CHAPTER 4 | Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
... The oxidation number for hydrogen in these species is +1. The oxidation number for nitrogen will be negative and can be determined by: Oxidation number on N = charge on species – (number of H atoms) (+1) Solve (a) N2: oxidation number on N = 0 – 0(+1) = 0 (b) N2H4: oxidation number on N = 0 – 4(+1 ...
... The oxidation number for hydrogen in these species is +1. The oxidation number for nitrogen will be negative and can be determined by: Oxidation number on N = charge on species – (number of H atoms) (+1) Solve (a) N2: oxidation number on N = 0 – 0(+1) = 0 (b) N2H4: oxidation number on N = 0 – 4(+1 ...
Introduction to Chemical Reactions
... The reactants are used up in forming the product The arrow shows the direction of the reaction ...
... The reactants are used up in forming the product The arrow shows the direction of the reaction ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2006-2007
... a) __ FeCl3 + __ NaOH → __ Fe(OH)3 + __ NaCl b) __ Al + __ O2 → __ Al2O3 c) __ C2H2 + __ O2 → __ CO2 + __ H2O d) __ Na + __ H2O → __ NaOH + __ H2 e) __ KClO3 → __ KCl + __ O2 4. Know how to predict products as in the problems below. Example: a) Al + N2 → b) H2O → c) Ca + H2O → d) Cl2 + NaBr → e) FeS ...
... a) __ FeCl3 + __ NaOH → __ Fe(OH)3 + __ NaCl b) __ Al + __ O2 → __ Al2O3 c) __ C2H2 + __ O2 → __ CO2 + __ H2O d) __ Na + __ H2O → __ NaOH + __ H2 e) __ KClO3 → __ KCl + __ O2 4. Know how to predict products as in the problems below. Example: a) Al + N2 → b) H2O → c) Ca + H2O → d) Cl2 + NaBr → e) FeS ...
2009 U. S. NATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD
... b. Account for the fact that standard enthalpies of formation of compounds at 25˚C may be either positive or negative. c. Explain why all elements and compounds have positive S˚ values at 25˚C. d. Give an example of a chemical species that does not have a positive S˚ value at 25 ˚C and explain why i ...
... b. Account for the fact that standard enthalpies of formation of compounds at 25˚C may be either positive or negative. c. Explain why all elements and compounds have positive S˚ values at 25˚C. d. Give an example of a chemical species that does not have a positive S˚ value at 25 ˚C and explain why i ...
AP® Chemistry 2009 Free-Response Questions - AP Central
... mass of a sealed 843 mL rigid flask that contained dry air. The student then flushed the flask with the unknown gas, resealed it, and measured the mass again. Both the air and the unknown gas were at 23.0°C and 750. torr. The data for the experiment are shown in the table below. Volume of sealed fla ...
... mass of a sealed 843 mL rigid flask that contained dry air. The student then flushed the flask with the unknown gas, resealed it, and measured the mass again. Both the air and the unknown gas were at 23.0°C and 750. torr. The data for the experiment are shown in the table below. Volume of sealed fla ...
this PDF file
... and amount of the solid and gaseous species present in the system. These can be determined from the calculation of the thermodynamic equilibrium (i.e. the equilibrium partial pressures of the system species) at a given set of processing conditions such as reaction temperature, pressure and reactant ...
... and amount of the solid and gaseous species present in the system. These can be determined from the calculation of the thermodynamic equilibrium (i.e. the equilibrium partial pressures of the system species) at a given set of processing conditions such as reaction temperature, pressure and reactant ...
Final Exam Practice 2016 (MC)
... d) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should instead be a double bond with one of oxygen’s lone pairs. 23. The molecules CO2 and SO2 have very similar formulas yet make a different shape. What is different about their Lewis structures that give them a different sha ...
... d) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should instead be a double bond with one of oxygen’s lone pairs. 23. The molecules CO2 and SO2 have very similar formulas yet make a different shape. What is different about their Lewis structures that give them a different sha ...
Exam 3 - Canvas by Instructure
... 5. The next step in the synthesis of nitric acid involves nitrogen monoxide being oxidized to nitrogen dioxide: 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) If this reaction is performed inside a rigid container under constant temperature conditions, how will the pressure inside the reaction vessel change? A. The pr ...
... 5. The next step in the synthesis of nitric acid involves nitrogen monoxide being oxidized to nitrogen dioxide: 2 NO(g) + O2(g) → 2 NO2(g) If this reaction is performed inside a rigid container under constant temperature conditions, how will the pressure inside the reaction vessel change? A. The pr ...
1.0 basic concepts
... • This means that water, H2O cannot be formed, therefore H2 is the product • If you look at the reactants in (a) – (d), you’ll notice that the metal has oxygen present. • This means that water, H2O can be formed, therefore H2O is the product Carbon dioxide or not • If you look at the reactants in (d ...
... • This means that water, H2O cannot be formed, therefore H2 is the product • If you look at the reactants in (a) – (d), you’ll notice that the metal has oxygen present. • This means that water, H2O can be formed, therefore H2O is the product Carbon dioxide or not • If you look at the reactants in (d ...
2.4 Chemical equilibria
... At equilibrium, the rate of each reaction will be the same. What effect will this have on the amounts of A, B, C and D? Remember both reactions are still happening, but because they are doing so at the same rate the amounts of reactants and products remain constant. (It’s a bit like going up an esca ...
... At equilibrium, the rate of each reaction will be the same. What effect will this have on the amounts of A, B, C and D? Remember both reactions are still happening, but because they are doing so at the same rate the amounts of reactants and products remain constant. (It’s a bit like going up an esca ...
Review Package KCI 2017 Sem 1
... the catalyst can help break the bonds in the reactant particles, provide a surface for the necessary collisions, and allow the reactants’ atoms to recombine in new ways catalysts are involved in the reaction mechanism at some point, but are regenerated before the reaction is complete ...
... the catalyst can help break the bonds in the reactant particles, provide a surface for the necessary collisions, and allow the reactants’ atoms to recombine in new ways catalysts are involved in the reaction mechanism at some point, but are regenerated before the reaction is complete ...
+ H 2
... • Na2CO3 + HCl ? o Na+1 combines with Cl-1 to form NaCl o H+ combines with CO32- to form H2CO3 o Na2CO3 + 2HCl 2NaCl + H2CO3 • this reaction does not normally happen this way • It is a metal carbonate in a strong acid, so… o Na2CO3+2HCl--> 2NaCl+CO2+H20 ...
... • Na2CO3 + HCl ? o Na+1 combines with Cl-1 to form NaCl o H+ combines with CO32- to form H2CO3 o Na2CO3 + 2HCl 2NaCl + H2CO3 • this reaction does not normally happen this way • It is a metal carbonate in a strong acid, so… o Na2CO3+2HCl--> 2NaCl+CO2+H20 ...
File
... Cations (+) and Anions (-): the cations will be attracted to the negative electrode & the anions will be attracted to the positive electrode. This movement sets up an electric current that is equivalent to the flow of electrons along a metal wire. ...
... Cations (+) and Anions (-): the cations will be attracted to the negative electrode & the anions will be attracted to the positive electrode. This movement sets up an electric current that is equivalent to the flow of electrons along a metal wire. ...
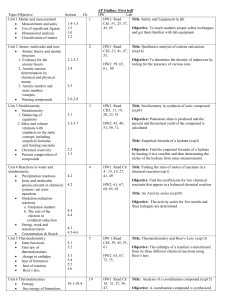
Topic/Objective - cloudfront.net
... Objective: The total rate law for the oxidation of iodide by bromate ion in the presence of an acid is determined. The order for each of the reactants is found by varying the concentration of each reactant individually. Once the rate law is determined then the rate law is calculated and the activati ...
... Objective: The total rate law for the oxidation of iodide by bromate ion in the presence of an acid is determined. The order for each of the reactants is found by varying the concentration of each reactant individually. Once the rate law is determined then the rate law is calculated and the activati ...
COVENANT UNIVERSITY College of Science and Technology
... A selection of experiments designed to provide illustrations of the important parts of the lectures in CHM226 Course. The experiments will afford the students the opportunity to develop their quantitative and analytical skills. Topics include chemical equilibria, kinetics of iodination of acetone, d ...
... A selection of experiments designed to provide illustrations of the important parts of the lectures in CHM226 Course. The experiments will afford the students the opportunity to develop their quantitative and analytical skills. Topics include chemical equilibria, kinetics of iodination of acetone, d ...