... blood vessels walls and glomeruli leading to vasculitis and/or glomerulonephritis. • Less frequent is the situation when immune complexes deposit in the place of their formation (large complexes with excess of antibodies). They deposit in the place of their formation. • By activation of the compleme ...
Biology 12 Mr. Kruger - Kevan Kruger
... Biological Molecules & Compounds 1. Illustrate the structure of water molecules: Show bonding within and between molecules 2. Describe the important functions water plays in the body & the property of water they are related to 3. Describe the pH scale; Give examples of typical pH values in different ...
... Biological Molecules & Compounds 1. Illustrate the structure of water molecules: Show bonding within and between molecules 2. Describe the important functions water plays in the body & the property of water they are related to 3. Describe the pH scale; Give examples of typical pH values in different ...
biochemistry - Kuliah FTSL
... • Certain important pathways e.g. Glycolysis is found in almost all organisms. • All organisms use the same type of molecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids & nucleic acids. • Instructions for growth, reproduction and developments for each organism is encoded in their DNA ...
... • Certain important pathways e.g. Glycolysis is found in almost all organisms. • All organisms use the same type of molecules: carbohydrates, proteins, lipids & nucleic acids. • Instructions for growth, reproduction and developments for each organism is encoded in their DNA ...
What are Viruses? - Northwest ISD Moodle
... These antibodies will protect the baby for a short period of time following birth while its immune system develops. What Why doesn’t the mother just endocrine gland is pass on the WBCs that ...
... These antibodies will protect the baby for a short period of time following birth while its immune system develops. What Why doesn’t the mother just endocrine gland is pass on the WBCs that ...
Chapter 16: Lymphatic System and Immunity
... 9. A clone is a cell that is identical to the cell from which it was derived. 10. Different varieties of T cells and B cells have a particular type of antigen receptor on their cell membranes that can respond only to a specific antigen. E. T Cells and the Cellular Immune Response ...
... 9. A clone is a cell that is identical to the cell from which it was derived. 10. Different varieties of T cells and B cells have a particular type of antigen receptor on their cell membranes that can respond only to a specific antigen. E. T Cells and the Cellular Immune Response ...
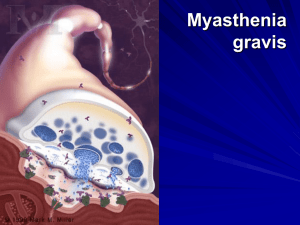
Myasthenia gravis
... differentiation and maturation of B cells and plasma cells. Although the mechanism(s) by which BAFF and its receptors help regulate B-cell function and tolerance is not known, it may play a significant role in the immune process involved in myasthenia gravis. Serum BAFF levels were found to be signi ...
... differentiation and maturation of B cells and plasma cells. Although the mechanism(s) by which BAFF and its receptors help regulate B-cell function and tolerance is not known, it may play a significant role in the immune process involved in myasthenia gravis. Serum BAFF levels were found to be signi ...
Brochure - ECFG21 Electro-Cell Fusion Generator
... Tough Antigens. Easy Hybridomas It’s not well understood, but certain antigens are just extraordinarily difficult to raise monoclonal antibodies. What is known is that challenging antigens seem to produce B-cells that are either quite rare, or very sensitive to hybridoma creation. For these antigens ...
... Tough Antigens. Easy Hybridomas It’s not well understood, but certain antigens are just extraordinarily difficult to raise monoclonal antibodies. What is known is that challenging antigens seem to produce B-cells that are either quite rare, or very sensitive to hybridoma creation. For these antigens ...
5echap24guidedreading
... 3. Which innate defense actually help prevent infection and which come into play only after infection has occurred? ...
... 3. Which innate defense actually help prevent infection and which come into play only after infection has occurred? ...
Six Grade Science Vocabulary
... The measure of the force with which air molecules push on a surface. The measure of the force with which air molecules push on a surface. A fan-shaped mass of rock material deposited by a stream when the slope of the land decreases sharply. Tiny, thin-walled, capillary-rich sac in the lungs where th ...
... The measure of the force with which air molecules push on a surface. The measure of the force with which air molecules push on a surface. A fan-shaped mass of rock material deposited by a stream when the slope of the land decreases sharply. Tiny, thin-walled, capillary-rich sac in the lungs where th ...
How to Interpret Hepatitis B Antibody and Viral Tests
... is capable of infecting others. When HBV replicates in the liver, it produces more surface antigen than is needed to generate new viruses. These excess surface antigens clump together in the bloodstream and are easily identified by lab tests. Laboratory tests can usually identify surface antigen abo ...
... is capable of infecting others. When HBV replicates in the liver, it produces more surface antigen than is needed to generate new viruses. These excess surface antigens clump together in the bloodstream and are easily identified by lab tests. Laboratory tests can usually identify surface antigen abo ...
MU Brno - Masaryk University
... distal interphalangeal joints) and then spreads to involve more proximal joints. The synovial membrane undergoes infiltration by lymphocytes (lymphoid follicles arise) causing villous hypertrophy. MHC class II molecules are strongly expressed on B cells and synovial lining cells. It is thought that ...
... distal interphalangeal joints) and then spreads to involve more proximal joints. The synovial membrane undergoes infiltration by lymphocytes (lymphoid follicles arise) causing villous hypertrophy. MHC class II molecules are strongly expressed on B cells and synovial lining cells. It is thought that ...
Abstract adult stem cells reduce autism behaviors in mouse model
... Injections of adult stem cells reduce autism behaviors in mouse model Sung Ji Ha and her colleagues at Seoul National University College of Medicine relieved autism behaviors in a mouse model of autism with injections of human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs). This type of stem cell is derived fr ...
... Injections of adult stem cells reduce autism behaviors in mouse model Sung Ji Ha and her colleagues at Seoul National University College of Medicine relieved autism behaviors in a mouse model of autism with injections of human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs). This type of stem cell is derived fr ...
Environmental microbiology File
... Observe or Count cells in known volume of sample microscopically Cells often hard to see, so some sort of staining procedure commonly used Two classes of stain: Specifically stain nucleic acids or proteins by adsorption onto these materials Stains that react (fluoresce) as a result of metabolic ...
... Observe or Count cells in known volume of sample microscopically Cells often hard to see, so some sort of staining procedure commonly used Two classes of stain: Specifically stain nucleic acids or proteins by adsorption onto these materials Stains that react (fluoresce) as a result of metabolic ...
"Immunity to Infection". In: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences (ELS)
... This antibody is produced before the B cell undergoes somatic hypermutation and is therefore of low affinity. However, IgM forms pentameric molecules, and the many antigen-binding sites confer high avidity instead. Because of the large size of the pentamers, IgM is primarily found in the blood. Here i ...
... This antibody is produced before the B cell undergoes somatic hypermutation and is therefore of low affinity. However, IgM forms pentameric molecules, and the many antigen-binding sites confer high avidity instead. Because of the large size of the pentamers, IgM is primarily found in the blood. Here i ...
Stage 1 Biology – Semester 1 Program 2 This program articulates
... Discussion on what distinguishes infectious disease from non-infectious diseases including genetic and lifestyle diseases Use examples of pathogens to describe how pathogens may be transmitted between hosts e.g. air = common cold (through droplets) or faeces = Salmonella or worms. Consider the lifec ...
... Discussion on what distinguishes infectious disease from non-infectious diseases including genetic and lifestyle diseases Use examples of pathogens to describe how pathogens may be transmitted between hosts e.g. air = common cold (through droplets) or faeces = Salmonella or worms. Consider the lifec ...
8a Lab Instructions
... Use the form on the next page to record whether each well was positive or negative. If the first well was yellow, that is positive for glucose, so go to the bottom of the form (see below image) and circle the number “2” under glucose. If that same well has a large gas bubble in it, circle the number ...
... Use the form on the next page to record whether each well was positive or negative. If the first well was yellow, that is positive for glucose, so go to the bottom of the form (see below image) and circle the number “2” under glucose. If that same well has a large gas bubble in it, circle the number ...
Plant cell Animal cell
... temperature (37oC) and pH. Enzymes have an active site and this allows it to join together with the substrate. Some proteins are hormones which are chemical messengers that travel to specific parts of the body. Antibodies are also proteins and these are specific molecules that attach to and destroy ...
... temperature (37oC) and pH. Enzymes have an active site and this allows it to join together with the substrate. Some proteins are hormones which are chemical messengers that travel to specific parts of the body. Antibodies are also proteins and these are specific molecules that attach to and destroy ...
Mammalian and Drosophila Blood: Minireview JAK of All Trades?
... place during development. Primitive hematopoiesis consists of embryonic red cells produced by the blood islands of the yolk sac. Definitive hematopoiesis (all lineages) originates from a dorsal (aortic/mesonephros/ gonad) compartment; it then switches to the fetal liver and ultimately to the bone ma ...
... place during development. Primitive hematopoiesis consists of embryonic red cells produced by the blood islands of the yolk sac. Definitive hematopoiesis (all lineages) originates from a dorsal (aortic/mesonephros/ gonad) compartment; it then switches to the fetal liver and ultimately to the bone ma ...
(b).
... **** does NOT need a living cell to reproduce food source What is needed for viruses to reproduce? a host – a living cell Explain ways that bacteria are helpful and harmful used in food (helpful) cause disease (harmful) Are antibiotics used to fight bacteria or viruses? bacteria ...
... **** does NOT need a living cell to reproduce food source What is needed for viruses to reproduce? a host – a living cell Explain ways that bacteria are helpful and harmful used in food (helpful) cause disease (harmful) Are antibiotics used to fight bacteria or viruses? bacteria ...
Current Clinical Therapies for HIV Remission
... • Are broad neutralizing antibodies -- bind virions and infected cells: DH542 (V3 glycan bnAb), CH557 (CD4bs bnAb), DH511-K3 (gp41 MPER bnAb) • Are ADCC mediating antibodies -- bind only infected cells: (7B2, gp41 ...
... • Are broad neutralizing antibodies -- bind virions and infected cells: DH542 (V3 glycan bnAb), CH557 (CD4bs bnAb), DH511-K3 (gp41 MPER bnAb) • Are ADCC mediating antibodies -- bind only infected cells: (7B2, gp41 ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.