know the physics of how a laser works, but you need to assume the following: (i) Only a single longitudinal and transverse mode of the cavity will be occupied with light. (ii) One of the mirrors is just ...
JC2315121515
... measurement speed is much higher, they can measure surfaces through transparent medium such as glass or plastic film. It can be used on soft materials like lenses, floppy discs. Disadvantages are it requires specimens must be small enough in order to fit into the specimen cell of the microscope, the ...
... measurement speed is much higher, they can measure surfaces through transparent medium such as glass or plastic film. It can be used on soft materials like lenses, floppy discs. Disadvantages are it requires specimens must be small enough in order to fit into the specimen cell of the microscope, the ...
Microscopy Overview
... source is usually used. In critical illumination, the source is focused on to the object by a condenser lens. The disadvantage of this approach is that variations in emission of the source are imaged directly into the image. Cheaper microscopes avoid this problem by using a diffuser. Better microsco ...
... source is usually used. In critical illumination, the source is focused on to the object by a condenser lens. The disadvantage of this approach is that variations in emission of the source are imaged directly into the image. Cheaper microscopes avoid this problem by using a diffuser. Better microsco ...
Aalborg Universitet Transfer function and near-field detection of evanescent waves
... distribution can be decomposed into two orthogonally polarized fiber modes, whose amplitudes we shall denote as Ax and Ay. It should be mentioned in passing that the origin of the probed field [see Eq. (1)] is irrelevant in this consideration and that the sample surface serves merely as a reference ...
... distribution can be decomposed into two orthogonally polarized fiber modes, whose amplitudes we shall denote as Ax and Ay. It should be mentioned in passing that the origin of the probed field [see Eq. (1)] is irrelevant in this consideration and that the sample surface serves merely as a reference ...
Plasmonic waveguide filters with nanodisk resonators
... Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are waves trapped on the surfaces of metals owing to the interaction between the free electrons in a metal and the electromagnetic field in a dielectric, and attenuating exponentially in the direction perpendicular to the interface. [1] ...
... Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are waves trapped on the surfaces of metals owing to the interaction between the free electrons in a metal and the electromagnetic field in a dielectric, and attenuating exponentially in the direction perpendicular to the interface. [1] ...
Towards resonant-state THz laser based on strained p
... 1V.A. Kotel’nikov Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Ac. Sci., Moscow, Russia; ...
... 1V.A. Kotel’nikov Institute of Radio Engineering and Electronics, Russian Ac. Sci., Moscow, Russia; ...
EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES
... solvent. The difference between TSSG and other flux techniques is that crystals grow in a crystal seed placed in contact with the surface of the solution. With this technique, when the solution is cooled slowly, the crystal starts to grow in the supersaturated melt and continues to grow while the te ...
... solvent. The difference between TSSG and other flux techniques is that crystals grow in a crystal seed placed in contact with the surface of the solution. With this technique, when the solution is cooled slowly, the crystal starts to grow in the supersaturated melt and continues to grow while the te ...
V807 -Photon-Counting Avalanche Photodiodes – A Primer
... mode APD or PMT will vary depending upon the bias across the multiplication stage; η is a more useful basis for comparison between different detectors if it expresses the ability to deliver primary photocarriers to the multiplication stages of these devices rather than the total quantum yield at a g ...
... mode APD or PMT will vary depending upon the bias across the multiplication stage; η is a more useful basis for comparison between different detectors if it expresses the ability to deliver primary photocarriers to the multiplication stages of these devices rather than the total quantum yield at a g ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... chemical compound changes. Some common redox reactions include fire, rusting of metals, browning of fruit, and photosynthesis. In simpler terms, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one substance to another. In a redox reaction, electrons can never be “lost”; if one substance loses ...
... chemical compound changes. Some common redox reactions include fire, rusting of metals, browning of fruit, and photosynthesis. In simpler terms, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one substance to another. In a redox reaction, electrons can never be “lost”; if one substance loses ...
arXiv:quant-ph/0602132 v2 20 Feb 2006
... analysis, it is important to note that the spatial features of the beam used could, in principle, be at the diffraction limit. In order to resolve the encoded longitudinal phase of the beam, an interferometric scheme is required. To resolve the spatial phase profile of the beam, a multi-segment phot ...
... analysis, it is important to note that the spatial features of the beam used could, in principle, be at the diffraction limit. In order to resolve the encoded longitudinal phase of the beam, an interferometric scheme is required. To resolve the spatial phase profile of the beam, a multi-segment phot ...
EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA 7.0 by extrinsic factors (test conditions), such as hydrodynamics,
... may be used. To remove such materials from the compressed by means of a repeatability determination. gas, a dryer with a filter can be used. Any vacuum unit should be located away from the measurement zone, so that its output The attainable repeatability of the method mainly depends on the character ...
... may be used. To remove such materials from the compressed by means of a repeatability determination. gas, a dryer with a filter can be used. Any vacuum unit should be located away from the measurement zone, so that its output The attainable repeatability of the method mainly depends on the character ...
High-resolution measurement of phase singularities
... difference between two subsequent diffraction orders is exactly equal to one wavelength. This means that the screw-like phase distribution produced by the CGH has an additional 2p phase shift. This will lead to a beam in the second order which carries a singularity that has twice the strength of the s ...
... difference between two subsequent diffraction orders is exactly equal to one wavelength. This means that the screw-like phase distribution produced by the CGH has an additional 2p phase shift. This will lead to a beam in the second order which carries a singularity that has twice the strength of the s ...
Gaseous detection device
The gaseous detection device-GDD is a method and apparatus for the detection of signals in the gaseous environment of an environmental scanning electron microscope (ESEM) and all scanned beam type of instruments that allow a minimum gas pressure for the detector to operate.