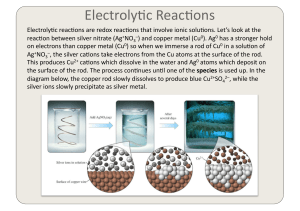
Connect the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) into the circuit shown in
... To observe the operation of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) when used in an electronic switching application. ...
... To observe the operation of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) when used in an electronic switching application. ...
Honors Chemistry Final Review
... apart on the _________________ In fact, the further apart, the more ionic! A covalent bond forms from the combination of ______________________, including ___________ It has an electronegativity difference that is ___________ which means that the two combining elements will not be far apart on the p ...
... apart on the _________________ In fact, the further apart, the more ionic! A covalent bond forms from the combination of ______________________, including ___________ It has an electronegativity difference that is ___________ which means that the two combining elements will not be far apart on the p ...
Tutorial 3 Solutions - NUS Physics Department
... The planes of the two loops are parallel, and perpendicular to the common axis. (a) Suppose current I flows in the big loop. Find the flux through the little loop. The little loop is so small that you may consider the field of the big loop to be essentially constant. (b) Suppose current I flows in t ...
... The planes of the two loops are parallel, and perpendicular to the common axis. (a) Suppose current I flows in the big loop. Find the flux through the little loop. The little loop is so small that you may consider the field of the big loop to be essentially constant. (b) Suppose current I flows in t ...
Unit Objectives- States of Matter
... 9. Explain Graham’s Law of Effusion and justify with calculations. 10. Explain the difference between a solution, colloid, and a suspension. 11. Define a solute, a solvent, and a solution. 12. Describe the process by which solutes dissolve in solvents. 13. Determine if a solute will be able to disso ...
... 9. Explain Graham’s Law of Effusion and justify with calculations. 10. Explain the difference between a solution, colloid, and a suspension. 11. Define a solute, a solvent, and a solution. 12. Describe the process by which solutes dissolve in solvents. 13. Determine if a solute will be able to disso ...
Practice Test for Exam 2
... 27. Color code the elements to distinguish metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. ---The dots associated with each element symbol represent the number of outer electrons that each atom has. The elements in the final family or column (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn) will not interact with the other elements and ...
... 27. Color code the elements to distinguish metals, nonmetals, and metalloids. ---The dots associated with each element symbol represent the number of outer electrons that each atom has. The elements in the final family or column (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn) will not interact with the other elements and ...
1 EXPERIMENT No
... 2) The voltmeter is connected in parallel connection across the given coil. The circuit is closed. 3) Now the rheostat is adjusted so that a constant current flows through the coil. Note down the ammeter reading I and the corresponding potential difference across the coil in the voltmeter as V. Use ...
... 2) The voltmeter is connected in parallel connection across the given coil. The circuit is closed. 3) Now the rheostat is adjusted so that a constant current flows through the coil. Note down the ammeter reading I and the corresponding potential difference across the coil in the voltmeter as V. Use ...
Previous Lecture 1
... One volt is the potential difference (voltage) between two points when one joule of energy is used to move one coulomb from one point to the other. One ampere is the amount of current that exists when one coulomb of charge moves through a given crosssectional area of a material in one second. One oh ...
... One volt is the potential difference (voltage) between two points when one joule of energy is used to move one coulomb from one point to the other. One ampere is the amount of current that exists when one coulomb of charge moves through a given crosssectional area of a material in one second. One oh ...
Solution - UD Physics
... plate. The electron enters a uniform field of 10V/m generated by another two parallel plates. (Assuming E becomes zero outside and no edge effect). The separation of two plates is 2.0 cm. Calculate (a) (10pts) the velocity of the electron before it enters E field; (b) (10 pts) the acceleration of th ...
... plate. The electron enters a uniform field of 10V/m generated by another two parallel plates. (Assuming E becomes zero outside and no edge effect). The separation of two plates is 2.0 cm. Calculate (a) (10pts) the velocity of the electron before it enters E field; (b) (10 pts) the acceleration of th ...
2 Basic Components and Electric Circuits
... c=centi= 10−2 , m=milli= 10−3 , µ=micro= 10−6 n=nano= 10−9 , p=pico= 10−12 , f=femto= 10−15 a=atto= 10−18 ...
... c=centi= 10−2 , m=milli= 10−3 , µ=micro= 10−6 n=nano= 10−9 , p=pico= 10−12 , f=femto= 10−15 a=atto= 10−18 ...
Chapter 2
... c=centi= 10−2 , m=milli= 10−3 , µ=micro= 10−6 n=nano= 10−9 , p=pico= 10−12 , f=femto= 10−15 a=atto= 10−18 ...
... c=centi= 10−2 , m=milli= 10−3 , µ=micro= 10−6 n=nano= 10−9 , p=pico= 10−12 , f=femto= 10−15 a=atto= 10−18 ...
02 Guided notes material
... mower cuts the electrical wire). When this happens, the current can flow with very little restriction because the resistance of the loop formed by the two conductors is very weak. The high amount of current heats up the wires and can cause a fire. Fuses and circuit breakers detect unusually high cur ...
... mower cuts the electrical wire). When this happens, the current can flow with very little restriction because the resistance of the loop formed by the two conductors is very weak. The high amount of current heats up the wires and can cause a fire. Fuses and circuit breakers detect unusually high cur ...
Quiz 1
... 7. Which of the following is a correct statement concerning solution A with a pH of 11.5 compared to solution B with a pH of 10.0? Solution A… a. has a smaller [OH¯] than solution B b. has a larger number of [H+] than solution B c. is more basic than solution B d. is more acidic than solution B e. h ...
... 7. Which of the following is a correct statement concerning solution A with a pH of 11.5 compared to solution B with a pH of 10.0? Solution A… a. has a smaller [OH¯] than solution B b. has a larger number of [H+] than solution B c. is more basic than solution B d. is more acidic than solution B e. h ...
Nanofluidic circuitry
Nanofluidic circuitry is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic counterparts. Its typical characteristic dimensions fall within the range of 1–100 nm. At least one dimension of the structure is in nanoscopic scale. Phenomena of fluids in nano-scale structure are discovered to be of different properties in electrochemistry and fluid dynamics.