Cognition and Perception as Interactive Activation
... represents the posterior probability that the state corresponds to the correct interpretation of the input. ...
... represents the posterior probability that the state corresponds to the correct interpretation of the input. ...
Document
... represented in the mind by a single unit, we consider the possibility that it could be represented by a pattern of activation a over population of units. • The elements of the pattern may represent (approximately) some feature or sensible combination of features but they need not. • What is crucial ...
... represented in the mind by a single unit, we consider the possibility that it could be represented by a pattern of activation a over population of units. • The elements of the pattern may represent (approximately) some feature or sensible combination of features but they need not. • What is crucial ...
Neural Networks: An Application Of Linear Algebra
... What happened in ML since 1987 Computers got faster Larger data sets became available ...
... What happened in ML since 1987 Computers got faster Larger data sets became available ...
Western (U - Claremont Center for the Mathematical Sciences
... networks in the nervous system. In all these cases, the component units (the genes, proteins or neurons) can be activated (turned on, excited) or deactivated (turned off, inhibited) to varying degrees at different times by other units in the network. For example, when a gene is turned on it is trans ...
... networks in the nervous system. In all these cases, the component units (the genes, proteins or neurons) can be activated (turned on, excited) or deactivated (turned off, inhibited) to varying degrees at different times by other units in the network. For example, when a gene is turned on it is trans ...
Pattern Theory: the Mathematics of Perception
... Probability distributions of 1 and 2 filters, estimated from natural image data. a) Top plot is for values of horizontal first difference of pixel values; middle plot is for random 0-mean 8x8 filters. Vertical axis in top 2 plots is ...
... Probability distributions of 1 and 2 filters, estimated from natural image data. a) Top plot is for values of horizontal first difference of pixel values; middle plot is for random 0-mean 8x8 filters. Vertical axis in top 2 plots is ...
F. Villa_Forecast electricity prices_v.5_Fer
... maximize their own profits. All firms compete to provide generation services at a price set by the market through two basic mechanisms: bilateral contracts between agents and the trading done on energy spot market. Stock price forecast is a particularly complex problem due to the amount and complexi ...
... maximize their own profits. All firms compete to provide generation services at a price set by the market through two basic mechanisms: bilateral contracts between agents and the trading done on energy spot market. Stock price forecast is a particularly complex problem due to the amount and complexi ...
NeuralNets273ASpring09
... in (1 in )Wij3 jn (1 jn )hkn1 in (1 in )Wij3 jn (1 jn ) ( Wkl1 xln bk1 ) ...
... in (1 in )Wij3 jn (1 jn )hkn1 in (1 in )Wij3 jn (1 jn ) ( Wkl1 xln bk1 ) ...
Supervised learning
... The neuron can be in two states • excited, if s = 1 • not excited, if s = 0 Thus, a neuron is going to separate the space of inputs with an hyperplan. This is why a neural network is good at classification. The action of a single neuron is quite easy ; only the cooperation of a great number of neuro ...
... The neuron can be in two states • excited, if s = 1 • not excited, if s = 0 Thus, a neuron is going to separate the space of inputs with an hyperplan. This is why a neural network is good at classification. The action of a single neuron is quite easy ; only the cooperation of a great number of neuro ...
Slide ()
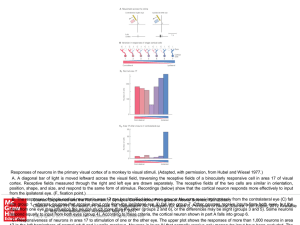
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
... Responses of neurons in the primary visual cortex of a monkey to visual stimuli. (Adapted, with permission, from Hubel and Wiesel 1977.) A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. ...
Samantha Zarati - A critical review of computational neurological models
... However, specifically, I will focus on the use of GPU implementations for spiking neuron models, wherein discrete events (spikes) are modeled, rather than gap junctions, as to the best of the author’s knowledge, this usage is extremely well-documented. The spiking neuron model can be broken down int ...
... However, specifically, I will focus on the use of GPU implementations for spiking neuron models, wherein discrete events (spikes) are modeled, rather than gap junctions, as to the best of the author’s knowledge, this usage is extremely well-documented. The spiking neuron model can be broken down int ...