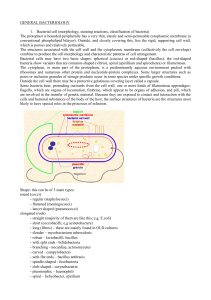
GENERAL BACTERIOLOGY 1. Bacterial cell
... Bacterial cells may have two basic shapes: spherical (coccus) or rod-shaped (bacillus); the rod-shaped bacteria show variants that are common-shaped (vibrio), spiral (spirillium and spirochetes) or filamentous. The cytoplasm, or main part of the protoplasm, is a predominantly aqueous environment pac ...
... Bacterial cells may have two basic shapes: spherical (coccus) or rod-shaped (bacillus); the rod-shaped bacteria show variants that are common-shaped (vibrio), spiral (spirillium and spirochetes) or filamentous. The cytoplasm, or main part of the protoplasm, is a predominantly aqueous environment pac ...
Pharyngeal diphtheria
... Patients and asymptomatic carriers Patients: Transmission time is variable, usually persist 12 days or less, and seldom more than 4 weeks, without antibiotics. ...
... Patients and asymptomatic carriers Patients: Transmission time is variable, usually persist 12 days or less, and seldom more than 4 weeks, without antibiotics. ...
Hepatitis C and HIV/HCV Coinfection
... MEASURE OF INFLAMMATION EXTENT OF SCARRING (IF ANY) NON-INVASIVE METHODS – NOT AS ACCURATE ...
... MEASURE OF INFLAMMATION EXTENT OF SCARRING (IF ANY) NON-INVASIVE METHODS – NOT AS ACCURATE ...
The First Aid Industry and Hepatitis B
... Having unprotected sex with an infected person. Even having oral sex can transmit hepatitis B. (Note: 80% of people with hepatitis B do not know) There is a small risk of contracting the virus from sharing toothbrushes, razors, and other such items which may be contaminated with blood. The virus can ...
... Having unprotected sex with an infected person. Even having oral sex can transmit hepatitis B. (Note: 80% of people with hepatitis B do not know) There is a small risk of contracting the virus from sharing toothbrushes, razors, and other such items which may be contaminated with blood. The virus can ...
Smallpox: an old disease but still a threat in the XXI century
... microscope (0.2 μm = 200 nm). They are also different from the majority of viruses because they are virus with double stranded DNA and because they replicate in the cytoplasm and have enzymes to synthesize messenger RNA. They have proteins that serve to evade mechanisms of immunity of the host. The ...
... microscope (0.2 μm = 200 nm). They are also different from the majority of viruses because they are virus with double stranded DNA and because they replicate in the cytoplasm and have enzymes to synthesize messenger RNA. They have proteins that serve to evade mechanisms of immunity of the host. The ...
diseases of oral cavity
... filiform papillae resembling hairlike projections Associated with - heavy tobacco use, mouth breathing, antibiotic therapy, poor oral hygiene, general debilitation, radiation therapy, chronic use of bismuth containing antacids, lack of dietary roughage White, yellow green, brown, or black color ...
... filiform papillae resembling hairlike projections Associated with - heavy tobacco use, mouth breathing, antibiotic therapy, poor oral hygiene, general debilitation, radiation therapy, chronic use of bismuth containing antacids, lack of dietary roughage White, yellow green, brown, or black color ...
Physician Specialty Definitions
... A field of comprehensive medical care for a patient with a life-threatening disease or terminal illness that is not responsive to curative treatment. The care focuses on relieving symptoms, controlling pain, minimizing suffering, providing emotional and psychological support and managing complicatio ...
... A field of comprehensive medical care for a patient with a life-threatening disease or terminal illness that is not responsive to curative treatment. The care focuses on relieving symptoms, controlling pain, minimizing suffering, providing emotional and psychological support and managing complicatio ...
Friday, August 7, 2015
... your muscles to tighten all over your body, and it results in death in 10% of cases. The bacteria that causes meningococcal 1 dose if you’ve disease is transmitted by saliva, such as from previously received kissing or coughing. So it’s important for the vaccine before young adults living in close c ...
... your muscles to tighten all over your body, and it results in death in 10% of cases. The bacteria that causes meningococcal 1 dose if you’ve disease is transmitted by saliva, such as from previously received kissing or coughing. So it’s important for the vaccine before young adults living in close c ...
vaccination
... Other strains are quite innocent and about ten percent of population has meningococcus in their throat ...
... Other strains are quite innocent and about ten percent of population has meningococcus in their throat ...
vaccination
... Other strains are quite innocent and about ten percent of population has meningococcus in their throat ...
... Other strains are quite innocent and about ten percent of population has meningococcus in their throat ...
epidemiology 230 - UCLA Fielding School of Public Health
... Each student complete a take-home final covering the concepts presented in the course. The final is due at 12 Noon on Thursday, June 11 (50% of grade). ...
... Each student complete a take-home final covering the concepts presented in the course. The final is due at 12 Noon on Thursday, June 11 (50% of grade). ...
DOL_Ch02_Transmittal_Final_CW
... 1. Place 1 drop of water in a large bucket. This drop represents the size of the starting population. Predict how full the bucket will be after the population has doubled 10 times. 2. Create a table similar to Table 1 to keep track of the size of the population. 3. Add 1 more drop of water to the b ...
... 1. Place 1 drop of water in a large bucket. This drop represents the size of the starting population. Predict how full the bucket will be after the population has doubled 10 times. 2. Create a table similar to Table 1 to keep track of the size of the population. 3. Add 1 more drop of water to the b ...
17 Lyme Disease: the Great Controversy 17.1 Background
... although such fragments may be speciÞc for B. burgdorferi, their presence does not prove active infection. Consequently, diagnosis has relied almost exclusively on demonstrating a speciÞc host antibody response to the microorganism. However, this too has important pitfalls. The presence of speciÞc a ...
... although such fragments may be speciÞc for B. burgdorferi, their presence does not prove active infection. Consequently, diagnosis has relied almost exclusively on demonstrating a speciÞc host antibody response to the microorganism. However, this too has important pitfalls. The presence of speciÞc a ...
Animal Health
... • once there, it must be able to adapt to the host environment and multiply; • at some point it must be able to exit the host; • and then it must be able to infect another host; Introduction to Animal Science, 5e W. Stephen Damron ...
... • once there, it must be able to adapt to the host environment and multiply; • at some point it must be able to exit the host; • and then it must be able to infect another host; Introduction to Animal Science, 5e W. Stephen Damron ...
infection prevention and control guidance for ems providers
... Emergency Medical Services (EMS) providers play an important role in the prevention and control of infections. EMS providers are at the front line of medical care and have a high risk of exposure to patients with known or unknown infectious diseases or germs. The emergence of antimicrobial-resistant ...
... Emergency Medical Services (EMS) providers play an important role in the prevention and control of infections. EMS providers are at the front line of medical care and have a high risk of exposure to patients with known or unknown infectious diseases or germs. The emergence of antimicrobial-resistant ...
Clostridium Difficile Decontamination Guidelines Using
... microorganisms, most of which are either helpful or harmless under normal, healthy conditions. However, when something upsets the natural balance of these microbes, these otherwise harmless bacteria can proliferate and make people sick. Although rare when compared to other bacteria found in the huma ...
... microorganisms, most of which are either helpful or harmless under normal, healthy conditions. However, when something upsets the natural balance of these microbes, these otherwise harmless bacteria can proliferate and make people sick. Although rare when compared to other bacteria found in the huma ...
A 46-year-old female with dyspnoea, stridor and chronic cough CASE FOR DIAGNOSIS
... The differential diagnosis of tracheal wall narrowing includes infectious, inflammatory and neoplastic processes. In the paediatric population, infectious processes, such as acute tracheobronchitis (croup) or acute bacterial membranous tracheitis, which is less common, may cause stridor and tracheal ...
... The differential diagnosis of tracheal wall narrowing includes infectious, inflammatory and neoplastic processes. In the paediatric population, infectious processes, such as acute tracheobronchitis (croup) or acute bacterial membranous tracheitis, which is less common, may cause stridor and tracheal ...
The pathogenesis of influenza virus infections: the contributions of
... PA and PB2 support better replication of avian viruses in mammalian cells (Table 1) [18–22]. Therefore, it is important to monitor mutations in the genes of the RNA polymerase complex to detect viruses that replicate well in humans. A/Vietnam/1203/04 (VN1203) H5N1 virus, which was isolated from a fa ...
... PA and PB2 support better replication of avian viruses in mammalian cells (Table 1) [18–22]. Therefore, it is important to monitor mutations in the genes of the RNA polymerase complex to detect viruses that replicate well in humans. A/Vietnam/1203/04 (VN1203) H5N1 virus, which was isolated from a fa ...
Infectious Mononucleosis
... humans only and results in a lifelong infection. Although the overwhelming majority of cases of infectious mononucleosis occur during primary EBV infection, infectious mononucleosis syndromes have also been reported in chronically infected persons after T-lymphocyte depletion with monoclonal antibod ...
... humans only and results in a lifelong infection. Although the overwhelming majority of cases of infectious mononucleosis occur during primary EBV infection, infectious mononucleosis syndromes have also been reported in chronically infected persons after T-lymphocyte depletion with monoclonal antibod ...
Persistence of Mycoplasmal Infections and Various Clinical Conditions
... explains their need for host nutritional molecules. A significant number of mycoplasmal genes appear to be devoted to cell adhesion and attachment organelles as well as variable membrane surface antigens to maintain parasitism and evade host immune and nonimmune surveillance systems. Mycoplasma spec ...
... explains their need for host nutritional molecules. A significant number of mycoplasmal genes appear to be devoted to cell adhesion and attachment organelles as well as variable membrane surface antigens to maintain parasitism and evade host immune and nonimmune surveillance systems. Mycoplasma spec ...
EHEC
... • person-to-person contact: oral-faecal route (asymptomatic carriers) • contaminated water (can survive for months) • in this case probably contaminated vegetables which got in contact with faeces of infected animals ...
... • person-to-person contact: oral-faecal route (asymptomatic carriers) • contaminated water (can survive for months) • in this case probably contaminated vegetables which got in contact with faeces of infected animals ...
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Infectious diseases and
... TNF-α) as described, but not shown, in chapter 4 and reference 1 and 2.1;2 Although inflammation is a key process in the host response to bacterial infection, excessive and prolonged exposure of different body tissues to inflammation can result in tissue damage, ultimately leading to multiple organ ...
... TNF-α) as described, but not shown, in chapter 4 and reference 1 and 2.1;2 Although inflammation is a key process in the host response to bacterial infection, excessive and prolonged exposure of different body tissues to inflammation can result in tissue damage, ultimately leading to multiple organ ...
Infect Immun
... Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA. ...
... Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Sciences, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853, USA. ...
Enigmatic dual symbiosis in the excretory organ of Nautilus
... numerous spherical electron-dense bodies. The apical pole of ECs is covered by bacteria, which are located in the pericardial lumen (lu). (b) Higher magnification of the excretory epithelium. Epithelial cells are characterized by numerous mitochondria (m) and the presence of basal infoldings (mp) in ...
... numerous spherical electron-dense bodies. The apical pole of ECs is covered by bacteria, which are located in the pericardial lumen (lu). (b) Higher magnification of the excretory epithelium. Epithelial cells are characterized by numerous mitochondria (m) and the presence of basal infoldings (mp) in ...
Kawasaki disease in East Mazandaran, Islamic Republic of Iran
... extremities were seen in more than 80% of the patients and were consistent with the findings of other studies [1,2,9,16–18] as well as one report from southern Islamic Republic of Iran of Iran [21]. Cardiovascular complications are the most common cause of both short- and long-term morbidity and mor ...
... extremities were seen in more than 80% of the patients and were consistent with the findings of other studies [1,2,9,16–18] as well as one report from southern Islamic Republic of Iran of Iran [21]. Cardiovascular complications are the most common cause of both short- and long-term morbidity and mor ...























