DO NOW
... • A current of 5.0 A passes through the bulb in 20 µs. What is the quantity of charge flowing through the bulb? • How long does it take a current of 5.0 mA to deliver 15 C of charge? • HOME WORK – Prepare for Test on Friday ...
... • A current of 5.0 A passes through the bulb in 20 µs. What is the quantity of charge flowing through the bulb? • How long does it take a current of 5.0 mA to deliver 15 C of charge? • HOME WORK – Prepare for Test on Friday ...
CH 17 – Current and Resistance
... direction of the flow of positive charge. In a metal, however, current consists of electron flow, so that the current direction is opposite to the flow of electrons. In electrostatics the electric field inside a metal is zero, the electric potential is constant, and the charges are at rest. If a met ...
... direction of the flow of positive charge. In a metal, however, current consists of electron flow, so that the current direction is opposite to the flow of electrons. In electrostatics the electric field inside a metal is zero, the electric potential is constant, and the charges are at rest. If a met ...
Unit 2 Assignments Answers
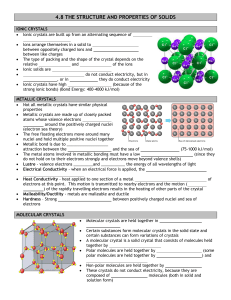
... Unlike gases, molecules in liquid phase have significantly less spaces between them. Hence, there is not enough room to compact these molecules to a smaller volume. Therefore, liquids are incompressible. Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid ...
... Unlike gases, molecules in liquid phase have significantly less spaces between them. Hence, there is not enough room to compact these molecules to a smaller volume. Therefore, liquids are incompressible. Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch or increase the surface of a liquid ...
L26 - University of Iowa Physics
... something moving with constant velocity • So, why is it necessary to keep pushing the charges to keep them moving in a wire? • As they move through the wire, the electrons collide with the atoms, so there is a type of friction involved; in this case a force is required to keep the electrons moving • ...
... something moving with constant velocity • So, why is it necessary to keep pushing the charges to keep them moving in a wire? • As they move through the wire, the electrons collide with the atoms, so there is a type of friction involved; in this case a force is required to keep the electrons moving • ...
2 - CronScience
... end up with (meaning: balanced!) A balanced equation has the same number of each element on both sides of the equation. ...
... end up with (meaning: balanced!) A balanced equation has the same number of each element on both sides of the equation. ...
Chapter 2 - Voltage, Current, and Resistance
... move away from an atom, the atom is left with a net positive charge (positive ion) • If an atom acquires an extra electron in its outer shell, it has a net negative charge (negative ion) ...
... move away from an atom, the atom is left with a net positive charge (positive ion) • If an atom acquires an extra electron in its outer shell, it has a net negative charge (negative ion) ...
electrons
... move away from an atom, the atom is left with a net positive charge (positive ion) • If an atom acquires an extra electron in its outer shell, it has a net negative charge (negative ion) ...
... move away from an atom, the atom is left with a net positive charge (positive ion) • If an atom acquires an extra electron in its outer shell, it has a net negative charge (negative ion) ...
Chapter 23 Clicker questions.
... electrical resistance is low enough. a potential difference exists. the circuit is grounded. electrical devices in the circuit are not ...
... electrical resistance is low enough. a potential difference exists. the circuit is grounded. electrical devices in the circuit are not ...
Electric & Gravitational Fields and Electric Potentials
... • Electric Potential Energy (ePE) is due to a charge’s location in an electric field • ePE is the amount of work needed to move a charge to that location – Similar to gravitational potential energy depends on the height of an object ...
... • Electric Potential Energy (ePE) is due to a charge’s location in an electric field • ePE is the amount of work needed to move a charge to that location – Similar to gravitational potential energy depends on the height of an object ...
No Slide Title
... “Potential Energy Difference” and “Potential Difference” Potential Energy Difference PEA,B is the change in PE the particular charge feels when it is moved from one location to another. Potential Difference VA,B is the change in PE a positive 1C charge would feel if it were moved from one locatio ...
... “Potential Energy Difference” and “Potential Difference” Potential Energy Difference PEA,B is the change in PE the particular charge feels when it is moved from one location to another. Potential Difference VA,B is the change in PE a positive 1C charge would feel if it were moved from one locatio ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... B. The theory states “Repulsion between the sets of valence-level electrons surrounding an atom causes these sets to be oriented as far apart as possible.” 1. “Shared pairs” of electrons are as far apart as possible. 2. “Lone pairs” (unshared) electrons occupy space around the central atom. a. Some ...
... B. The theory states “Repulsion between the sets of valence-level electrons surrounding an atom causes these sets to be oriented as far apart as possible.” 1. “Shared pairs” of electrons are as far apart as possible. 2. “Lone pairs” (unshared) electrons occupy space around the central atom. a. Some ...
Chemistry IGCSE Revision PDF File
... Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the ____________ ...
... Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the ____________ ...
Lecture35
... always appears in the form of magnetic dipoles. If this were true, it would look like the regular gauss law. ...
... always appears in the form of magnetic dipoles. If this were true, it would look like the regular gauss law. ...
Chapter 4 Notes: Types of Reactions & Solution
... Species Present before rxn occurs: H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) (b/c HCl is a strong acid and NaOH is a strong base=complete dissociation of both acid & base) NaCl is soluble in water (check your table) so Na+ & Cl- are ...
... Species Present before rxn occurs: H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) + Na+ (aq) + OH- (aq) (b/c HCl is a strong acid and NaOH is a strong base=complete dissociation of both acid & base) NaCl is soluble in water (check your table) so Na+ & Cl- are ...
Current Electricity (R)
... While the electric field travels at nearly the speed of light, the overall drift speed of the electron from one end of the conductor to the other is quite slow and random in direction due to collisions. For a 20A circuit in your home with 1A of current flow, the electrons would only travel 0.08 m (8 ...
... While the electric field travels at nearly the speed of light, the overall drift speed of the electron from one end of the conductor to the other is quite slow and random in direction due to collisions. For a 20A circuit in your home with 1A of current flow, the electrons would only travel 0.08 m (8 ...
Nanofluidic circuitry
Nanofluidic circuitry is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic counterparts. Its typical characteristic dimensions fall within the range of 1–100 nm. At least one dimension of the structure is in nanoscopic scale. Phenomena of fluids in nano-scale structure are discovered to be of different properties in electrochemistry and fluid dynamics.