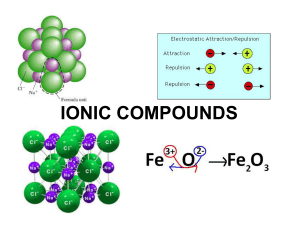
Ionic Bonding
... (b) H2O(l) (c) CH4(g) (d) PCl3(s) (e) H2S(g) (f) SiO2(s) 2. Draw Lewis structures and structural formulas for each of the following molecules: (a) H2(g) (d) NF3(g) (b) O3(g) (e) N2H2(g) (c) OF2(g) (f) P2H4(g) 3. Draw Lewis structures and structural formulas for each of the following polyatomic ions: ...
... (b) H2O(l) (c) CH4(g) (d) PCl3(s) (e) H2S(g) (f) SiO2(s) 2. Draw Lewis structures and structural formulas for each of the following molecules: (a) H2(g) (d) NF3(g) (b) O3(g) (e) N2H2(g) (c) OF2(g) (f) P2H4(g) 3. Draw Lewis structures and structural formulas for each of the following polyatomic ions: ...
Recording Measurements
... 63. In a laboratory activity, 0.500 mole of NaOH(s) is completely dissolved in distilled water to form 400. milliliters of NaOH(aq). This solution is then used to titrate a solution of HNO3(aq). (a) Identify the negative ion produced when the NaOH(s) is dissolved in distilled water. ________ (b) ...
... 63. In a laboratory activity, 0.500 mole of NaOH(s) is completely dissolved in distilled water to form 400. milliliters of NaOH(aq). This solution is then used to titrate a solution of HNO3(aq). (a) Identify the negative ion produced when the NaOH(s) is dissolved in distilled water. ________ (b) ...
Practice Qs - Unit 10 Acid Base
... (4) KOH 6. The Arrhenius theory explains the behavior of (1) acids and bases (2) alcohols and amines (3) isomers and isotopes (4) metals and nonmetals 7. Which two compounds are electrolytes? (1) C6H12O6 and CH3CH2OH (2) C6H12O6 and HCl (3) NaOH and HCl (4) NaOH and CH3CHOH 8. Given the equation: HC ...
... (4) KOH 6. The Arrhenius theory explains the behavior of (1) acids and bases (2) alcohols and amines (3) isomers and isotopes (4) metals and nonmetals 7. Which two compounds are electrolytes? (1) C6H12O6 and CH3CH2OH (2) C6H12O6 and HCl (3) NaOH and HCl (4) NaOH and CH3CHOH 8. Given the equation: HC ...
Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... 34. given a molecular formula, be able to determine the molecular shape for a molecule or ion [you will have your molecular shape sheet] 35. given a Lewis structure, be able to compute the formal charge for an atom 36. know which elements are found in nature as diatomic molecules (e.g., H2) 37. give ...
... 34. given a molecular formula, be able to determine the molecular shape for a molecule or ion [you will have your molecular shape sheet] 35. given a Lewis structure, be able to compute the formal charge for an atom 36. know which elements are found in nature as diatomic molecules (e.g., H2) 37. give ...
Section 1e chemical formulae and chemical equations
... 1. 416 g anhydrous barium chloride were obtained when 488g of the hydrated salt were heated. Calculate n in the formula BaCl2.nH2O 2. A sample of magnesium sulphate crystals weighing 0.942 g was heated to drive off the water of crystallization. When it reached constant mass, the mass of the residue ...
... 1. 416 g anhydrous barium chloride were obtained when 488g of the hydrated salt were heated. Calculate n in the formula BaCl2.nH2O 2. A sample of magnesium sulphate crystals weighing 0.942 g was heated to drive off the water of crystallization. When it reached constant mass, the mass of the residue ...
PS_CHEM7_ch4 - WordPress.com
... can assume that all acid molecules dissociate completely to yield H+ ions and associated anions. One mole of HBr, HI, and HNO3 each produce one mole of H+ upon dissociation, so moles H+ = moles acid. Molarity is expressed as moles/L instead of as M. a) Moles H+ = mol HBr = (1.4 mL) (10–3 L/1mL) (0.7 ...
... can assume that all acid molecules dissociate completely to yield H+ ions and associated anions. One mole of HBr, HI, and HNO3 each produce one mole of H+ upon dissociation, so moles H+ = moles acid. Molarity is expressed as moles/L instead of as M. a) Moles H+ = mol HBr = (1.4 mL) (10–3 L/1mL) (0.7 ...
Percent Composition
... When the Formula of a Compound is Known • When we already know the formula of a compound then we can use percent composition based on the formula and compare it to values determined experimentally (by reacting the sample) to see how pure the sample was that was used in the reaction. • We can also u ...
... When the Formula of a Compound is Known • When we already know the formula of a compound then we can use percent composition based on the formula and compare it to values determined experimentally (by reacting the sample) to see how pure the sample was that was used in the reaction. • We can also u ...
chemistry_chapter_3
... 1. How many grams are in 9.45 mol of dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3) ? a. Calculate the grams in one mole b. Multiply the grams by the number of moles 2. Find the number of moles in 92.2 g of iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3). a. Calculate the grams in one mole b. Divide the given grams by the grams in one mole ...
... 1. How many grams are in 9.45 mol of dinitrogen trioxide (N2O3) ? a. Calculate the grams in one mole b. Multiply the grams by the number of moles 2. Find the number of moles in 92.2 g of iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3). a. Calculate the grams in one mole b. Divide the given grams by the grams in one mole ...
Example 1: An experiment shows that 64g of
... 1. 416 g anhydrous barium chloride were obtained when 488g of the hydrated salt were heated. Calculate n in the formula BaCl2.nH2O 2. A sample of magnesium sulphate crystals weighing 0.942 g was heated to drive off the water of crystallization. When it reached constant mass, the mass of the residue ...
... 1. 416 g anhydrous barium chloride were obtained when 488g of the hydrated salt were heated. Calculate n in the formula BaCl2.nH2O 2. A sample of magnesium sulphate crystals weighing 0.942 g was heated to drive off the water of crystallization. When it reached constant mass, the mass of the residue ...
Example 1: An experiment shows that 64g of
... 1. 416 g anhydrous barium chloride were obtained when 488g of the hydrated salt were heated. Calculate n in the formula BaCl2.nH2O 2. A sample of magnesium sulphate crystals weighing 0.942 g was heated to drive off the water of crystallization. When it reached constant mass, the mass of the residue ...
... 1. 416 g anhydrous barium chloride were obtained when 488g of the hydrated salt were heated. Calculate n in the formula BaCl2.nH2O 2. A sample of magnesium sulphate crystals weighing 0.942 g was heated to drive off the water of crystallization. When it reached constant mass, the mass of the residue ...
SM2H Unit 3 – Solving Quadratic Equations
... Why have three different forms of a Quadratic Equation? Each form of a quadratic equation gives us easy access to important information – either about the solutions of the equation or about the graph of the quadratic function. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. (You’ll learn mor ...
... Why have three different forms of a Quadratic Equation? Each form of a quadratic equation gives us easy access to important information – either about the solutions of the equation or about the graph of the quadratic function. The graph of a quadratic function is called a parabola. (You’ll learn mor ...
7.3 GUIDE TO FINDING FORMULA MASS/MOLAR MASS OF A
... number c. If result from step “b” gives a ratio with a decimal, convert it to a fraction and multiply all the ratios by the denominator of the fraction to get whole numbers d. Use the resulting values as the subscripts for each element Example: Analysis of a 10.150 g sample of a compound known to co ...
... number c. If result from step “b” gives a ratio with a decimal, convert it to a fraction and multiply all the ratios by the denominator of the fraction to get whole numbers d. Use the resulting values as the subscripts for each element Example: Analysis of a 10.150 g sample of a compound known to co ...
Chapter 3
... Sulfur dioxide reacts with chlorine to produce thionyl chloride (used as a drying agent for inorganic halides) and dichlorine monoxide (used as a bleach for wood, pulp and textiles). SO2(g) + 2Cl2(g) → SOCl2(g) + Cl2O(g) If 0.400 mol of Cl2 reacts with excess SO2, how many moles of Cl2O are formed? ...
... Sulfur dioxide reacts with chlorine to produce thionyl chloride (used as a drying agent for inorganic halides) and dichlorine monoxide (used as a bleach for wood, pulp and textiles). SO2(g) + 2Cl2(g) → SOCl2(g) + Cl2O(g) If 0.400 mol of Cl2 reacts with excess SO2, how many moles of Cl2O are formed? ...