Physics 2140, Dr
... 1. The direction of the inducted current in a loop always opposes the ______ in magnetic ____that induces the current? 2. In the diagram below three rod loops are moving to the right. a. What is the current for motional EMF in terms of v, B, L, and R? b. The current in this conductor moving through ...
... 1. The direction of the inducted current in a loop always opposes the ______ in magnetic ____that induces the current? 2. In the diagram below three rod loops are moving to the right. a. What is the current for motional EMF in terms of v, B, L, and R? b. The current in this conductor moving through ...
All Charged Up, Grades 4-5 Program Desciption
... batteries, and bulbs. b. how to build a simple compass and use it to detect magnetic effects, including Earth's magnetic field. c. electric currents produce magnetic fields and how to build a simple electromagnet. d. the role of electromagnets in the construction of electric motors, electric generat ...
... batteries, and bulbs. b. how to build a simple compass and use it to detect magnetic effects, including Earth's magnetic field. c. electric currents produce magnetic fields and how to build a simple electromagnet. d. the role of electromagnets in the construction of electric motors, electric generat ...
G2 Chemical Patterns – revision checklist
... appreciate that the resistance of connecting wires is so small that it can usually be ignored; ...
... appreciate that the resistance of connecting wires is so small that it can usually be ignored; ...
Electromagnetic induction
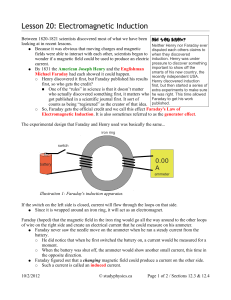
... Electromagnetic induction 1. To produce electricity from magnetism the wire or magnet must move. What is the effect on the voltage produced of: (a) moving the wire more slowly (b) more turns of wire on the coil A (c) a stronger magnet? Figure 1 ...
... Electromagnetic induction 1. To produce electricity from magnetism the wire or magnet must move. What is the effect on the voltage produced of: (a) moving the wire more slowly (b) more turns of wire on the coil A (c) a stronger magnet? Figure 1 ...
Energy, Electricity, and Magnetism
... The voltage across the bulb is 4.0 V. What is the bulb’s resistance? • A waffle iron has a 12 A current. If the resistance of the coils is 10 Ω, what is the ...
... The voltage across the bulb is 4.0 V. What is the bulb’s resistance? • A waffle iron has a 12 A current. If the resistance of the coils is 10 Ω, what is the ...
magnetic - Timber Ridge Elementary
... In our planet we have the North and South Poles. Earth acts like a giant magnet and is surrounded by a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to point either North or South. ...
... In our planet we have the North and South Poles. Earth acts like a giant magnet and is surrounded by a magnetic field. Earth’s magnetic field is what causes the needle of a compass to point in different directions and causes the poles of a magnet to point either North or South. ...
Assignment 11
... (a) If R is such that the potential difference per centimetre along the 150-cm long wire AB is 0.010 V cm–1, find (i) the required value of R, (ii) the power provided by the driver cell, and (iii) the power dissipated in the potentiometer wire. (b) Discuss whether the value of R1 affects the balance ...
... (a) If R is such that the potential difference per centimetre along the 150-cm long wire AB is 0.010 V cm–1, find (i) the required value of R, (ii) the power provided by the driver cell, and (iii) the power dissipated in the potentiometer wire. (b) Discuss whether the value of R1 affects the balance ...
Position and Motion Sensors
... The armature of the tachometer is coupled to the machine whose speed is to be measured. When the shaft of the machine revolves, armature of the tachometer revolves in the magnetic field producing an emf proportional to the speed. The polarity of the output voltage indicates the direction of rotation ...
... The armature of the tachometer is coupled to the machine whose speed is to be measured. When the shaft of the machine revolves, armature of the tachometer revolves in the magnetic field producing an emf proportional to the speed. The polarity of the output voltage indicates the direction of rotation ...
Galvanometer

A galvanometer is a type of sensitive ammeter: an instrument for detecting electric current. It is an analog electromechanical actuator that produces a rotary deflection of some type of pointer in response to electric current through its coil in a magnetic field.Galvanometers were the first instruments used to detect and measure electric currents. Sensitive galvanometers were used to detect signals from long submarine cables, and to discover the electrical activity of the heart and brain. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals. Initially a laboratory instrument relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electrotechnology. A type of galvanometer that records measurements permanently is the chart recorder. The term has expanded to include use of the same mechanism in recording, positioning, and servomechanism equipment.