Stoichiometry and Balanced Reactions Chemical Accounting
... • Reactions are balanced on a per-molecule (or per-atom) basis – But individual molecules are fairly impractical to handle! – Fortunately, stoichiometric ratios apply for larger numbers of molecules (dozens, hundreds, millions…and more – In the laboratory, it is more practical to do things in terms ...
... • Reactions are balanced on a per-molecule (or per-atom) basis – But individual molecules are fairly impractical to handle! – Fortunately, stoichiometric ratios apply for larger numbers of molecules (dozens, hundreds, millions…and more – In the laboratory, it is more practical to do things in terms ...
Chapter 8
... form different substances. • The substances entering the reaction are called reactants. • The substances formed in the reaction are called products. • During reactions, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed. ...
... form different substances. • The substances entering the reaction are called reactants. • The substances formed in the reaction are called products. • During reactions, chemical bonds are broken and new bonds are formed. ...
Empirical Formula Lab
... no more HCl left • What remains is your zinc chloride product • Zinc chloride has a special property that allows it to “take in” water from the air so it’s constantly “soupy” • We don’t want this water involved in our product… ...
... no more HCl left • What remains is your zinc chloride product • Zinc chloride has a special property that allows it to “take in” water from the air so it’s constantly “soupy” • We don’t want this water involved in our product… ...
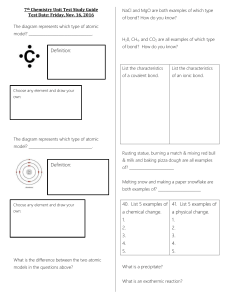
Review 3
... 1. State Charles’s Law, and be able to apply the law to changes given. 2. Know the ideal gas law, and what each symbol stands for. 3. Be able to apply the gas laws to a certain change of conditions. 4. State Boyle’s Law, and be able to apply the law to changes given. 5. Be able to solve an ideal gas ...
... 1. State Charles’s Law, and be able to apply the law to changes given. 2. Know the ideal gas law, and what each symbol stands for. 3. Be able to apply the gas laws to a certain change of conditions. 4. State Boyle’s Law, and be able to apply the law to changes given. 5. Be able to solve an ideal gas ...
AS Paper 1 Practice Paper 16 - A
... The equation for the reaction between magnesium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is given below. MgCO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O + CO2 When 75.0 cm3 of 0.500 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid were added to 1.25 g of impure MgCO3 some acid was left unreacted. This unreacted acid required 21.6 cm3 of a 0.500 mol d ...
... The equation for the reaction between magnesium carbonate and hydrochloric acid is given below. MgCO3 + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2O + CO2 When 75.0 cm3 of 0.500 mol dm–3 hydrochloric acid were added to 1.25 g of impure MgCO3 some acid was left unreacted. This unreacted acid required 21.6 cm3 of a 0.500 mol d ...
File
... 5. In an equilibrium reaction with a Keq of 1 x108 a. reactants are favored. c. products are favored. b. the reaction is nonspontaneous. d. the reaction is exothermic. 6. What is the effect of adding more CO2 to the following equilibrium reaction? CO2 + H2O↔ H2CO3 a. More H2CO3 is produced. b. More ...
... 5. In an equilibrium reaction with a Keq of 1 x108 a. reactants are favored. c. products are favored. b. the reaction is nonspontaneous. d. the reaction is exothermic. 6. What is the effect of adding more CO2 to the following equilibrium reaction? CO2 + H2O↔ H2CO3 a. More H2CO3 is produced. b. More ...
Factors that affect the rate of reactions
... Surface area is a measure of how much area is exposed. If the surface area is large, then there is a better chance of hitting another reactant so the reaction rate will be high. The greater the surface area the higher the reaction rate. Surface area ONLY affect reactants that are in DIFFERENT phases ...
... Surface area is a measure of how much area is exposed. If the surface area is large, then there is a better chance of hitting another reactant so the reaction rate will be high. The greater the surface area the higher the reaction rate. Surface area ONLY affect reactants that are in DIFFERENT phases ...
Chapter 2: Chemical Reactions Section 1
... reaction in which energy is absorbed – More energy is required to break the bond of the reactants than is released by the formation of the new products – Examples: baking soda and vinegar gets cooler when ...
... reaction in which energy is absorbed – More energy is required to break the bond of the reactants than is released by the formation of the new products – Examples: baking soda and vinegar gets cooler when ...
Chemical Synthesis (sat6)
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... 1. Oxidation number of an element in its elementary or uncombined state is 0. 2. In an ionic compound, the oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the same as its charge. 3. Certain elements almost always have the same oxidation number. a. Group 1A elements = +1 b. Group 2A elements = +2 c. Group 3A ...
... 1. Oxidation number of an element in its elementary or uncombined state is 0. 2. In an ionic compound, the oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the same as its charge. 3. Certain elements almost always have the same oxidation number. a. Group 1A elements = +1 b. Group 2A elements = +2 c. Group 3A ...
PAP Chemistry - Fall Final Review
... 47. What is a subscript? What is a coefficient? Where are the products and reactants located in a chemical reaction? 48. Be able to balance chemical equations. a. Al4C3 + H2O CH4 + Al(OH)3 b. How many moles of hydrogen ions are present in Al(OH)3 c. How many moles of oxygen atoms are present in C ...
... 47. What is a subscript? What is a coefficient? Where are the products and reactants located in a chemical reaction? 48. Be able to balance chemical equations. a. Al4C3 + H2O CH4 + Al(OH)3 b. How many moles of hydrogen ions are present in Al(OH)3 c. How many moles of oxygen atoms are present in C ...
CH225h - Oregon State chemistry
... The rms speeds are inversely proportional to the square root of mass, so the ratio of Ar speed / He speed is ≈ sqrt (4/40) ≈ 0.3 (b) If Ar, He, and Xe are mixed with equal partial pressures in a gas sample, which will effuse most rapidly through a small hole in the container ? Explain briefly. He. E ...
... The rms speeds are inversely proportional to the square root of mass, so the ratio of Ar speed / He speed is ≈ sqrt (4/40) ≈ 0.3 (b) If Ar, He, and Xe are mixed with equal partial pressures in a gas sample, which will effuse most rapidly through a small hole in the container ? Explain briefly. He. E ...
Class: 11 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Equilibrium No. of
... 7. Le chatelier’s principle is applicable only to a A. homogeneous reaction B. heterogeneous reaction C. system in equilibrium D. irreversible reaction Sol: C ...
... 7. Le chatelier’s principle is applicable only to a A. homogeneous reaction B. heterogeneous reaction C. system in equilibrium D. irreversible reaction Sol: C ...