The Immune System - Blue Valley School District
... inflammation fail. Phagocytic cells produce cytokines that initiate the acquired immune response. • Specialized lymphocytes called B and T-cells initiate the humoral and cellmediated responses, respectively. ...
... inflammation fail. Phagocytic cells produce cytokines that initiate the acquired immune response. • Specialized lymphocytes called B and T-cells initiate the humoral and cellmediated responses, respectively. ...
Langerhans` cells can take up antigen in the skin and migrate to
... The specialized regions of lymphoid tissue provide and environment where antigen-specific B cells can interact with armed helper T cells specific for the same antigen. ...
... The specialized regions of lymphoid tissue provide and environment where antigen-specific B cells can interact with armed helper T cells specific for the same antigen. ...
Allergic Reaction
... chicken pox so the next time you are exposed the immune system has a head start for a fast response. Note: Most severe: Type 1 reactions release IgE and are the fast acting anaphylaxis reactions. Note: Length of exposure is important but not to the same degree an frequency of exposure. Note: Mast ce ...
... chicken pox so the next time you are exposed the immune system has a head start for a fast response. Note: Most severe: Type 1 reactions release IgE and are the fast acting anaphylaxis reactions. Note: Length of exposure is important but not to the same degree an frequency of exposure. Note: Mast ce ...
Immunity web
... • The body has a number of defenses in the immune system that fight off pathogens • Some defenses are considered non-specific because they are not aimed at a specific pathogen • Help to prevent a disease • If disease does occur, this helps to slow the spread of the ...
... • The body has a number of defenses in the immune system that fight off pathogens • Some defenses are considered non-specific because they are not aimed at a specific pathogen • Help to prevent a disease • If disease does occur, this helps to slow the spread of the ...
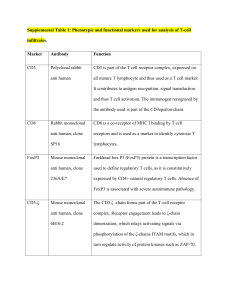
12967_2016_983_MOESM1_ESM
... all mature T lymphocyte and thus used as a T cell marker. It contributes to antigen recognition, signal transduction and thus T cell activation. The immunogen recognized by the antibody used is part of the CD3epsilon chain. ...
... all mature T lymphocyte and thus used as a T cell marker. It contributes to antigen recognition, signal transduction and thus T cell activation. The immunogen recognized by the antibody used is part of the CD3epsilon chain. ...
23. Frenkel lecture: FMD vaccine development - past and future
... Foot-and-mouth Disease Virus (FMDV) causes a highly contagious acute vesicular disease affecting a number of economically important animal species. Little is known about the interaction of the virus with cattle dendritic cells (DC). Development of a comprehensive protective T and B cell response req ...
... Foot-and-mouth Disease Virus (FMDV) causes a highly contagious acute vesicular disease affecting a number of economically important animal species. Little is known about the interaction of the virus with cattle dendritic cells (DC). Development of a comprehensive protective T and B cell response req ...
DISEASE - IMMUNE SYSTEM
... This results in white blood cells called phagocytes being transported to the site of the infection. The phagocytes ingest the pathogens and damaged tissue, resulting in the formation of puss. This usually kills the pathogen, but sometimes the infection gets to the lymphatic system and causes the lym ...
... This results in white blood cells called phagocytes being transported to the site of the infection. The phagocytes ingest the pathogens and damaged tissue, resulting in the formation of puss. This usually kills the pathogen, but sometimes the infection gets to the lymphatic system and causes the lym ...
Adaptive Immunity
... Process Ag by MHC II pathway but: B cells engulf Ag by receptor mediated endocytosis BCRs are surface antibodies anchored in plasma membrane Affinity of BCR for an Ag epitope is so high that the B cell can internalize the Ag at concentrations thousands of times smaller than needed for a macrophage C ...
... Process Ag by MHC II pathway but: B cells engulf Ag by receptor mediated endocytosis BCRs are surface antibodies anchored in plasma membrane Affinity of BCR for an Ag epitope is so high that the B cell can internalize the Ag at concentrations thousands of times smaller than needed for a macrophage C ...
Chapter 21 The Immune System
... • New Terms: – Antigen: usually a protein found on the cell membrane of the pathogen that has attacked the body – Antibody: protein (nonliving) that reacts w/ antigen to mark the pathogen allowing it to be recognized & then eaten by a phagocyte ...
... • New Terms: – Antigen: usually a protein found on the cell membrane of the pathogen that has attacked the body – Antibody: protein (nonliving) that reacts w/ antigen to mark the pathogen allowing it to be recognized & then eaten by a phagocyte ...
The Immune System Learning Module | Vaccine Education Center
... White Blood Cells Courtesy CDC, PHIL ...
... White Blood Cells Courtesy CDC, PHIL ...
The Immune System Learning Module | Vaccine Education Center
... White Blood Cells Courtesy CDC, PHIL ...
... White Blood Cells Courtesy CDC, PHIL ...
The Immune System - Children`s Hospital of Philadelphia
... White Blood Cells Courtesy CDC, PHIL ...
... White Blood Cells Courtesy CDC, PHIL ...
File
... MOLECULE ON A PATHOGEN OR A TOXIN. • ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES MAY INACTIVATE A PATHOGEN OR TOXIN OR RENDER IT MORE SUSCEPTIBLE TO PHAGOCYTOSIS. • IN OTHER CASES THE ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEX STIMULATES A RESPONSE WHICH RESULTS IN CELL LYSIS. • B LYMPHOCYTES ACTIVATED BY ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS AND ...
... MOLECULE ON A PATHOGEN OR A TOXIN. • ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEXES MAY INACTIVATE A PATHOGEN OR TOXIN OR RENDER IT MORE SUSCEPTIBLE TO PHAGOCYTOSIS. • IN OTHER CASES THE ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY COMPLEX STIMULATES A RESPONSE WHICH RESULTS IN CELL LYSIS. • B LYMPHOCYTES ACTIVATED BY ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS AND ...
Cells of the innate immune system
... • Secreted antibodies by plasma cells, 109 different specificities! • 5 classes (isotypes: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, IgE) • Effector functions eliminate antigen ...
... • Secreted antibodies by plasma cells, 109 different specificities! • 5 classes (isotypes: IgM, IgD, IgG, IgA, IgE) • Effector functions eliminate antigen ...
Non-specific Immune Response
... recognised as being non-self by the immune system and stimulates the immune response. (anti –antibody, gen-generator) – Usually proteins or glycoproteins on the cell plasma membrane or cell wall of invading pathogen. ...
... recognised as being non-self by the immune system and stimulates the immune response. (anti –antibody, gen-generator) – Usually proteins or glycoproteins on the cell plasma membrane or cell wall of invading pathogen. ...
File - The Building Blocks For Learning
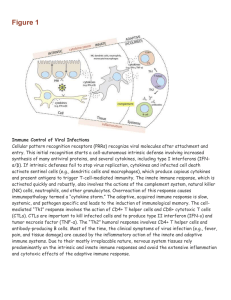
... Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNα/β). If intrinsic ...
... Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNα/β). If intrinsic ...
Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibodies
... forty years, scientists have been able to harness this knowledge to develop an array of biological assays that have since become essential in the modern molecular biology laboratory. Polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes of a given antigen and are produced by (1) immunizing a mammal – ofte ...
... forty years, scientists have been able to harness this knowledge to develop an array of biological assays that have since become essential in the modern molecular biology laboratory. Polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes of a given antigen and are produced by (1) immunizing a mammal – ofte ...
Induction of primary immune responses Induction of a primary
... Induction of primary immune responses Induction of a primary immune response begins when an antigen penetrates epithelial surfaces. It will eventually come into contact with macrophages or certain other classes of Antigen Presenting cells (APCs), which include B cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, La ...
... Induction of primary immune responses Induction of a primary immune response begins when an antigen penetrates epithelial surfaces. It will eventually come into contact with macrophages or certain other classes of Antigen Presenting cells (APCs), which include B cells, monocytes, dendritic cells, La ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.