Session Three: Market economy vs. planned economy: how China is
... Market vs. planned economy • Arguments for centrally planned economy: – The main argument is that the collective ownership of the means of production “by the people for the people” is preferable to a situation in which the ownership of the means of production is in the hands of the “capitalist clas ...
... Market vs. planned economy • Arguments for centrally planned economy: – The main argument is that the collective ownership of the means of production “by the people for the people” is preferable to a situation in which the ownership of the means of production is in the hands of the “capitalist clas ...
Chapter 15
... Reducing risk: While correlations among the developed markets are increasing, emerging markets show little correlation with developed markets or with one another. ...
... Reducing risk: While correlations among the developed markets are increasing, emerging markets show little correlation with developed markets or with one another. ...
Ruang Lingkup Makro Ekonomi
... concerning taxes and expenditures. • Monetary policy consists of tools used by the Federal Reserve to control the money supply. • Growth policies are government policies that focus on stimulating aggregate supply instead of aggregate demand. ...
... concerning taxes and expenditures. • Monetary policy consists of tools used by the Federal Reserve to control the money supply. • Growth policies are government policies that focus on stimulating aggregate supply instead of aggregate demand. ...
Further Reforms after the “BIG BANG”: The JGB Market
... Impede Market Efficiency? (II) Significant Negative Reaction to Short Sale Information is Found Negative returns are approximately -0.02% over 20 trades after short-sales information is released [Aitken, Frino, McCorry, and Swan (1998)] High degree of transparency is desired since short sales convey ...
... Impede Market Efficiency? (II) Significant Negative Reaction to Short Sale Information is Found Negative returns are approximately -0.02% over 20 trades after short-sales information is released [Aitken, Frino, McCorry, and Swan (1998)] High degree of transparency is desired since short sales convey ...
**This review should be used along with the review sheets for
... Competitive firms short-run supply curve Competitive firms long-run supply curve Market supply curve Increasing (decreasing and constant) cost industry Concepts Price taker: a firm that can’t significantly affect market price through its output decisions Profits = revenues minus costs The mark ...
... Competitive firms short-run supply curve Competitive firms long-run supply curve Market supply curve Increasing (decreasing and constant) cost industry Concepts Price taker: a firm that can’t significantly affect market price through its output decisions Profits = revenues minus costs The mark ...
The Free Market Price: EQUILIBRIUM Ch. 6
... The Market Price • Remember the “invisible hand”? When consumers and producers willingly interact in order to buy/sell g/s? ...
... The Market Price • Remember the “invisible hand”? When consumers and producers willingly interact in order to buy/sell g/s? ...
Syllabus
... The goal of this course is to introduce students to the subject of microeconomics, its central concepts and methods of analysis. The emphasis will be on teaching students economic way of thinking that provides a new perspective on human behavior and interaction as well as helps to solve every-day pr ...
... The goal of this course is to introduce students to the subject of microeconomics, its central concepts and methods of analysis. The emphasis will be on teaching students economic way of thinking that provides a new perspective on human behavior and interaction as well as helps to solve every-day pr ...
2. Triggers for growth and jobs in the Single Market
... when it comes to transposing and implementing rules. It pleads for fast-track infringement procedures where problems remain. As the table in the Annex shows, we are not yet there. Only one Member State (DK) already complies with all the targets set in the June 2012 Communication, while more than hal ...
... when it comes to transposing and implementing rules. It pleads for fast-track infringement procedures where problems remain. As the table in the Annex shows, we are not yet there. Only one Member State (DK) already complies with all the targets set in the June 2012 Communication, while more than hal ...
Lecture II: Demand and Supply Models
... For both demadn curves the monopolists profit maximizing output is where MR = MC, which is 10 units and MC at this point is 20 $. ...
... For both demadn curves the monopolists profit maximizing output is where MR = MC, which is 10 units and MC at this point is 20 $. ...
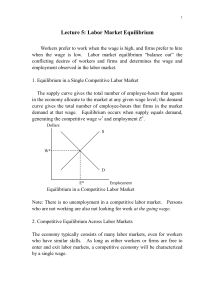
Lecture 5 Labor Market Equilibrium
... Our analysis of labor market equilibrium assumes that markets adjust instantaneously to shifts in either supply or demand curves, so that wages and employment change swiftly from the old equilibrium levels to the new equilibrium level. Many labor markets, however, do not adjust so quickly to shifts ...
... Our analysis of labor market equilibrium assumes that markets adjust instantaneously to shifts in either supply or demand curves, so that wages and employment change swiftly from the old equilibrium levels to the new equilibrium level. Many labor markets, however, do not adjust so quickly to shifts ...
Lecture 5 Labor Market Equilibrium
... Our analysis of labor market equilibrium assumes that markets adjust instantaneously to shifts in either supply or demand curves, so that wages and employment change swiftly from the old equilibrium levels to the new equilibrium level. Many labor markets, however, do not adjust so quickly to shifts ...
... Our analysis of labor market equilibrium assumes that markets adjust instantaneously to shifts in either supply or demand curves, so that wages and employment change swiftly from the old equilibrium levels to the new equilibrium level. Many labor markets, however, do not adjust so quickly to shifts ...
1 - Carlos Pitta
... Question # 9: Here you need to calculate two areas: the rectangle with an area (BASE*HEIGHT) equal to: (Height: 22-16=6, in the price axis) times (Base: 0 to 40=40, in the quantity axis)= 240 PLUS, the triangle Base (80 – 40=40, in the quantity axis) times (Height: 22-16=6, en the price axis) times ...
... Question # 9: Here you need to calculate two areas: the rectangle with an area (BASE*HEIGHT) equal to: (Height: 22-16=6, in the price axis) times (Base: 0 to 40=40, in the quantity axis)= 240 PLUS, the triangle Base (80 – 40=40, in the quantity axis) times (Height: 22-16=6, en the price axis) times ...
Firm`s Decision - Profit Maximization
... LR Competitive Industry Supply You can not simply sum supply curves as in the SR, since there is an additional source of supply changes (new firms entering or old firms leaving industry). Assume:Input Prices and Technology Fixed, U-shaped AC curve With demand curve D, the number of firms in the mar ...
... LR Competitive Industry Supply You can not simply sum supply curves as in the SR, since there is an additional source of supply changes (new firms entering or old firms leaving industry). Assume:Input Prices and Technology Fixed, U-shaped AC curve With demand curve D, the number of firms in the mar ...
Chapter 28 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Provide a public good? How much should be provided? Resources are limited Marginal-cost-marginal-benefit rule • Allocate government resources to maximize net benefit ...
... Provide a public good? How much should be provided? Resources are limited Marginal-cost-marginal-benefit rule • Allocate government resources to maximize net benefit ...
Answer key
... a. Under perfect competition, a firm is always guaranteed to earn positive economic profits if it produces where marginal cost equals price. False. Producing the quantity at which MC = P is in many cases a good idea, since itwill maximize the firm’s profit or minimize its losses. Which of the two is ...
... a. Under perfect competition, a firm is always guaranteed to earn positive economic profits if it produces where marginal cost equals price. False. Producing the quantity at which MC = P is in many cases a good idea, since itwill maximize the firm’s profit or minimize its losses. Which of the two is ...
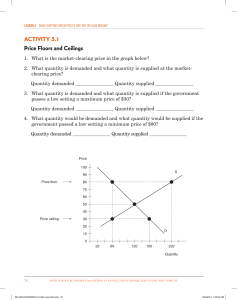
Economics Unit II Test Review Sheet
... 18. Price floor-The minimum price for a good or service (Ex. Minimum Wage) 19. Rationing-A system of allocating/ distributing scare goods and services using criteria other than price 20. Why was there government rationing during World War II? – -The government wanted to ensure that every civilian ha ...
... 18. Price floor-The minimum price for a good or service (Ex. Minimum Wage) 19. Rationing-A system of allocating/ distributing scare goods and services using criteria other than price 20. Why was there government rationing during World War II? – -The government wanted to ensure that every civilian ha ...
The Role of Profits and Markets
... TC = FC – VC where: FC = Fixed Costs (overheads) VC = Variable Costs (direct costs or cost of sales) Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed ...
... TC = FC – VC where: FC = Fixed Costs (overheads) VC = Variable Costs (direct costs or cost of sales) Copyright 2006 – Biz/ed ...
profit and loss presentation
... TC = FC – VC where: FC = Fixed Costs (overheads) VC = Variable Costs (direct costs or cost of sales) Copyright 2005 – Biz/ed ...
... TC = FC – VC where: FC = Fixed Costs (overheads) VC = Variable Costs (direct costs or cost of sales) Copyright 2005 – Biz/ed ...
1st 9 weeks
... EC.30 Examine informational text in diverse formats and media to analyze how investment in research and development, equipment and technology, and training of workers increases productivity. ...
... EC.30 Examine informational text in diverse formats and media to analyze how investment in research and development, equipment and technology, and training of workers increases productivity. ...
Download Document
... Treasury bonds, the expected cash flows are essentially certain, while for another investment such as a “start-up” technology company, the future cash flows (earnings) expectation would be that earnings will grow in the future, but that expectation will be highly uncertain. Financial theory says tha ...
... Treasury bonds, the expected cash flows are essentially certain, while for another investment such as a “start-up” technology company, the future cash flows (earnings) expectation would be that earnings will grow in the future, but that expectation will be highly uncertain. Financial theory says tha ...
EC 220 Microeconomics - College of Micronesia
... their influences in the decision-making process of individual consumers, groups of consumers, and firms. The course examines: price mechanism (demand, supply and price) and allocation of resources; comparative advantage and specialization; the theory of the firm – short run and long run cost/revenue ...
... their influences in the decision-making process of individual consumers, groups of consumers, and firms. The course examines: price mechanism (demand, supply and price) and allocation of resources; comparative advantage and specialization; the theory of the firm – short run and long run cost/revenue ...