Activity 10: Image Formation From a Curved Mirror
... An incident ray that moves towards the center reflects back on itself. An incident ray that moves towards the focal point reflects parallel to the optical axis. The first incident ray that is parallel to the optical axis is already shown below. Draw all three principal rays below and their corre ...
... An incident ray that moves towards the center reflects back on itself. An incident ray that moves towards the focal point reflects parallel to the optical axis. The first incident ray that is parallel to the optical axis is already shown below. Draw all three principal rays below and their corre ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... the form of concentric rings formed from a light source after passing a plano-convex lens, could not be explained by simply regarding light as rays that propagate along straight lines. English physicist Thomas Young explained Newton's rings as an interference phenomenon, which is a characteristic of ...
... the form of concentric rings formed from a light source after passing a plano-convex lens, could not be explained by simply regarding light as rays that propagate along straight lines. English physicist Thomas Young explained Newton's rings as an interference phenomenon, which is a characteristic of ...
About Optical Fiber - University of Vaasa
... Optical Fiber provides a very large bandwidth data rates. Based on its requirements and needs, Networks communication ...
... Optical Fiber provides a very large bandwidth data rates. Based on its requirements and needs, Networks communication ...
Color Astronomical Imaging Using Polarizing Filters
... Previous work by Malin and Pasachoff* used a photographic technique for performing the differencing of the polarizer channels. While an ingenious process, practical considerations involving the film medium made the process somewhat difficult in comparison with today’s digital methods. In this work t ...
... Previous work by Malin and Pasachoff* used a photographic technique for performing the differencing of the polarizer channels. While an ingenious process, practical considerations involving the film medium made the process somewhat difficult in comparison with today’s digital methods. In this work t ...
chapter 5 linear and nonlinear optical properties of
... magnitude of nonlinear optical (NLO) efficiency (Blanchard-Desce et al ...
... magnitude of nonlinear optical (NLO) efficiency (Blanchard-Desce et al ...
CP1: Investigation into the Feasibility of a Three Axis
... Another issue in biological settings involves the restrictions that the shape and size of the sample (and its necessary environment) pose. A great variety of situations of this kind arise. Cells under inspection may need to be imaged whilst immersed in growth media, they may form just a small sectio ...
... Another issue in biological settings involves the restrictions that the shape and size of the sample (and its necessary environment) pose. A great variety of situations of this kind arise. Cells under inspection may need to be imaged whilst immersed in growth media, they may form just a small sectio ...
Optical Term Definitions
... BACK FOCAL LENGTH (FB) This length is the distance from the secondary vertex (A2) to the rear focal point (F"). ...
... BACK FOCAL LENGTH (FB) This length is the distance from the secondary vertex (A2) to the rear focal point (F"). ...
n 1n d
... The corresponding modulation of the coherent scattering length density b1 is two orders of magnitude larger than in the best PNR materials reported up to now!! b1 = (bN), due to phase separation of the constituent compounds (b) can be large even if (N) is relatively small !!! M. Fally, I. Dreve ...
... The corresponding modulation of the coherent scattering length density b1 is two orders of magnitude larger than in the best PNR materials reported up to now!! b1 = (bN), due to phase separation of the constituent compounds (b) can be large even if (N) is relatively small !!! M. Fally, I. Dreve ...
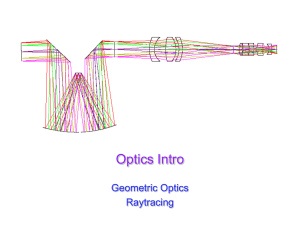
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester Lecture 30 – Geometric Optics
... Pellin-Broca Prism One color is refracted through exactly 90°. Rotating the prism about point A selects different colors. Ideal for selecting a particular wavelength with minimal change to an optical system. ...
... Pellin-Broca Prism One color is refracted through exactly 90°. Rotating the prism about point A selects different colors. Ideal for selecting a particular wavelength with minimal change to an optical system. ...
PPT
... Raytracing Algorithm • Detailed math available on website (raytrace link) • Basically, compute intersection of ray with surface, then apply Snell’s Law ...
... Raytracing Algorithm • Detailed math available on website (raytrace link) • Basically, compute intersection of ray with surface, then apply Snell’s Law ...
Chapter 8 Wave Optics
... Please read your English text book and find out what wavelength light you can see. 8.1.5 Air wedge The abrupt phase change occurs at the lower surface of the air wedge. For the wedge its refractive index is equal to 1. The condition for destructive interference is simpler 2d m m = 0, 1, 2, … Exam ...
... Please read your English text book and find out what wavelength light you can see. 8.1.5 Air wedge The abrupt phase change occurs at the lower surface of the air wedge. For the wedge its refractive index is equal to 1. The condition for destructive interference is simpler 2d m m = 0, 1, 2, … Exam ...
PDF only - at www.arxiv.org.
... Already in his seminal paper about the unique counter-example to Schiff’s conjecture giving rise to CPR, Ni57 suggested that observations of polarized astrophysical sources could give constraints on the CPR. However, only in 1990, the polarization at radio wavelengths of RGs and quasars was used for ...
... Already in his seminal paper about the unique counter-example to Schiff’s conjecture giving rise to CPR, Ni57 suggested that observations of polarized astrophysical sources could give constraints on the CPR. However, only in 1990, the polarization at radio wavelengths of RGs and quasars was used for ...
Spectroscopic Imaging using Terahertz Time-Domain Signals
... window size (25 ps) limited the number of multiples. Obviously, both the stepping size and analysis window can be changed depending on the material under investigation. ...
... window size (25 ps) limited the number of multiples. Obviously, both the stepping size and analysis window can be changed depending on the material under investigation. ...
Impact of Liquid Crystals in Active and Adaptive Optics
... two main properties: polarization and birefringence. The term polarization (P) refers to two different magnitudes. In one hand it describes the dipole moment per unit volume of a material that points in the same direction as the average molecular dipole moment. On the other hand it refers to the vib ...
... two main properties: polarization and birefringence. The term polarization (P) refers to two different magnitudes. In one hand it describes the dipole moment per unit volume of a material that points in the same direction as the average molecular dipole moment. On the other hand it refers to the vib ...
Superprism phenomena in planar photonic crystals
... In Fig. 4(b), when the frequency is altered from 0.214 to 0.217, which corresponds to a wavelength change from 1310 nm to 1290 nm, the shape of the iso-frequency contour varies from a quasihexagram to a quasi-triangle. In order to explain our results, we proceeded as follows. The incident light is o ...
... In Fig. 4(b), when the frequency is altered from 0.214 to 0.217, which corresponds to a wavelength change from 1310 nm to 1290 nm, the shape of the iso-frequency contour varies from a quasihexagram to a quasi-triangle. In order to explain our results, we proceeded as follows. The incident light is o ...
PDF
... There is a growing interest in using the nematic liquid crystals (NLCs) in biological sensors as the medium that amplifies the molecular- and submicron-scale reactions such as ligand-receptor binding to the macro-scale accessible for optical detection [1–7]. Abbott et al. proposed a technique based ...
... There is a growing interest in using the nematic liquid crystals (NLCs) in biological sensors as the medium that amplifies the molecular- and submicron-scale reactions such as ligand-receptor binding to the macro-scale accessible for optical detection [1–7]. Abbott et al. proposed a technique based ...
Lecture 3
... Anisotropic crystals have crystallographically distinct axes and interact with light in a manner that is dependent upon the orientation of the crystalline lattice with respect to the incident light. When light enters the optical axis (c) of anisotropic crystals, it acts in a manner similar to intera ...
... Anisotropic crystals have crystallographically distinct axes and interact with light in a manner that is dependent upon the orientation of the crystalline lattice with respect to the incident light. When light enters the optical axis (c) of anisotropic crystals, it acts in a manner similar to intera ...
Organic Nonlinear Optic Devices
... • Fluorine content controls the refractive index of polyimide • Core and cladding layer can be made from the same polymer---polyimide. ...
... • Fluorine content controls the refractive index of polyimide • Core and cladding layer can be made from the same polymer---polyimide. ...
Birefringence
Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent (or birefractive). The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with asymmetric crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.Birefringence is responsible for the phenomenon of double refraction whereby a ray of light, when incident upon a birefringent material, is split by polarization into two rays taking slightly different paths. This effect was first described by the Danish scientist Rasmus Bartholin in 1669, who observed it in calcite, a crystal having one of the strongest birefringences. However it was not until the 19th century that Augustin-Jean Fresnel described the phenomenon in terms of polarization, understanding light as a wave with field components in transverse polarizations (perpendicular to the direction of the wave vector).