Laws of Demand and Supply
... • Business owners have to consider how the number of workers they hire will affect their total production. • ACTIVITY! • Marginal product of labor – change in output from hiring one additional worker. ...
... • Business owners have to consider how the number of workers they hire will affect their total production. • ACTIVITY! • Marginal product of labor – change in output from hiring one additional worker. ...
Factors Market
... • Term originally only applied to land • Payment for land above price necessary for land to be made available • A decrease in the payment for land will not reduce the quantity of land available for rent. ...
... • Term originally only applied to land • Payment for land above price necessary for land to be made available • A decrease in the payment for land will not reduce the quantity of land available for rent. ...
Split UP Economics Class XII - Kendriya Vidyalaya No. 1, Dehu
... Meaning of microeconomics and macroeconomics What is an economy? Central problems of an economy: what, how and for whom to produce; concepts of production possibility frontier and opportunity cost. Consumer's Equilibrium and Demand 34 Periods Consumer's equilibrium - meaning of utility, marginal uti ...
... Meaning of microeconomics and macroeconomics What is an economy? Central problems of an economy: what, how and for whom to produce; concepts of production possibility frontier and opportunity cost. Consumer's Equilibrium and Demand 34 Periods Consumer's equilibrium - meaning of utility, marginal uti ...
EconCh06 - Blountstown High School
... In some cases the government steps in to control prices. These interventions appear as price ceilings and price floors. • A price ceiling is a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good. • An example of a price ceiling is rent control, a situation where a government sets a maximum amount t ...
... In some cases the government steps in to control prices. These interventions appear as price ceilings and price floors. • A price ceiling is a maximum price that can be legally charged for a good. • An example of a price ceiling is rent control, a situation where a government sets a maximum amount t ...
Competition and Market Structures
... 1) Make a list of as many clothing stores in this area as ...
... 1) Make a list of as many clothing stores in this area as ...
Money Market Securities
... Interbank lending and borrowing Federal funds rate usually slightly higher than Tbill rate Fed district bank debits and credits accounts for purchase (borrowing) and sale (lending) Federal funds brokers may match up buyers and sellers using telecommunications network ...
... Interbank lending and borrowing Federal funds rate usually slightly higher than Tbill rate Fed district bank debits and credits accounts for purchase (borrowing) and sale (lending) Federal funds brokers may match up buyers and sellers using telecommunications network ...
ECON 2010-200 Principles of Microeconomics
... The individual must decide what goods to buy, how much to save and how hard to work. The fim1 must decide how much to produce and with what technology. The course explores how "the magic of the market" coordinates these decisons. In addition, the course considers such questions as: Why is competitio ...
... The individual must decide what goods to buy, how much to save and how hard to work. The fim1 must decide how much to produce and with what technology. The course explores how "the magic of the market" coordinates these decisons. In addition, the course considers such questions as: Why is competitio ...
Navigating 5 years of emerging market corporate debt
... • Investing globally can bring additional returns and diversify risk. However, currency exchange rate fluctuations may have a positive or negative impact on the value of your investment. • Bonds are affected by changes in interest rates, inflation and any decline in creditworthiness of the bond is ...
... • Investing globally can bring additional returns and diversify risk. However, currency exchange rate fluctuations may have a positive or negative impact on the value of your investment. • Bonds are affected by changes in interest rates, inflation and any decline in creditworthiness of the bond is ...
View PDF Report
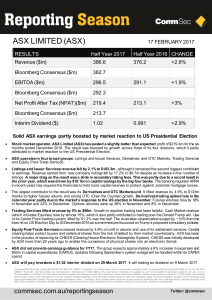
... Equity Post-Trade Services increased revenue by 3.8% on a lift in volume and use of its settlement services. Central clearing helps protect buyers and sellers of shares from the risk of default by their market counterparty. ASX has been in the process of replacing its CHESS (Clearing House Electroni ...
... Equity Post-Trade Services increased revenue by 3.8% on a lift in volume and use of its settlement services. Central clearing helps protect buyers and sellers of shares from the risk of default by their market counterparty. ASX has been in the process of replacing its CHESS (Clearing House Electroni ...
When a government imposes penalties on both sellers and buyers
... b) a decrease in the price firms expect to receive in the future c) a rise in the wages paid workers d) development of new technology ...
... b) a decrease in the price firms expect to receive in the future c) a rise in the wages paid workers d) development of new technology ...
ECO352_13.pdf
... Each firm's average cost curve downward-sloping as its own output increases Market structure must be imperfectly competitive, oligopoly if only a few (2-3) firms survive: aircraft monopolistic competition if several (10 or more) survive, free entry: autos In principle, scale economies are an added r ...
... Each firm's average cost curve downward-sloping as its own output increases Market structure must be imperfectly competitive, oligopoly if only a few (2-3) firms survive: aircraft monopolistic competition if several (10 or more) survive, free entry: autos In principle, scale economies are an added r ...
New Banks, New Currencies and New Markets in a
... attribute, for example, organic, recyclable, fair trade, fair labor, sustainable materials-sourced, or whatever the affinities or attributes of concern are. Affinity-directed capital can influence both cash inflows and cash outflows. Affinity inflows are monies earned. To a greater degree than was p ...
... attribute, for example, organic, recyclable, fair trade, fair labor, sustainable materials-sourced, or whatever the affinities or attributes of concern are. Affinity-directed capital can influence both cash inflows and cash outflows. Affinity inflows are monies earned. To a greater degree than was p ...
MARKETS - Man Group
... indices are shown for illustrative purposes only, may not be available for direct investment, are unmanaged, assume reinvestment of income, do not reflect the impact of any management incentive fees and have limitations when used for comparison or other purposes because they may have different volat ...
... indices are shown for illustrative purposes only, may not be available for direct investment, are unmanaged, assume reinvestment of income, do not reflect the impact of any management incentive fees and have limitations when used for comparison or other purposes because they may have different volat ...
Ch3 - YSU
... are not shared by others. (Efficiency Principle) – Buyers and sellers are only concerned about their own marginal benefit and marginal cost. – If the production of a good creates benefits or costs to other groups, the market equilibrium would not achieve economic efficiency. ...
... are not shared by others. (Efficiency Principle) – Buyers and sellers are only concerned about their own marginal benefit and marginal cost. – If the production of a good creates benefits or costs to other groups, the market equilibrium would not achieve economic efficiency. ...
ProVia Positions for Growth
... been with ProVia Door since 1989, and has served in several positions, most recently as the company’s Director of Marketing. Phil will be responsible for the corporate level strategies related to market growth, customer and market research & analysis, new product development, and management of intel ...
... been with ProVia Door since 1989, and has served in several positions, most recently as the company’s Director of Marketing. Phil will be responsible for the corporate level strategies related to market growth, customer and market research & analysis, new product development, and management of intel ...
Introduction to Business Economics
... • seeks to determine the aggregate (total) effect of interaction between all buyers and sellers in a market by measuring: 1. gross domestic product (GDP): the total amount of goods and services a country (the United States, for example) produces in a year. 2. rate of inflation: how much prices go up ...
... • seeks to determine the aggregate (total) effect of interaction between all buyers and sellers in a market by measuring: 1. gross domestic product (GDP): the total amount of goods and services a country (the United States, for example) produces in a year. 2. rate of inflation: how much prices go up ...
File
... 8. Marginal Cost is the: A) total costs divided by the quantity produced. B) change in fixed cost from producing one additional unit of output. C) market value of all resources used to produce a good. D) change in total cost from producing one additional unit of output. ...
... 8. Marginal Cost is the: A) total costs divided by the quantity produced. B) change in fixed cost from producing one additional unit of output. C) market value of all resources used to produce a good. D) change in total cost from producing one additional unit of output. ...
The “Gezi” Resistance in Turkey. Gökçer Özgür and
... Therefore, from a social‐theoretical point of view, Polanyi’s overall account of the market system provides us with three important points. First, Polanyi’s argument is that market society is inherently unstable; in other words, his critique is directed to the invisible ha ...
... Therefore, from a social‐theoretical point of view, Polanyi’s overall account of the market system provides us with three important points. First, Polanyi’s argument is that market society is inherently unstable; in other words, his critique is directed to the invisible ha ...