Chapter 4 (Supply and Demand)
... • Read your market and the scenario. • Determine if the scenario would have an impact on supply or demand. • Then, graph and provide a written description of the market change ...
... • Read your market and the scenario. • Determine if the scenario would have an impact on supply or demand. • Then, graph and provide a written description of the market change ...
Building Sub-national Debt Markets
... resulting in moral hazard. The second agency problem is that of hidden information, in which sub-national borrowers as agents have an incentive not to reveal certain characteristics about themselves to lenders as principals, resulting in adverse selection. The incidence of both agency problems varie ...
... resulting in moral hazard. The second agency problem is that of hidden information, in which sub-national borrowers as agents have an incentive not to reveal certain characteristics about themselves to lenders as principals, resulting in adverse selection. The incidence of both agency problems varie ...
Microeconomics - Exercises
... 2. Demand 2.1 Price Changes Exercise 2.1.1 a) Suppose there are two goods a consumer can choose between, and that the prices are equal. First, construct a diagram, with quantities on the X- and Y-axes, where you show a utility maximizing choice for the consumer. b) Then, show what happens if you var ...
... 2. Demand 2.1 Price Changes Exercise 2.1.1 a) Suppose there are two goods a consumer can choose between, and that the prices are equal. First, construct a diagram, with quantities on the X- and Y-axes, where you show a utility maximizing choice for the consumer. b) Then, show what happens if you var ...
Microeconomics excercises
... A basic assumption about consumers in microeconomics is that they have preferences over different baskets of goods. Explain the concepts “preference”, “preference order”, and “basket of goods”. Exercise 1.1.2 a) If there are only two goods, it is possible to illustrate a consumer’s preferences over ...
... A basic assumption about consumers in microeconomics is that they have preferences over different baskets of goods. Explain the concepts “preference”, “preference order”, and “basket of goods”. Exercise 1.1.2 a) If there are only two goods, it is possible to illustrate a consumer’s preferences over ...
Corporate Bond Markets: A Global Perspective
... Corporate bond markets can be considered an important ingredient in economic growth, financial stability and economic recovery, particularly in the wake of the crisis. 2 They provide a key capital funding flow to firms allowing them to expand, innovate, offer employment, and provide the goods and se ...
... Corporate bond markets can be considered an important ingredient in economic growth, financial stability and economic recovery, particularly in the wake of the crisis. 2 They provide a key capital funding flow to firms allowing them to expand, innovate, offer employment, and provide the goods and se ...
Monopoly, Monopoly Regulation, Price discrimination
... Natural monopoly: due to high entry costs in the industry, economies of scale or scope, it is less costly for one firm to produce than for several. Entry barriers: due to some market characteristics (high costs or existence of an essential facility) or threats coming from firms already present in th ...
... Natural monopoly: due to high entry costs in the industry, economies of scale or scope, it is less costly for one firm to produce than for several. Entry barriers: due to some market characteristics (high costs or existence of an essential facility) or threats coming from firms already present in th ...
The Impact of Collateral
... cleared derivatives markets over time. And there was an expectation that EMIR would heavily impact firms’ collateral management functions (see ‘Key takeaways’ box for more detail). Mike Shipton, CEO of DTCC-Euroclear GlobalCollateral Ltd, the collateral processing joint venture, says that the task f ...
... cleared derivatives markets over time. And there was an expectation that EMIR would heavily impact firms’ collateral management functions (see ‘Key takeaways’ box for more detail). Mike Shipton, CEO of DTCC-Euroclear GlobalCollateral Ltd, the collateral processing joint venture, says that the task f ...
Market Power, Toeholds and the Takeover Premium
... direction of the relation between Size and Premium being indeterminable ex ante. The second target characteristic included in the model accounts for a target’s stock exchange listing (Major Exchange). This binary variable is one if the target is listed on the American Stock Exchange, the NYSE or the ...
... direction of the relation between Size and Premium being indeterminable ex ante. The second target characteristic included in the model accounts for a target’s stock exchange listing (Major Exchange). This binary variable is one if the target is listed on the American Stock Exchange, the NYSE or the ...
Investigating Stock Market Indices of India - Empirical Analysis
... In Indian context, the authors came across only two studies on indices, one by Narasimhan and Balasubramanian (1999) and the other by Dharani and Natarajan (2011). While Narasimhan and Balasubramanian (1999) compared risk-return characteristics of only three indexes namely Sensex, Natex and BSE 200 ...
... In Indian context, the authors came across only two studies on indices, one by Narasimhan and Balasubramanian (1999) and the other by Dharani and Natarajan (2011). While Narasimhan and Balasubramanian (1999) compared risk-return characteristics of only three indexes namely Sensex, Natex and BSE 200 ...
Building Sub-national Debt Markets in Developing and
... Section A: Principal-agent relationships between central government, subnational entities, and lenders 10. Sub-national debt markets are characterized by a number of specific agency problems. The first agency problem is that of hidden action, in which sub-national borrowers as agents may have an in ...
... Section A: Principal-agent relationships between central government, subnational entities, and lenders 10. Sub-national debt markets are characterized by a number of specific agency problems. The first agency problem is that of hidden action, in which sub-national borrowers as agents may have an in ...
Introduction to Micro economics
... economics given by Alfred Marshall under the following points: 1. Classificatory: Marshall classified human activities into material and nonmaterial welfare, economic and non- economic goods but he could not distinguish the differences between these terms clearly. Therefore, his definition is classi ...
... economics given by Alfred Marshall under the following points: 1. Classificatory: Marshall classified human activities into material and nonmaterial welfare, economic and non- economic goods but he could not distinguish the differences between these terms clearly. Therefore, his definition is classi ...
Supply and Demand: An Introduction
... An Increase In Quantity Supplied vs. An Increase In Supplied Price ...
... An Increase In Quantity Supplied vs. An Increase In Supplied Price ...
DEBT CAPITAL MARKETS 2015 REVIEW AND 2016 FORECAST
... tighter relative levels post-swap than direct USD funding. ...
... tighter relative levels post-swap than direct USD funding. ...
DOCx
... a“business” or a “firm,” terms that connote a for-profit organization. And in some portions of the book, we discuss principles that presume the underlying goal of the organization is to create profit. However, managerial economics is relevant to nonprofit organizations and government agencies as wel ...
... a“business” or a “firm,” terms that connote a for-profit organization. And in some portions of the book, we discuss principles that presume the underlying goal of the organization is to create profit. However, managerial economics is relevant to nonprofit organizations and government agencies as wel ...
Credit default swaps. Contract characteristics and
... In addition to CDS contracts relating to a specific reference entity (“single name CDSs”), contracts on indexes representing a portfolio of issuers (“index” or “basket” CDSs) have also become popular. In this case, each reference entity equally contributes to the total nominal value of the contract. ...
... In addition to CDS contracts relating to a specific reference entity (“single name CDSs”), contracts on indexes representing a portfolio of issuers (“index” or “basket” CDSs) have also become popular. In this case, each reference entity equally contributes to the total nominal value of the contract. ...
Investing in Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs):
... portfolio performance will approximate stock market returns. Size of the core depends upon the amount of stock market risk that the investor is willing to assume. Investors, who are satisfied with realization of returns that approximate the market, will place a larger portion of their portfolio into ...
... portfolio performance will approximate stock market returns. Size of the core depends upon the amount of stock market risk that the investor is willing to assume. Investors, who are satisfied with realization of returns that approximate the market, will place a larger portion of their portfolio into ...
Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium
... illustrated in panel (A) of Figure 4.7. When demand changes, people want to buy more or less of a product at the same price. This is illustrated in panel (B) of Figure 4.7. Since the price of the good has not changed, the demand curve must have shifted. An increase in demand occurs when consumers wa ...
... illustrated in panel (A) of Figure 4.7. When demand changes, people want to buy more or less of a product at the same price. This is illustrated in panel (B) of Figure 4.7. Since the price of the good has not changed, the demand curve must have shifted. An increase in demand occurs when consumers wa ...
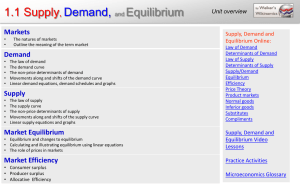
1.1 Supply, Demand, and Equilibrium
... All markets include buyers and sellers. The buyers in a market demand the product, but the sellers supply it. Definition of Supply: a schedule or curve showing how much of a product producers will supply at each of a range of possible prices during a specific time period. • Different producers have ...
... All markets include buyers and sellers. The buyers in a market demand the product, but the sellers supply it. Definition of Supply: a schedule or curve showing how much of a product producers will supply at each of a range of possible prices during a specific time period. • Different producers have ...
Econ 101: Principles of Microeconomics
... Government Intervention As Krugman and Wells note in their Principle #9: “When markets don’t achieve efficiency, government intervention can improve society’s welfare” resulting from ...
... Government Intervention As Krugman and Wells note in their Principle #9: “When markets don’t achieve efficiency, government intervention can improve society’s welfare” resulting from ...
File
... Increase in income. If a good is a normal good, an increase in income increases demand for the good. Restaurant meals would be an example of normal goods. Decrease in income. If a good is an inferior good, a decrease in income will increase demand. Store-brand cola would be an example of an infe ...
... Increase in income. If a good is a normal good, an increase in income increases demand for the good. Restaurant meals would be an example of normal goods. Decrease in income. If a good is an inferior good, a decrease in income will increase demand. Store-brand cola would be an example of an infe ...