Physics - No Brain Too Small
... When light travels from a medium to a less dense medium, a certain angle of incidence will produce an angle of refraction of 90o. This angle of incidence is the critical angle for this material. If the angle of incidence > critical angle, then total internal reflection occurs. Less than the critic ...
... When light travels from a medium to a less dense medium, a certain angle of incidence will produce an angle of refraction of 90o. This angle of incidence is the critical angle for this material. If the angle of incidence > critical angle, then total internal reflection occurs. Less than the critic ...
Introduction to light 2
... Therefore the index of refraction is higher for short wavelengths and lower for long wavelengths of light ...
... Therefore the index of refraction is higher for short wavelengths and lower for long wavelengths of light ...
revision_foundation_..
... • Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves and can therefore be polarised. • If a radio wave is transmitted from a vertical aerial then the wave will have vertical polarisation and any receiving aerial must also be positioned vertically. • The main transmitters in the U.K. send out signals which a ...
... • Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves and can therefore be polarised. • If a radio wave is transmitted from a vertical aerial then the wave will have vertical polarisation and any receiving aerial must also be positioned vertically. • The main transmitters in the U.K. send out signals which a ...
Opt001
... Prism spectrometers are used to measure the wavelengths of light emitted by a sample. The key to its operation is a glass prism, which disperses light into a spectrum. Experiment 1 develops your understanding of how the prism spectrometer works, as well as the skills necessary to using it - adjustme ...
... Prism spectrometers are used to measure the wavelengths of light emitted by a sample. The key to its operation is a glass prism, which disperses light into a spectrum. Experiment 1 develops your understanding of how the prism spectrometer works, as well as the skills necessary to using it - adjustme ...
The Faraday Effect
... If any transparent solid or liquid is placed in a uniform magnetic field, and a beam of plane polarized light is passed through it in the direction parallel to the magnetic lines of force (through holes in the pole shoes of a strong electromagnet), it is found that the transmitted light is still pla ...
... If any transparent solid or liquid is placed in a uniform magnetic field, and a beam of plane polarized light is passed through it in the direction parallel to the magnetic lines of force (through holes in the pole shoes of a strong electromagnet), it is found that the transmitted light is still pla ...
explanation
... invisible to the human eye, the magnified image has to be made visible via special techniques like fluorescence, photography and digital image acquisition. Can we go further down in wavelength? If we do, we enter the X-ray part of the spectrum. One of the problems here is that it is difficult to pro ...
... invisible to the human eye, the magnified image has to be made visible via special techniques like fluorescence, photography and digital image acquisition. Can we go further down in wavelength? If we do, we enter the X-ray part of the spectrum. One of the problems here is that it is difficult to pro ...
SI System of Measurement
... How far is it from Los Angeles to New York? Pretty far, but it can still be measured in miles or kilometers. How far is it from Earth to the sun? It’s about one hundred forty-nine million, six hundred thousand kilometers (149,600,000, or 1.496 108 km). Because this number is so large, and many oth ...
... How far is it from Los Angeles to New York? Pretty far, but it can still be measured in miles or kilometers. How far is it from Earth to the sun? It’s about one hundred forty-nine million, six hundred thousand kilometers (149,600,000, or 1.496 108 km). Because this number is so large, and many oth ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... Wave number: number of wave in a centimeter.from25000 for violet light, to 13.000 for red light. Ⅱ. Rays and Waves The path along which light travels are known as rays in a homogeneous medium, they are straight lines. ﹡The location and brightness of an image can be determined by ray method. ﹡ The fi ...
... Wave number: number of wave in a centimeter.from25000 for violet light, to 13.000 for red light. Ⅱ. Rays and Waves The path along which light travels are known as rays in a homogeneous medium, they are straight lines. ﹡The location and brightness of an image can be determined by ray method. ﹡ The fi ...
Bright Field Microscopy
... which results in different values being obtained when specimens are probed from several directions within the same material. Anisotropic crystals (i.e. quartz or calcite) exhibit double refraction (or birefringence) Light polarized parallel to the crystal orientation has a different index of refract ...
... which results in different values being obtained when specimens are probed from several directions within the same material. Anisotropic crystals (i.e. quartz or calcite) exhibit double refraction (or birefringence) Light polarized parallel to the crystal orientation has a different index of refract ...
Polarization rotation of slow light with orbital angular momentum in
... transitions induced by the control and probe laser fields. As a result, a weak probe pulse travels slowly and almost without a dissipation in a resonant medium controlled by another laser 关1–9兴. Electromagnetically induced transparency was shown not only to slow down dramatically laser pulses 关1–3兴 ...
... transitions induced by the control and probe laser fields. As a result, a weak probe pulse travels slowly and almost without a dissipation in a resonant medium controlled by another laser 关1–9兴. Electromagnetically induced transparency was shown not only to slow down dramatically laser pulses 关1–3兴 ...
Entangled states of light in classical polarization theory
... From Christian Huygens’ explanation of the fascinating birefringent property of the crystals called Iceland spar (i.e., calcite), through the much later work of Sir George Stokes [1], the formulation of polarization theory has continuously evolved and is now well established in terms of field correl ...
... From Christian Huygens’ explanation of the fascinating birefringent property of the crystals called Iceland spar (i.e., calcite), through the much later work of Sir George Stokes [1], the formulation of polarization theory has continuously evolved and is now well established in terms of field correl ...
28.1 Understanding Light Years
... How far is it from Los Angeles to New York? Pretty far, but it can still be measured in miles or kilometers. How far is it from Earth to the Sun? It’s about one hundred forty-nine million, six hundred thousand kilometers (149,600,000, or 1.496 × 108 km). Because this number is so large, and many oth ...
... How far is it from Los Angeles to New York? Pretty far, but it can still be measured in miles or kilometers. How far is it from Earth to the Sun? It’s about one hundred forty-nine million, six hundred thousand kilometers (149,600,000, or 1.496 × 108 km). Because this number is so large, and many oth ...
1.2 Understanding Light Years
... How far is it from Los Angeles to New York? Pretty far, but it can still be measured in miles or kilometers. How far is it from Earth to the Sun? It’s about one hundred forty-nine million, six hundred thousand kilometers (149,600,000, or 1.496 × 108 km). Because this number is so large, and many oth ...
... How far is it from Los Angeles to New York? Pretty far, but it can still be measured in miles or kilometers. How far is it from Earth to the Sun? It’s about one hundred forty-nine million, six hundred thousand kilometers (149,600,000, or 1.496 × 108 km). Because this number is so large, and many oth ...
3.7 Dielectrics and Optics 3.7.1 Basics
... If we now look at not-so-basic optics, we encounter the Fresnel laws of diffraction. Essentially, the Fresnel laws give the intensity of the reflected beam as a function of the angle of incidence, the polarization of the incident beam, and the index of refraction of the material. The Fresnel laws ar ...
... If we now look at not-so-basic optics, we encounter the Fresnel laws of diffraction. Essentially, the Fresnel laws give the intensity of the reflected beam as a function of the angle of incidence, the polarization of the incident beam, and the index of refraction of the material. The Fresnel laws ar ...
11.2 - Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection
... A glass prism can change the direction of light by creating the conditions for total internal reflection The critical angle between glass and air is less than 45°, so letting light hit an inner surface at exactly 45° will be totally reflected inside the glass When light enters ⊥ to the short side of ...
... A glass prism can change the direction of light by creating the conditions for total internal reflection The critical angle between glass and air is less than 45°, so letting light hit an inner surface at exactly 45° will be totally reflected inside the glass When light enters ⊥ to the short side of ...
Light Rays
... - Newton held that particles were emitted from a light source &they stimulated the sight sense upon entering the eye. - Reflection and refraction can be explained. However, light Interference phenomenon could not be explained. The wave model of light: This model was proposed that light might be so ...
... - Newton held that particles were emitted from a light source &they stimulated the sight sense upon entering the eye. - Reflection and refraction can be explained. However, light Interference phenomenon could not be explained. The wave model of light: This model was proposed that light might be so ...
PHE-09 (2007
... Two energy levels of an atomic system are separated by energy corresponding to frequency 5.01014 Hz. Assume that all atoms are in one or the other of these two energy levels. Compute the fraction of atoms in the upper energy level at temperature 600 K. Take kB = 1.38 1023 JK1 and h = 6.6 103 ...
... Two energy levels of an atomic system are separated by energy corresponding to frequency 5.01014 Hz. Assume that all atoms are in one or the other of these two energy levels. Compute the fraction of atoms in the upper energy level at temperature 600 K. Take kB = 1.38 1023 JK1 and h = 6.6 103 ...
CHAPTER 4 REFLECTED LIGHT OPTICS
... always less thanc ,n is always greater than 1.0,although for airn = 1.0003 (~I) . Since the refractive index is a ratio of two velocities, it is a dimensionless number. Those materials through which monochromatic light travels at the same speed, regardless of the direction oflight vibration relative ...
... always less thanc ,n is always greater than 1.0,although for airn = 1.0003 (~I) . Since the refractive index is a ratio of two velocities, it is a dimensionless number. Those materials through which monochromatic light travels at the same speed, regardless of the direction oflight vibration relative ...
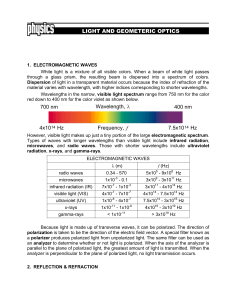
700 nm 400 nm Wavelength, λ Frequency, f 4x1014 Hz
... edges of openings or slits. The diffraction effect is greatest when the slit width is on the order of the wavelength of light that is being diffracted. In Young’s double-slit experiment, light emerging from the two slits is used as two coherent sources. When the light is projected onto a screen, an ...
... edges of openings or slits. The diffraction effect is greatest when the slit width is on the order of the wavelength of light that is being diffracted. In Young’s double-slit experiment, light emerging from the two slits is used as two coherent sources. When the light is projected onto a screen, an ...
Diffraction and Interference
... Annoying Diffraction • Ever wonder why you can’t make a microscope to “see” an atom in visible light? • If the size of object is the same as the wavelength of light, the image will be blurred by diffraction. Smaller objects won’t be seen at all • No optical microscope can be built big enough or des ...
... Annoying Diffraction • Ever wonder why you can’t make a microscope to “see” an atom in visible light? • If the size of object is the same as the wavelength of light, the image will be blurred by diffraction. Smaller objects won’t be seen at all • No optical microscope can be built big enough or des ...
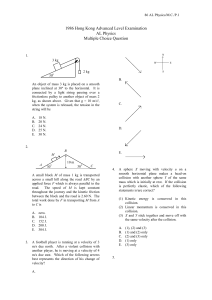
1. An object of mass 3 kg is placed on a smooth plane inclined at 30º
... In the diagram above, E1 and E represent (to scale) the energy levels of a hydrogen atom in its ground state and the ionised state, respectively. Which of the drawn lines represents the energy level of the atom in its ...
... In the diagram above, E1 and E represent (to scale) the energy levels of a hydrogen atom in its ground state and the ionised state, respectively. Which of the drawn lines represents the energy level of the atom in its ...
Lecture 1 - Engineering
... Phase of a wave is the offset of the wave from a reference point fo We typically talk about a phase shift When light interacts with matter (e.g. as it travels through a biological specimen), its speed of propagation slows down. The wave emanating from the specimen exhibits a phase shift when compare ...
... Phase of a wave is the offset of the wave from a reference point fo We typically talk about a phase shift When light interacts with matter (e.g. as it travels through a biological specimen), its speed of propagation slows down. The wave emanating from the specimen exhibits a phase shift when compare ...
Ch. 35: Reflection and Refraction of Light
... not change the medium through which it propagates (air, water, glass, plastic), or finds an obstacle (interface). The velocity of light in air is c c = 3x108 m/s The velocity of light in other media may be different from c (less than c). ...
... not change the medium through which it propagates (air, water, glass, plastic), or finds an obstacle (interface). The velocity of light in air is c c = 3x108 m/s The velocity of light in other media may be different from c (less than c). ...
Polarizer

A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that passes light of a specific polarization and blocks waves of other polarizations. It can convert a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam with well-defined polarization, polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and liquid crystal display technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.