Connective tissue mast cells
... (IL-2, 12, IFN, GM-CSF, lymphotoxin) Cytokines with anti-virus effect (IFN-, IFN- , IFN- ) ...
... (IL-2, 12, IFN, GM-CSF, lymphotoxin) Cytokines with anti-virus effect (IFN-, IFN- , IFN- ) ...
Rethinking Cancer
... Are little understood and clinically insuperable An even Greater Challenge is Posed by the Cancer–Immunity Interplay ...
... Are little understood and clinically insuperable An even Greater Challenge is Posed by the Cancer–Immunity Interplay ...
Kiadis Pharma`s Orphan Drug Designation for ATIR101
... Kiadis Pharma’s Orphan Drug Designation for ATIR101™ further expanded to include treatment in a hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 30, 2016 – Kiadis Pharma N.V. (“Kiadis Pharma” or the “Company”) (Euronext Amsterdam and Brussels: KDS), a clinical stage biopharma ...
... Kiadis Pharma’s Orphan Drug Designation for ATIR101™ further expanded to include treatment in a hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 30, 2016 – Kiadis Pharma N.V. (“Kiadis Pharma” or the “Company”) (Euronext Amsterdam and Brussels: KDS), a clinical stage biopharma ...
Materials and Methods - Welcome to the Biology Department
... (buttermilk, cheese, etc…) • Noninvasive (can’t multiply in vivo), nonpathogenic • Can serve as an antigen delivery vehicle ...
... (buttermilk, cheese, etc…) • Noninvasive (can’t multiply in vivo), nonpathogenic • Can serve as an antigen delivery vehicle ...
Key Concepts in B cell Activation-I
... Lymphoid organs, whereby encounter Ag presented by APCs (eg. DCs) and then become activated. 3. T-cell activation requires Two Signals: - Primary Signal-TCR/CD3 –Ag/MHC complex - Second Signal (Costimulatory)- Other T cell surface molecules (ex. CD28) interact with ligands from APCs. ...
... Lymphoid organs, whereby encounter Ag presented by APCs (eg. DCs) and then become activated. 3. T-cell activation requires Two Signals: - Primary Signal-TCR/CD3 –Ag/MHC complex - Second Signal (Costimulatory)- Other T cell surface molecules (ex. CD28) interact with ligands from APCs. ...
Unit 4: Infectious disease
... – Bacteria single-celled organisms that can live outside of the body – Fungi – Parasites (ex. Tapeworms, amoeba) • Survive by compromising host ...
... – Bacteria single-celled organisms that can live outside of the body – Fungi – Parasites (ex. Tapeworms, amoeba) • Survive by compromising host ...
T cell receptors
... Marcus’ T cells have CD4 and CD8. However, they have no CD3. Without CD3, the T cells cannot be activated. Marcus’ is scheduled for a bone marrow ...
... Marcus’ T cells have CD4 and CD8. However, they have no CD3. Without CD3, the T cells cannot be activated. Marcus’ is scheduled for a bone marrow ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Overview of the Immune Response
... Phagocytes have receptors that directly recognize bacteria and lead to phagocytosis, activation, microbicidal activity and cytokine ...
... Phagocytes have receptors that directly recognize bacteria and lead to phagocytosis, activation, microbicidal activity and cytokine ...
Basic Body Systems Unit 6 Immune System Lecture
... • Eventually there are so many new viruses made that the host membrane ruptures • All the viruses escape to attack new cells • Usually the host cell dies at this point • Some viruses , like HIV, don’t kill the host as the new viruses are released ...
... • Eventually there are so many new viruses made that the host membrane ruptures • All the viruses escape to attack new cells • Usually the host cell dies at this point • Some viruses , like HIV, don’t kill the host as the new viruses are released ...
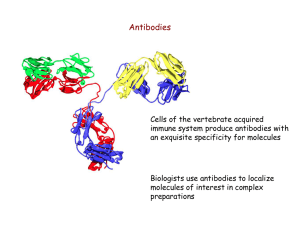
antibodies
... Lymphocytes can generate millions of different antigen binding sites by DNA rearrangement and mutation - processes restricted to immune cells!! Antigens bind hyper-variable regions at the tips of Fab fragments antigen binding has been compared to a lock-andkey fit (complementary surfaces) ...
... Lymphocytes can generate millions of different antigen binding sites by DNA rearrangement and mutation - processes restricted to immune cells!! Antigens bind hyper-variable regions at the tips of Fab fragments antigen binding has been compared to a lock-andkey fit (complementary surfaces) ...
6mb
... It must differentiate different forms of non-self Antigen (Ag)- the molecule or structure against which the immune response is directed The immune response only sees bio-organic molecules The antigenic universe is incredibly diverse This diversity must be overcome by the immune response ...
... It must differentiate different forms of non-self Antigen (Ag)- the molecule or structure against which the immune response is directed The immune response only sees bio-organic molecules The antigenic universe is incredibly diverse This diversity must be overcome by the immune response ...
Your Immune System - The School District of Palm Beach County
... Another kind of white blood cell makes chemicals called antibodies. For every type of microbe that invades the body, a special type of antibody is produced. The first time a germ gets into your body it may make you sick. Your body will detect the invader and produce antibodies for that specific type ...
... Another kind of white blood cell makes chemicals called antibodies. For every type of microbe that invades the body, a special type of antibody is produced. The first time a germ gets into your body it may make you sick. Your body will detect the invader and produce antibodies for that specific type ...
03-390 Immunology Exam I - 2014 Name:_____________________
... Choice B: How would a deficiency in any of the following: DAF, MCP, factor I, factor H, affect the well-being of an individual? Choice C: In what way(s) does the complement pathway lead to/cause the elimination of pathogens? Choice A: C4 is only required for the lectin and classical pathway, it is n ...
... Choice B: How would a deficiency in any of the following: DAF, MCP, factor I, factor H, affect the well-being of an individual? Choice C: In what way(s) does the complement pathway lead to/cause the elimination of pathogens? Choice A: C4 is only required for the lectin and classical pathway, it is n ...
BIOC39H – Immunology Winter 2016 Course Syllabus
... and virology. The concepts and methods of these disciplines are fundamental to the study of the immune system and as such, this course aims to provide students with an appreciation of the interdisciplinary relationship between these subjects. This course is designed to introduce the molecular and ce ...
... and virology. The concepts and methods of these disciplines are fundamental to the study of the immune system and as such, this course aims to provide students with an appreciation of the interdisciplinary relationship between these subjects. This course is designed to introduce the molecular and ce ...
TITLE of LESSON Immune system – Components of the immune
... Students discover the components of the immune system, regarding in overview the lymphatic system an in detail the structrure and function of a lymph node. Phagocytosis of white blood cells are identified as nonspecific immune response. The learning resources facilitate differentiated and collaborat ...
... Students discover the components of the immune system, regarding in overview the lymphatic system an in detail the structrure and function of a lymph node. Phagocytosis of white blood cells are identified as nonspecific immune response. The learning resources facilitate differentiated and collaborat ...
Sarah immunity ppt
... Inactivate antigens by: ◦ complement fixation - proteins bind to foreign cell and causing it to break apart ◦ neutralization – block harmful effects of toxins released from bacteria or virus ◦ agglutination – antibodies can bind to more than one antigen at a time and they can clump foreign cells tog ...
... Inactivate antigens by: ◦ complement fixation - proteins bind to foreign cell and causing it to break apart ◦ neutralization – block harmful effects of toxins released from bacteria or virus ◦ agglutination – antibodies can bind to more than one antigen at a time and they can clump foreign cells tog ...
Receptors
... • present on host cells or in soluble forme (proteins of complement • recognise different motives (patterns) present on microbes and not on self cells PAMP – pathogen ...
... • present on host cells or in soluble forme (proteins of complement • recognise different motives (patterns) present on microbes and not on self cells PAMP – pathogen ...
Autoimmunity
... b.____ Through the process of intermolecular epitope spreading, a B-cell specific for one epitope can potentially activate a T-Cell with a TCR for a different epitope. c. ____ ‘Molecular mimicry’ results from infections by two closely related bacterial species. d.____ The similarity between SLE and ...
... b.____ Through the process of intermolecular epitope spreading, a B-cell specific for one epitope can potentially activate a T-Cell with a TCR for a different epitope. c. ____ ‘Molecular mimicry’ results from infections by two closely related bacterial species. d.____ The similarity between SLE and ...
1 Defenders of the Body 2 Nonspecific Defenses 3 Specific
... • Helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells • Active an memory types of both cells are produced – Spurs activation of regulatory T cells • Limits immune system’s response • Protects body’s tissues from damage ...
... • Helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells • Active an memory types of both cells are produced – Spurs activation of regulatory T cells • Limits immune system’s response • Protects body’s tissues from damage ...
Novel treatment strategies for antibody
... cytokine production, than on the modest reduction of autoantibody levels. Importantly, at present, placebo-controlled trials proving the efficacy of rituximab in classical antibody-mediated diseases such as SLE are still warranted. CD22 is another B-cell antigen that can be therapeutically targeted. ...
... cytokine production, than on the modest reduction of autoantibody levels. Importantly, at present, placebo-controlled trials proving the efficacy of rituximab in classical antibody-mediated diseases such as SLE are still warranted. CD22 is another B-cell antigen that can be therapeutically targeted. ...
pathology-tumor_LÁ
... • Tolerance induction – Tumor antigens do exist – Recognized primarily by T lymphocytes – Induce tolerance ...
... • Tolerance induction – Tumor antigens do exist – Recognized primarily by T lymphocytes – Induce tolerance ...
Cancer immunotherapy

Cancer immunotherapy (immuno-oncology) is the use of the immune system to treat cancer. Immunotherapies fall into three main groups: cellular, antibody and cytokine. They exploit the fact that cancer cells often have subtly different molecules on their surface that can be detected by the immune system. These molecules, known as cancer antigens, are most commonly proteins, but also include molecules such as carbohydrates. Immunotherapy is used to provoke the immune system into attacking the tumor cells by using these antigens as targets.Antibody therapies are the most successful immunotherapy, treating a wide range of cancers. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that bind to a target antigen on the cell surface. In normal physiology the immune system uses them to fight pathogens. Each antibody is specific to one or a few proteins. Those that bind to cancer antigens are used to treat cancer. Cell surface receptors are common targets for antibody therapies and include the CD20, CD274, and CD279. Once bound to a cancer antigen, antibodies can induce antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, activate the complement system, or prevent a receptor from interacting with its ligand, all of which can lead to cell death. Multiple antibodies are approved to treat cancer, including Alemtuzumab, Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, Ofatumumab, and Rituximab.Cellular therapies, also known as cancer vaccines, usually involve the removal of immune cells from the blood or from a tumor. Immune cells specific for the tumor are activated, cultured and returned to the patient where the immune cells attack the cancer. Cell types that can be used in this way are natural killer cells, lymphokine-activated killer cells, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells. The only cell-based therapy approved in the US is Dendreon's Provenge, for the treatment of prostate cancer.Interleukin-2 and interferon-α are examples of cytokines, proteins that regulate and coordinate the behaviour of the immune system. They have the ability to enhance anti-tumor activity and thus can be used as cancer treatments. Interferon-α is used in the treatment of hairy-cell leukaemia, AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma, follicular lymphoma, chronic myeloid leukaemia and malignant melanoma. Interleukin-2 is used in the treatment of malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.