immobilised metal affinity chromatography (imac) beads for
... obtained by several techniques such as ion exchange chromatography, ultrafiltration and affinity chromatography. However rigorous limitations occur including lengthy steps, complicated and expensive for large scale production has hampered the applications. Separation technique for protein by Immobil ...
... obtained by several techniques such as ion exchange chromatography, ultrafiltration and affinity chromatography. However rigorous limitations occur including lengthy steps, complicated and expensive for large scale production has hampered the applications. Separation technique for protein by Immobil ...
The science of chemistry is concerned with the
... Dalton’s third postulate states that atoms are the units of chemical changes. What this means can be seen in the macroscopic and microscopic views of a chemical change in Plate 3. (Color plates will be found in Chap. 5). When macroscopic quantities of mercury and bromine are mixed at room temperatur ...
... Dalton’s third postulate states that atoms are the units of chemical changes. What this means can be seen in the macroscopic and microscopic views of a chemical change in Plate 3. (Color plates will be found in Chap. 5). When macroscopic quantities of mercury and bromine are mixed at room temperatur ...
topic: chemical formula, chemical equations and stoichiometry
... [Relative Atomic Mass; H,7; N,14;Mg, 24; S, 32; O,16] a. Relative molecule Mass of Ammonia, NH3 =Mass of one nitrogen atom + mass of three hydrogen atoms =RAM of nitrogen x number of nitrogen atom + RAM of hydrogen x number of hydrogen atom Molar Mass of ammonia, NH3 = 14 x1 + 1x3 = 17 b. The relati ...
... [Relative Atomic Mass; H,7; N,14;Mg, 24; S, 32; O,16] a. Relative molecule Mass of Ammonia, NH3 =Mass of one nitrogen atom + mass of three hydrogen atoms =RAM of nitrogen x number of nitrogen atom + RAM of hydrogen x number of hydrogen atom Molar Mass of ammonia, NH3 = 14 x1 + 1x3 = 17 b. The relati ...
key for Unit 1 pp 21
... and list the semimetals [the metalloids] boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and tellurium (Te). Polonium (Po) is often considered a metalloid, too). ...
... and list the semimetals [the metalloids] boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), and tellurium (Te). Polonium (Po) is often considered a metalloid, too). ...
The science of chemistry is concerned with the composition
... Dalton’s third postulate states that atoms are the units of chemical changes. What this means can be seen in the macroscopic and microscopic views of a chemical change in Plate 3. (Color plates will be found in Chap. 5). When macroscopic quantities of mercury and bromine are mixed at room temperatur ...
... Dalton’s third postulate states that atoms are the units of chemical changes. What this means can be seen in the macroscopic and microscopic views of a chemical change in Plate 3. (Color plates will be found in Chap. 5). When macroscopic quantities of mercury and bromine are mixed at room temperatur ...
CHAPTER 3 STOICHIOMETRY:
... reactants are LR reactions. Convert grams of reactants to moles. Divide the results of each mole on its coefficient in the balanced equation. The smallest value is for the LR substance. Your calculations should be based on the LR. ...
... reactants are LR reactions. Convert grams of reactants to moles. Divide the results of each mole on its coefficient in the balanced equation. The smallest value is for the LR substance. Your calculations should be based on the LR. ...
File - Roden`s AP Chemistry
... centration of Br- ions increase and force the equilibrium aqueous solution of NH4Cl. (Molecular weight: to shift to the left (LeChatelier’s principle) where the NH4Cl = 53.5) concentrations of the ions in solution decrease and less (b) If this NH4Cl solution is assumed to be ideal and is can dissolv ...
... centration of Br- ions increase and force the equilibrium aqueous solution of NH4Cl. (Molecular weight: to shift to the left (LeChatelier’s principle) where the NH4Cl = 53.5) concentrations of the ions in solution decrease and less (b) If this NH4Cl solution is assumed to be ideal and is can dissolv ...
File
... use these as the subscripts for the formula. If the numbers are not whole numbers, multiply each by a factor that will make them ...
... use these as the subscripts for the formula. If the numbers are not whole numbers, multiply each by a factor that will make them ...
chapter4-bur.2917051..
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
Determination of Amino Acids in Wort and Beer by Reverse
... system as it forms low-polarity products and reaction occurs in an aqueous medium, is quick at room temperature, is reproducible and quantitative, and generates highly fluorescent derivatives. When 2-ME is present, OPA reacts with primary amino acids to form substituted isoindole products (Fig. 1). ...
... system as it forms low-polarity products and reaction occurs in an aqueous medium, is quick at room temperature, is reproducible and quantitative, and generates highly fluorescent derivatives. When 2-ME is present, OPA reacts with primary amino acids to form substituted isoindole products (Fig. 1). ...
Energy Matters - Perth Grammar
... The number of H+ (aq) ions in the beaker decreased. The pH of the solution decreased. The number of SO42−(aq) ions in the beaker decreased. Water molecules formed during the reaction. A precipitate formed during the reaction. The final solution contained equal numbers of H+(aq) and OH− (aq) ions. ...
... The number of H+ (aq) ions in the beaker decreased. The pH of the solution decreased. The number of SO42−(aq) ions in the beaker decreased. Water molecules formed during the reaction. A precipitate formed during the reaction. The final solution contained equal numbers of H+(aq) and OH− (aq) ions. ...
Some basic concepts of chemistry
... The masses of oxygen which combine with same mass of hydrogen in these two compounds bear a simple ratio 1 : 2. Law of reciprocal proportions: This law was given by Richter in 1794. Statement: It states that, “When two different elements combine separately with the same weight of a third element, th ...
... The masses of oxygen which combine with same mass of hydrogen in these two compounds bear a simple ratio 1 : 2. Law of reciprocal proportions: This law was given by Richter in 1794. Statement: It states that, “When two different elements combine separately with the same weight of a third element, th ...
The Citric Acid Cycle
... acid cycle to yield electrons with high transfer potential. Then, this electron-motive force is converted into a proton-motive force and, finally, the proton-motive force is converted into phosphoryl transfer potential. The conversion of electron-motive force into proton-motive force is carried out ...
... acid cycle to yield electrons with high transfer potential. Then, this electron-motive force is converted into a proton-motive force and, finally, the proton-motive force is converted into phosphoryl transfer potential. The conversion of electron-motive force into proton-motive force is carried out ...
FREE Sample Here
... 38) Which one of the following is a function of a protein? A) stores genetic material and enables its transmission to the next generation B) acts as a catalyst, speeding up chemical reactions C) is a major subunit of cellulose D) is a primary structural component of a cell membrane E) provides energ ...
... 38) Which one of the following is a function of a protein? A) stores genetic material and enables its transmission to the next generation B) acts as a catalyst, speeding up chemical reactions C) is a major subunit of cellulose D) is a primary structural component of a cell membrane E) provides energ ...
Human Biology, 7e (Johnson) Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Living
... 38) Which one of the following is a function of a protein? A) stores genetic material and enables its transmission to the next generation B) acts as a catalyst, speeding up chemical reactions C) is a major subunit of cellulose D) is a primary structural component of a cell membrane E) provides energ ...
... 38) Which one of the following is a function of a protein? A) stores genetic material and enables its transmission to the next generation B) acts as a catalyst, speeding up chemical reactions C) is a major subunit of cellulose D) is a primary structural component of a cell membrane E) provides energ ...
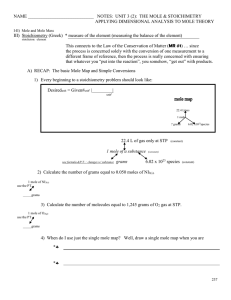
Unit 3 2 Basic Mole Conversions and Mole Maps
... This connects to the Law of the Conservation of Matter (MR #1) … since the process is concerned solely with the conversion of one measurement to a different frame of reference, then the process is really concerned with ensuring that whatever you “put into the reaction”, you somehow, “get out” with p ...
... This connects to the Law of the Conservation of Matter (MR #1) … since the process is concerned solely with the conversion of one measurement to a different frame of reference, then the process is really concerned with ensuring that whatever you “put into the reaction”, you somehow, “get out” with p ...
Compositional and structural investigation of HCN polymer through
... meteorites and comets. To better understand the structure and composition of this natural organic material, laboratory analogs have been studied. Though HCN polymers have been studied since the beginning of the 19th century, their structure and composition are still poorly understood. In this work w ...
... meteorites and comets. To better understand the structure and composition of this natural organic material, laboratory analogs have been studied. Though HCN polymers have been studied since the beginning of the 19th century, their structure and composition are still poorly understood. In this work w ...
analytical chemistry - Львівський національний медичний
... Substances with definite properties are united in special analytical groups. This reactions use for: a) detection the present analytical group; b) selection this analytical group from another during systematic path (way) of analysis; c) concentration of small amounts of substances; d) separation gro ...
... Substances with definite properties are united in special analytical groups. This reactions use for: a) detection the present analytical group; b) selection this analytical group from another during systematic path (way) of analysis; c) concentration of small amounts of substances; d) separation gro ...
Chapter 11 – The Mole
... Molecular formulas o The formula that specifies the actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule of a substance. Ex] Succinic acid: 40.68% C, 5.08% H, 54.24% O Molar mass = 118.1 g/mol Step 1 – Convert % to mass and them convert grams to moles using each element’s molar mass. ...
... Molecular formulas o The formula that specifies the actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule of a substance. Ex] Succinic acid: 40.68% C, 5.08% H, 54.24% O Molar mass = 118.1 g/mol Step 1 – Convert % to mass and them convert grams to moles using each element’s molar mass. ...
Glossary - Chemistry (Intro)
... Noble Gas: Nonmetallic elements in group 8A; He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn. Transition Metal.: Elements that have incompletely filled d subshells or readily give rise to cations that have incompletely filled d subshells; i.e.: it belongs to the central part of the periodic table, between Groups II and ...
... Noble Gas: Nonmetallic elements in group 8A; He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, and Rn. Transition Metal.: Elements that have incompletely filled d subshells or readily give rise to cations that have incompletely filled d subshells; i.e.: it belongs to the central part of the periodic table, between Groups II and ...
Sample
... 38) Which one of the following is a function of a protein? A) stores genetic material and enables its transmission to the next generation B) acts as a catalyst, speeding up chemical reactions C) is a major subunit of cellulose D) is a primary structural component of a cell membrane E) provides energ ...
... 38) Which one of the following is a function of a protein? A) stores genetic material and enables its transmission to the next generation B) acts as a catalyst, speeding up chemical reactions C) is a major subunit of cellulose D) is a primary structural component of a cell membrane E) provides energ ...
Net ionic equation
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
Microbial production of hyaluronic acid: current state, challenges
... production. The pH and temperature for HA production by S. zooepidemicus were usually at 7.0 and 37°C, respectively [26,27]. The microbial HA production by S. zooepidemicus is a typically viscous process, and thus mixing performance and oxygen mass transfer rate significantly influence HA production ...
... production. The pH and temperature for HA production by S. zooepidemicus were usually at 7.0 and 37°C, respectively [26,27]. The microbial HA production by S. zooepidemicus is a typically viscous process, and thus mixing performance and oxygen mass transfer rate significantly influence HA production ...
Size-exclusion chromatography

Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a chromatographic method in which molecules in solution are separated by their size, and in some cases molecular weight. It is usually applied to large molecules or macromolecular complexes such as proteins and industrial polymers. Typically, when an aqueous solution is used to transport the sample through the column, the technique is known as gel-filtration chromatography, versus the name gel permeation chromatography, which is used when an organic solvent is used as a mobile phase. SEC is a widely used polymer characterization method because of its ability to provide good molar mass distribution (Mw) results for polymers.