Sept2_Lecture3
... • Survey of important human infectious diseases and pathogens (including a few eukaryotic pathogens) ...
... • Survey of important human infectious diseases and pathogens (including a few eukaryotic pathogens) ...
TEST immune 2012 markscheme
... alleles for resistance can be passed from one cell to another by exchange of plasmids/conjugation; some varieties are more resistant than others; bacteria reproduce very rapidly and have high mutation rate; evolution can occur rapidly; increased exposure to antibiotics is the environmental change th ...
... alleles for resistance can be passed from one cell to another by exchange of plasmids/conjugation; some varieties are more resistant than others; bacteria reproduce very rapidly and have high mutation rate; evolution can occur rapidly; increased exposure to antibiotics is the environmental change th ...
NOSOCOMIAL INFECTIONS
... and spatially separating patients with respiratory infections from other patients when feasible. - using hand hygiene after contact with respiratory secretions. ...
... and spatially separating patients with respiratory infections from other patients when feasible. - using hand hygiene after contact with respiratory secretions. ...
TB - Global Tuberculosis Institute
... decreased by approximately 5.6% each year • From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% • 25,313 cases reported in 1993 • Since 1993, cases are steadily declining ...
... decreased by approximately 5.6% each year • From 1985 to 1992, reported cases increased by 20% • 25,313 cases reported in 1993 • Since 1993, cases are steadily declining ...
Human Welfare.pmd
... by an infected person or even by sharing glasses and utensils with an infected person. Dysentery, plague, diphtheria, etc., are some of the other bacterial diseases in man. Many viruses also cause diseases in human beings. Rhino viruses represent one such group of viruses which cause one of the most ...
... by an infected person or even by sharing glasses and utensils with an infected person. Dysentery, plague, diphtheria, etc., are some of the other bacterial diseases in man. Many viruses also cause diseases in human beings. Rhino viruses represent one such group of viruses which cause one of the most ...
医学史简论 A Brief History of Medicine
... Heterozygote--carriers of a single sickle cell allele are 810% The sickle cells have protection from malaria (plasmodium can not parasite), it may be the results of evolution (mutant events back to 70-150,000 years ago) ...
... Heterozygote--carriers of a single sickle cell allele are 810% The sickle cells have protection from malaria (plasmodium can not parasite), it may be the results of evolution (mutant events back to 70-150,000 years ago) ...
Many protists exist as parasites that infect and cause
... Members of the genus Plasmodium must colonize both a mosquito and a vertebrate to complete their life cycle. In vertebrates, the parasite develops in liver cells and goes on to infect red blood cells, bursting from and destroying the blood cells with each asexual replication cycle . Of the fourPlasm ...
... Members of the genus Plasmodium must colonize both a mosquito and a vertebrate to complete their life cycle. In vertebrates, the parasite develops in liver cells and goes on to infect red blood cells, bursting from and destroying the blood cells with each asexual replication cycle . Of the fourPlasm ...
Cockroaches & Diseases
... • People can become infected with Chagas by • unknowingly touching their eyes, mouth, or open cuts after having come into contact with infective triatome bug feces • bugs directly depositing infected feces in their eyes • eating uncooked food contaminated with triatome bug feces • receiving infectio ...
... • People can become infected with Chagas by • unknowingly touching their eyes, mouth, or open cuts after having come into contact with infective triatome bug feces • bugs directly depositing infected feces in their eyes • eating uncooked food contaminated with triatome bug feces • receiving infectio ...
Infection Control - Bridgepoint Health
... 6. The health care provider understands and applies basic microbiology concepts; understands and applies the principles and practices of asepsis and sterile technique 7. The health care provider understands their responsibility and performs surveillance through assessing and communicating unusual oc ...
... 6. The health care provider understands and applies basic microbiology concepts; understands and applies the principles and practices of asepsis and sterile technique 7. The health care provider understands their responsibility and performs surveillance through assessing and communicating unusual oc ...
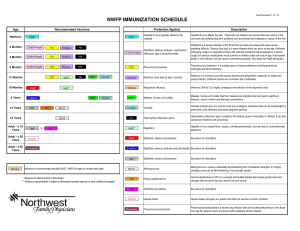
NWFP Immunization Schedule
... breathing difficulty. Tetanus (lock jaw) is a nerve disease which can occur at any age. Pertussis (whooping cough) is a respiratory illness with cold-like symptoms that progresses to a severe cough and serious complications more common in children under one year of age. Poliomyelitis (polio) is vira ...
... breathing difficulty. Tetanus (lock jaw) is a nerve disease which can occur at any age. Pertussis (whooping cough) is a respiratory illness with cold-like symptoms that progresses to a severe cough and serious complications more common in children under one year of age. Poliomyelitis (polio) is vira ...
18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotics KEY CONCEPT
... • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making ...
... • Bacteria cause disease by invading tissues or making ...
Chapter 21 Microbial Diseases of the Skin
... how proper and handling techniques can prevent transmission of foodborne pathogens. ...
... how proper and handling techniques can prevent transmission of foodborne pathogens. ...
AEROSOL TRANSMISSIBLE DISEASE STANDARD
... Surge Procedures • All DOPH employees are designated as disaster workers and are expected to respond in an emergency • Staff must complete NIMS/SEMS training and core public health competencies at level I, II or III as determined by supervisor/manager • Each branch is to maintain an emergency notif ...
... Surge Procedures • All DOPH employees are designated as disaster workers and are expected to respond in an emergency • Staff must complete NIMS/SEMS training and core public health competencies at level I, II or III as determined by supervisor/manager • Each branch is to maintain an emergency notif ...
Immunizations and Vaccine preventable childhood diseases
... Hepatitis is an acute inflammation of the liver. Acute viral Hepatitis (A,B,C,D,E,G) is the most common cause of hepatitis. . Hepatitis can also be caused by drugs (`including alcohol) chemicals and autoimmune liver disease . It is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in world wide. The ch ...
... Hepatitis is an acute inflammation of the liver. Acute viral Hepatitis (A,B,C,D,E,G) is the most common cause of hepatitis. . Hepatitis can also be caused by drugs (`including alcohol) chemicals and autoimmune liver disease . It is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in world wide. The ch ...
Presentation
... Surge Procedures • All DOPH employees are designated as disaster workers and are expected to respond in an emergency • Staff must complete NIMS/SEMS training and core public health competencies at level I, II or III as determined by supervisor/manager • Each branch is to maintain an emergency notif ...
... Surge Procedures • All DOPH employees are designated as disaster workers and are expected to respond in an emergency • Staff must complete NIMS/SEMS training and core public health competencies at level I, II or III as determined by supervisor/manager • Each branch is to maintain an emergency notif ...
Microbes and diseases: what to study-1
... Microbes and diseases: what to study-2 • 4. Diagnosis: How does the lab usually identify the causative agent? • 5. Treatment: antibiotics prescribed (or not- no cell wall, no penicillin) or other treatment (oral rehydration therapy for cholera). • 6. Prevention and control (stop the spread; condoms ...
... Microbes and diseases: what to study-2 • 4. Diagnosis: How does the lab usually identify the causative agent? • 5. Treatment: antibiotics prescribed (or not- no cell wall, no penicillin) or other treatment (oral rehydration therapy for cholera). • 6. Prevention and control (stop the spread; condoms ...
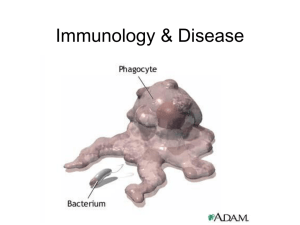
Lecture 7 Host Defense Against Infection
... Ex. sexually transmitted diseases and enteric diseases such as shigella, giardia and campylobacter. Ex. contact with soil - mycotic (fungal) diseases. ...
... Ex. sexually transmitted diseases and enteric diseases such as shigella, giardia and campylobacter. Ex. contact with soil - mycotic (fungal) diseases. ...
Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infectious Diseases
... A chain has the inhibitory activity against some vital function B chain binds to a receptor and promotes entry of the A chain Back Mode of action Inhibition of ...
... A chain has the inhibitory activity against some vital function B chain binds to a receptor and promotes entry of the A chain Back Mode of action Inhibition of ...
Chapter 6 Pathogenci Microorganisms
... Disk method: inhibition of growth around disk indicates sensitivity to antibiotic. BACTERIAL RESISTANCE TO ANTIBIOTICS Bacteria develop enzymes that inactivate antibiotic—for example, penicillinase. Bacteria develop other mechanisms that circumvent effects of antibiotics. ADVERSE EFFECTS OF ANTIBIOT ...
... Disk method: inhibition of growth around disk indicates sensitivity to antibiotic. BACTERIAL RESISTANCE TO ANTIBIOTICS Bacteria develop enzymes that inactivate antibiotic—for example, penicillinase. Bacteria develop other mechanisms that circumvent effects of antibiotics. ADVERSE EFFECTS OF ANTIBIOT ...
Strep Throat - Allegan County
... Strep throat is a contagious infection of the throat and tonsils caused by streptococcal bacteria. It can occur at any age, but is most prevalent among school-aged children. How is it spread? It is spread from person-to-person mainly by direct contact with infectious droplets from the upper respirat ...
... Strep throat is a contagious infection of the throat and tonsils caused by streptococcal bacteria. It can occur at any age, but is most prevalent among school-aged children. How is it spread? It is spread from person-to-person mainly by direct contact with infectious droplets from the upper respirat ...
The Black Death - AP European History at University High School
... • Year-round, far-reaching trade • Mongols controlled Eurasian landmass – facilitated long-distance trade (Silk Road) • “Great Famine” from 1315-1322 – Greater susceptibility to disease ...
... • Year-round, far-reaching trade • Mongols controlled Eurasian landmass – facilitated long-distance trade (Silk Road) • “Great Famine” from 1315-1322 – Greater susceptibility to disease ...
Ch.40 - Jamestown School District
... Bioterrorism involves treating pathogens to maximize their ability to infect & cause disease Anthrax is a disease common in cattleranching areas, not life-threatening The spores can be treated to be spread in the air & inhaled, producing a fatal infection ...
... Bioterrorism involves treating pathogens to maximize their ability to infect & cause disease Anthrax is a disease common in cattleranching areas, not life-threatening The spores can be treated to be spread in the air & inhaled, producing a fatal infection ...