CHAPTER OVERVIEW
... of the graphs. Most students who have not used graphs extensively will get lost without specific examples. Approach the process systematically, and offer an example of each type of shift. Spend extra time on examples of substitute and complementary goods. 3. The concepts introduced in Chapter 3 are ...
... of the graphs. Most students who have not used graphs extensively will get lost without specific examples. Approach the process systematically, and offer an example of each type of shift. Spend extra time on examples of substitute and complementary goods. 3. The concepts introduced in Chapter 3 are ...
MICRO ECONOMICS II BA ECONOMICS UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT
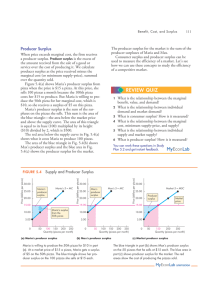
... The above figures shows the perfectly competitive firm and industry’s short run supply curve because it shows the quantity of the commodity that the firm would supply in the short run at various prices. For example, the firm supplies 3 units of the commodity at the price of Rs. 25 (point C in the le ...
... The above figures shows the perfectly competitive firm and industry’s short run supply curve because it shows the quantity of the commodity that the firm would supply in the short run at various prices. For example, the firm supplies 3 units of the commodity at the price of Rs. 25 (point C in the le ...
Chapter 3: “Supply and Prices”
... demand curves with different elasticity's. Explain the difference between slope of a line and the elasticity between two points on a line. ...
... demand curves with different elasticity's. Explain the difference between slope of a line and the elasticity between two points on a line. ...
Microeconomics_Part 2
... never talk about efficiency. Instead, they talk about equity or fairness. The claim that is often made is that it is unfair for profit-seeking dealers to cheat the victims of natural disaster. Similarly, when low-skilled people work for a wage that is below what most would regard as a “living wage,” ...
... never talk about efficiency. Instead, they talk about equity or fairness. The claim that is often made is that it is unfair for profit-seeking dealers to cheat the victims of natural disaster. Similarly, when low-skilled people work for a wage that is below what most would regard as a “living wage,” ...
Order Exposure and Liquidity Coordination
... two counteracting mechanisms exist. In line with Harris (1997), we find that a larger tick size reduces the likelihood of overbidding and therefore increases the incentives for order exposure. However, we also illustrate that a larger tick size reduces the incentives of latent traders to trade in th ...
... two counteracting mechanisms exist. In line with Harris (1997), we find that a larger tick size reduces the likelihood of overbidding and therefore increases the incentives for order exposure. However, we also illustrate that a larger tick size reduces the incentives of latent traders to trade in th ...
The Market Forces of Supply and Demand
... If warnings on cigarette packages convince smokers to smoke less, the demand curve for cigarettes shifts to the left. In panel (a), the demand curve shifts from D1 to D2. At a price of $2.00 per pack, the quantity demanded falls from 20 to 10 cigarettes per day, as reflected by the shift from point ...
... If warnings on cigarette packages convince smokers to smoke less, the demand curve for cigarettes shifts to the left. In panel (a), the demand curve shifts from D1 to D2. At a price of $2.00 per pack, the quantity demanded falls from 20 to 10 cigarettes per day, as reflected by the shift from point ...
Chpt. 4 Part I -Supply and Demand
... An event that reduces quantity supplied at any given price shifts the supply curve to the left. The equilibrium price rises, and the equilibrium quantity falls. Here an increase in the price of sugar (an input) causes sellers to supply less ice cream. The supply curve shifts from S 1 to S2, which ca ...
... An event that reduces quantity supplied at any given price shifts the supply curve to the left. The equilibrium price rises, and the equilibrium quantity falls. Here an increase in the price of sugar (an input) causes sellers to supply less ice cream. The supply curve shifts from S 1 to S2, which ca ...
2 Sample - copyright Tactic Publications Demand and
... competitive market. Any market with a large number of relatively small firms selling very similar goods and/or services and with easy entry conditions is a competitive market. A market that is not competitive is called an imperfect or non-competitive market. A monopoly market would be an extreme typ ...
... competitive market. Any market with a large number of relatively small firms selling very similar goods and/or services and with easy entry conditions is a competitive market. A market that is not competitive is called an imperfect or non-competitive market. A monopoly market would be an extreme typ ...
market fundamentals
... find out how much people are willing to buy at different price levels. Let’s study the demand for chocolates “Milka”. The first thing that we learn is that there is not just demand. The demand is always for a particular good. Further, the demand is always in a particular market. If chocolates “Milka ...
... find out how much people are willing to buy at different price levels. Let’s study the demand for chocolates “Milka”. The first thing that we learn is that there is not just demand. The demand is always for a particular good. Further, the demand is always in a particular market. If chocolates “Milka ...
The Evolution Routines of Labor Division in New Classical Economics
... 2 Modern logistics results from the evolution of labor division in socialization and internationalization 2.1 A review on the classical, neoclassical and new classical economics The economics became knowledge of system, after Adam Smith’s “Wealth of Nations” was published. Classical economists that ...
... 2 Modern logistics results from the evolution of labor division in socialization and internationalization 2.1 A review on the classical, neoclassical and new classical economics The economics became knowledge of system, after Adam Smith’s “Wealth of Nations” was published. Classical economists that ...
Document
... 1) Michael Dell was the first individual who sold computers by mail order. The company founded by Dell is now one of the largest and most successful computer companies in the United States. Michael Dell would be classified as a(n) A) entrepreneur. B) opportunist. C) monopolist. D) socialist. Answer: ...
... 1) Michael Dell was the first individual who sold computers by mail order. The company founded by Dell is now one of the largest and most successful computer companies in the United States. Michael Dell would be classified as a(n) A) entrepreneur. B) opportunist. C) monopolist. D) socialist. Answer: ...
Market Demand
... Declining price consumption curve is associated with an increase in total expenditures on x1 Indicating elastic demand Negatively sloping portion of price consumption curve is associated with elastic portion of demand curve Positively sloping price consumption curve is associated with inelastic po ...
... Declining price consumption curve is associated with an increase in total expenditures on x1 Indicating elastic demand Negatively sloping portion of price consumption curve is associated with elastic portion of demand curve Positively sloping price consumption curve is associated with inelastic po ...
Macroeconomic Effects of Secondary Market
... high returns when this risk-taking behavior pays off. Indeed, because bankers highly value increased borrowing capacity when interest rates are low, financiers earn large rents by taking on risk-exposure when funding is cheap. As a result, secondary market booms are triggered by strong demand for fi ...
... high returns when this risk-taking behavior pays off. Indeed, because bankers highly value increased borrowing capacity when interest rates are low, financiers earn large rents by taking on risk-exposure when funding is cheap. As a result, secondary market booms are triggered by strong demand for fi ...
Demand and Supply - Tactic Publications
... Economic systems exist to attempt to deal with the economic problem. An economic system tries to coordinate the production and distribution of goods and services to satisfy the wants of society. In economics we refer to two important functions of an economic system: • The allocation of resources • ...
... Economic systems exist to attempt to deal with the economic problem. An economic system tries to coordinate the production and distribution of goods and services to satisfy the wants of society. In economics we refer to two important functions of an economic system: • The allocation of resources • ...