Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 24 :
... returns it to the venous circulation maintain blood volume levels prevent interstitial fluid levels from rising out of control. ...
... returns it to the venous circulation maintain blood volume levels prevent interstitial fluid levels from rising out of control. ...
Lecture_5
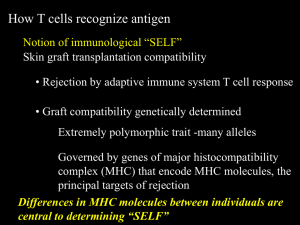
... Non-self peptides from pathogens, etc., are bound to MHC molecules and recognized by T cells because their peptides are partial mimics of self ...
... Non-self peptides from pathogens, etc., are bound to MHC molecules and recognized by T cells because their peptides are partial mimics of self ...
final round
... Exposed to the wrong type of blood for the first time, a person would a. have no immediate reaction. b. have an immediate, severe reaction. c. have an antibody response that would peak in approximately 10 days. d. have an antibody response that would ANSWER peak in 2 to 3 days. BACK TO GAME © 2012 P ...
... Exposed to the wrong type of blood for the first time, a person would a. have no immediate reaction. b. have an immediate, severe reaction. c. have an antibody response that would peak in approximately 10 days. d. have an antibody response that would ANSWER peak in 2 to 3 days. BACK TO GAME © 2012 P ...
HIV & AIDS
... This is why only certain body cells are damaged by certain viruses reflected in the symptoms associated with the particular infection • Ex: a cold virus locates the proteins on the mucus membrane cells in your nasal region and danger those cells • Results in swelling of the area and excessive mucus ...
... This is why only certain body cells are damaged by certain viruses reflected in the symptoms associated with the particular infection • Ex: a cold virus locates the proteins on the mucus membrane cells in your nasal region and danger those cells • Results in swelling of the area and excessive mucus ...
The Human Gene AHNAK Encodes a Large Phosphoprotein
... KIS4 recognized only the denatured form of AHNAK protein and gave no signal in immunofluorescence. In contrast, FEN2 reacted with both native and denatured protein, and could be used in immunofluorescence. Since immunoaffinity-purified KIS4 had a significantly higher titer than FEN2, we used KIS4 fo ...
... KIS4 recognized only the denatured form of AHNAK protein and gave no signal in immunofluorescence. In contrast, FEN2 reacted with both native and denatured protein, and could be used in immunofluorescence. Since immunoaffinity-purified KIS4 had a significantly higher titer than FEN2, we used KIS4 fo ...
Stem Cell Research - Evidence for God from Science
... provide tissue protection and directional guidance for axons after contusive spinal cord injury in rats. Exp. Neurol. 190:17-31. Li HJ, et. al. 2004. Transplantation of human umbilical cord stem cells improves neurological function recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. ...
... provide tissue protection and directional guidance for axons after contusive spinal cord injury in rats. Exp. Neurol. 190:17-31. Li HJ, et. al. 2004. Transplantation of human umbilical cord stem cells improves neurological function recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. ...
Low CD4+ T Cell Nadir Is an Independent Predictor of Lower HIV
... These data suggest that subjects with the lowest CD4+ T cell nadirs have variable recovery of their CD4+ T cell counts and that, even when there is recovery of CD4+ T cells, HIV-1– specific immune responses are not completely reconstituted. We found lower frequencies of IFN-g–secreting cells in resp ...
... These data suggest that subjects with the lowest CD4+ T cell nadirs have variable recovery of their CD4+ T cell counts and that, even when there is recovery of CD4+ T cells, HIV-1– specific immune responses are not completely reconstituted. We found lower frequencies of IFN-g–secreting cells in resp ...
Host defence mechanisms against bacterial aggression in
... to pathogenic microorganisms involves a complex network of cell and humoral components of the immune system, which interact with each other. The progression of gingivitis to periodontitis and the rate of progression of periodontitis cannot be explained solely by the presence of a microbiota. Presenc ...
... to pathogenic microorganisms involves a complex network of cell and humoral components of the immune system, which interact with each other. The progression of gingivitis to periodontitis and the rate of progression of periodontitis cannot be explained solely by the presence of a microbiota. Presenc ...
The Human Gene AHNAK Encodes a Large
... protein of exceptional size (c.a. 700 kD) and structure (7). AHNAK was first encountered as one of a group of eDNA clones isolated through subtractive cloning on the basis of differential expression in human tumors of neuroectodermal origin (6). Another eDNA clone from the subtraeted eDNA library wa ...
... protein of exceptional size (c.a. 700 kD) and structure (7). AHNAK was first encountered as one of a group of eDNA clones isolated through subtractive cloning on the basis of differential expression in human tumors of neuroectodermal origin (6). Another eDNA clone from the subtraeted eDNA library wa ...
Apoptosis in mouse J774 macrophages-a methodological study
... presence of Tubercular bacterium, because this macrophage cell death is one of an immune mediated defense against M. tuberculosis. Two types of control was there to obtain validity of the experiment with this J774 murine derived macrophage cell line. The positive control was exposed to different str ...
... presence of Tubercular bacterium, because this macrophage cell death is one of an immune mediated defense against M. tuberculosis. Two types of control was there to obtain validity of the experiment with this J774 murine derived macrophage cell line. The positive control was exposed to different str ...
D.Day 2011 Thursday, April 28th “What’s there for lunch today:
... environmental changes by modulating cellular functions at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. It has long been known that transcriptional regulation is crucial for this adaptation. However, translational regulation has recently been shown to be equally important, as it is rapid and ...
... environmental changes by modulating cellular functions at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. It has long been known that transcriptional regulation is crucial for this adaptation. However, translational regulation has recently been shown to be equally important, as it is rapid and ...
Different Nuclear Signals Are Activated by the B Cell
... transgenic mice provides a well-controlled model to explore the basis for positive versus negative signaling. When B cells that bear a uniform BCR specific for the antigen hen egg lysozyme (HEL) have matured in a mouse without being exposed to HEL, these naive cells make a positive initial response ...
... transgenic mice provides a well-controlled model to explore the basis for positive versus negative signaling. When B cells that bear a uniform BCR specific for the antigen hen egg lysozyme (HEL) have matured in a mouse without being exposed to HEL, these naive cells make a positive initial response ...
B-cell responses to vaccination at the extremes of age
... moreover, immature DC–T-cell interactions might also limit infant IgG responses. In addition, neonatal CD4+ T-cell responses differ from those elicited later in life, showing preferential T-helper-2-cell polarization (reviewed in ref. 10). This could either support or limit neonatal antibody respons ...
... moreover, immature DC–T-cell interactions might also limit infant IgG responses. In addition, neonatal CD4+ T-cell responses differ from those elicited later in life, showing preferential T-helper-2-cell polarization (reviewed in ref. 10). This could either support or limit neonatal antibody respons ...
AP CH12 - lambdinanatomyandphysiology
... RBCs carry oxygen from the lungs to the body cells Oxygen attaches to the hemoglobin. Four oxygen molecules bind to one hemoglobin molecule. RBCs carry carbon dioxide from body cells to the lungs. Carried three ways in the blood 1. 10% of the CO2 never enter the RBC- it is transported as a gas in th ...
... RBCs carry oxygen from the lungs to the body cells Oxygen attaches to the hemoglobin. Four oxygen molecules bind to one hemoglobin molecule. RBCs carry carbon dioxide from body cells to the lungs. Carried three ways in the blood 1. 10% of the CO2 never enter the RBC- it is transported as a gas in th ...
A-P Chapter 3
... 2. Endocytosis and Exocytosis a. In endocytosis, molecules that are too large to be transported by other means are engulfed by an invagination of the cell membrane and carried into the cell surrounded by a vesicle. b. Exocytosis is the reverse of endocytosis. ...
... 2. Endocytosis and Exocytosis a. In endocytosis, molecules that are too large to be transported by other means are engulfed by an invagination of the cell membrane and carried into the cell surrounded by a vesicle. b. Exocytosis is the reverse of endocytosis. ...
26492 Demonstrate and apply knowledge of the immune
... Specific defences are outlined in terms of the response to the presence of antigens. Range ...
... Specific defences are outlined in terms of the response to the presence of antigens. Range ...
Hematopoietic stem cells: insights into bone marrow biology
... Cancer stem cells Normal stem cells and cancer cells share the ability to self-renew and many signaling pathways involved in the regulaton of normal stem cell development are mutated or epigenetically activated in cancer. Leukemia stem cells: Transformed hematopoietic stem or commited progenitor ce ...
... Cancer stem cells Normal stem cells and cancer cells share the ability to self-renew and many signaling pathways involved in the regulaton of normal stem cell development are mutated or epigenetically activated in cancer. Leukemia stem cells: Transformed hematopoietic stem or commited progenitor ce ...
TLR4-dependent activation of dendritic cells by an HMGB1-derived peptide adjuvant
... dependent manner (Figure 1A), which plateaued between 10 and 30 minutes (Figure 1B). The control peptide, Hp121, which also corresponds to a sequence present in HMGB1 and has the same length, a similar charge, and isoelectric point as Hp91 was not taken up by DCs and uptake of a scrambled version of ...
... dependent manner (Figure 1A), which plateaued between 10 and 30 minutes (Figure 1B). The control peptide, Hp121, which also corresponds to a sequence present in HMGB1 and has the same length, a similar charge, and isoelectric point as Hp91 was not taken up by DCs and uptake of a scrambled version of ...
lecture1
... Metabolic pathways can be linear, e.g. glycolysis or can be cyclic, e.g. TCA. In general, the rate of catabolism is controlled not by the conc. of nutrients available in the environment of the cell, but by the cell’s need for energy in the form of ATP. Similarly, the rate of biosynthesis of cell com ...
... Metabolic pathways can be linear, e.g. glycolysis or can be cyclic, e.g. TCA. In general, the rate of catabolism is controlled not by the conc. of nutrients available in the environment of the cell, but by the cell’s need for energy in the form of ATP. Similarly, the rate of biosynthesis of cell com ...
Nanotoxicity and the importance of being earnest
... organs where they are deposited as discussed in several reports by Boczkowski et al. [12–14]. With regard to characterizing the immune effector mechanisms in action, it is now clear that the innate immune system in several ways is a major contributor to the response to nanomedicines. Important work ...
... organs where they are deposited as discussed in several reports by Boczkowski et al. [12–14]. With regard to characterizing the immune effector mechanisms in action, it is now clear that the innate immune system in several ways is a major contributor to the response to nanomedicines. Important work ...
the effect of low-dose naltrexone (ldn) on laboratory immune
... LESSENING SCORES QUANTITATIVELY FOR A t-TEST SIGNIFICANCE ON THE 95% LEVEL—THE ONLY SUCH QUANTITATIVE RESULT FOR THE GROUP OF CHILDREN. THIS MEANS WE CAN SAY THAT LDN SIGNIFICANTLY INCREASES THIS MARKER AT THE 95% CONFIDENCE LEVEL. THE AVERAGE INCREASE WAS 23%. TOTAL T3: ALL CHILDREN REMAINED WITHIN ...
... LESSENING SCORES QUANTITATIVELY FOR A t-TEST SIGNIFICANCE ON THE 95% LEVEL—THE ONLY SUCH QUANTITATIVE RESULT FOR THE GROUP OF CHILDREN. THIS MEANS WE CAN SAY THAT LDN SIGNIFICANTLY INCREASES THIS MARKER AT THE 95% CONFIDENCE LEVEL. THE AVERAGE INCREASE WAS 23%. TOTAL T3: ALL CHILDREN REMAINED WITHIN ...
Thai Journal of Veterinary Medicine
... because their culture is limited by the development of infectious diseases. As invertebrates, shrimp’s natural immunity acts as a fast and efficient defence mechanism against the pathogens. Their immune system involve hemocytes (for encapsulation, nodule formation and phagocytosis), several plasma c ...
... because their culture is limited by the development of infectious diseases. As invertebrates, shrimp’s natural immunity acts as a fast and efficient defence mechanism against the pathogens. Their immune system involve hemocytes (for encapsulation, nodule formation and phagocytosis), several plasma c ...
chapter 5 complement
... restored its capacity to specifically lyse cholera targets. Thus, the ability of immune serum to lyse bacteria depends not only on antibodies specific for C. vibrio, but also on a non-specific heat-labile substance found in normal serum. This substance became known as COMPLEMENT, since it "complemen ...
... restored its capacity to specifically lyse cholera targets. Thus, the ability of immune serum to lyse bacteria depends not only on antibodies specific for C. vibrio, but also on a non-specific heat-labile substance found in normal serum. This substance became known as COMPLEMENT, since it "complemen ...
Polyclonal B cell response
Polyclonal B cell response is a natural mode of immune response exhibited by the adaptive immune system of mammals. It ensures that a single antigen is recognized and attacked through its overlapping parts, called epitopes, by multiple clones of B cell.In the course of normal immune response, parts of pathogens (e.g. bacteria) are recognized by the immune system as foreign (non-self), and eliminated or effectively neutralized to reduce their potential damage. Such a recognizable substance is called an antigen. The immune system may respond in multiple ways to an antigen; a key feature of this response is the production of antibodies by B cells (or B lymphocytes) involving an arm of the immune system known as humoral immunity. The antibodies are soluble and do not require direct cell-to-cell contact between the pathogen and the B-cell to function.Antigens can be large and complex substances, and any single antibody can only bind to a small, specific area on the antigen. Consequently, an effective immune response often involves the production of many different antibodies by many different B cells against the same antigen. Hence the term ""polyclonal"", which derives from the words poly, meaning many, and clones (""Klon""=Greek for sprout or twig); a clone is a group of cells arising from a common ""mother"" cell. The antibodies thus produced in a polyclonal response are known as polyclonal antibodies. The heterogeneous polyclonal antibodies are distinct from monoclonal antibody molecules, which are identical and react against a single epitope only, i.e., are more specific.Although the polyclonal response confers advantages on the immune system, in particular, greater probability of reacting against pathogens, it also increases chances of developing certain autoimmune diseases resulting from the reaction of the immune system against native molecules produced within the host.