In vitro effects of different innate-immune stimulants on
... In addition, we tried to acquire an antibody for Atlantic salmon cathelicidin by immunization of rabbit with synthetic peptides derived from cathelicidin. Specific cathelicidin antibodies were not obtained in this experiment. The findings might contribute to the development of alternatives to the cl ...
... In addition, we tried to acquire an antibody for Atlantic salmon cathelicidin by immunization of rabbit with synthetic peptides derived from cathelicidin. Specific cathelicidin antibodies were not obtained in this experiment. The findings might contribute to the development of alternatives to the cl ...
TREM2-Transduced Myeloid Precursors Mediate Nervous Tissue
... that there is a continuous and lifelong turnover of perivascular brain macrophages replenished by bone marrow– derived cells. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that bone marrow cells are recruited to sites of axonal degeneration [4,5] or to beta-amyloid depositions in Alzheimer disease animal mo ...
... that there is a continuous and lifelong turnover of perivascular brain macrophages replenished by bone marrow– derived cells. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that bone marrow cells are recruited to sites of axonal degeneration [4,5] or to beta-amyloid depositions in Alzheimer disease animal mo ...
Inflammation
... formation, a reversible process (see Fig. 2-4B). This break in the endothelial barrier leads to extravasation (leakage) of intravascular fluids into the extravascular space. Mild direct injury to the endothelium results in a biphasic response: an early change in permeability occurs within 30 minutes ...
... formation, a reversible process (see Fig. 2-4B). This break in the endothelial barrier leads to extravasation (leakage) of intravascular fluids into the extravascular space. Mild direct injury to the endothelium results in a biphasic response: an early change in permeability occurs within 30 minutes ...
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Effector Function in a Murine Model of
... Mucosal immune homeostasis requires a balanced interplay between effector and regulatory T cells (Tregs). Naive T cells differentiate into effector cells that are divided into three distinctive types, Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells, depending on the type of cytokines secreted. The fate of T cell different ...
... Mucosal immune homeostasis requires a balanced interplay between effector and regulatory T cells (Tregs). Naive T cells differentiate into effector cells that are divided into three distinctive types, Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells, depending on the type of cytokines secreted. The fate of T cell different ...
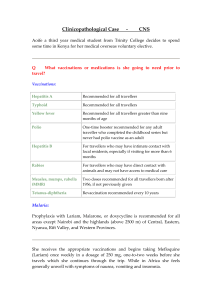
CNS-CPC - Trinity College Dublin
... special problems in pregnancy and in children. It can be due to multiple causes. Repeated hemolysis of infected red cells is the most important cause for a reduction in haemoglobin levels. Anaemia depends on the degree of parasitemia, duration of the acute illness and the number of febrile paroxysms ...
... special problems in pregnancy and in children. It can be due to multiple causes. Repeated hemolysis of infected red cells is the most important cause for a reduction in haemoglobin levels. Anaemia depends on the degree of parasitemia, duration of the acute illness and the number of febrile paroxysms ...
Prima BioMed Ltd (Form: 6-K, Received: 07/10/2015
... dollar milestone payment from GSK triggered a payment of approximately the same amount to the former owners of Immutep, so it was partly a “self-funding” transaction. All potential future GSK milestone payments, which are substantial, as well as all potential future royalties, will be retained by Pr ...
... dollar milestone payment from GSK triggered a payment of approximately the same amount to the former owners of Immutep, so it was partly a “self-funding” transaction. All potential future GSK milestone payments, which are substantial, as well as all potential future royalties, will be retained by Pr ...
Recognition of viruses in the cytoplasm by RLRs and other
... 740 Recognition of viruses in the cytoplasm by RLRs and other helicases mainly function as cytoplasmic sensors for a broad range of viruses, whereas TLRs are well characterized and are known to detect a broad range of pathogens. Recent studies have also provided us important insights about the mec ...
... 740 Recognition of viruses in the cytoplasm by RLRs and other helicases mainly function as cytoplasmic sensors for a broad range of viruses, whereas TLRs are well characterized and are known to detect a broad range of pathogens. Recent studies have also provided us important insights about the mec ...
The immune response during hepatitis B virus infection
... Additional experiments in HBV patients or woodchucks demonstrate the importance of a coordinated helper and cytotoxic T-cell response in controlling hepadnavirus infection. In woodchucks, a reduced early expansion of virusspecific T cells was associated with virus persistence (Menne et al., 2002), w ...
... Additional experiments in HBV patients or woodchucks demonstrate the importance of a coordinated helper and cytotoxic T-cell response in controlling hepadnavirus infection. In woodchucks, a reduced early expansion of virusspecific T cells was associated with virus persistence (Menne et al., 2002), w ...
How Mycobacterium tuberculosis Manipulates Innate and Adaptive Immunity: New Views of
... inhibit phagosomal maturation is well established, the mechanism by which it causes this effect has not been addressed by many groups. To date, there is no mycobacterial strain, which is specifically deficient in the production of ManLAM, making mechanistic studies difficult. A frequently used model ...
... inhibit phagosomal maturation is well established, the mechanism by which it causes this effect has not been addressed by many groups. To date, there is no mycobacterial strain, which is specifically deficient in the production of ManLAM, making mechanistic studies difficult. A frequently used model ...
Sequence analysis of T-cell repertoires in health and disease
... during T-cell and B-cell maturation provide each of us with the personalized armamentarium necessary for defining and defending our own cellular space. T cells, which mediate cellular immunity, express heterodimeric (αβ or γδ) cell surface receptors (T-cell receptors, or TCRs). The vast majority of ...
... during T-cell and B-cell maturation provide each of us with the personalized armamentarium necessary for defining and defending our own cellular space. T cells, which mediate cellular immunity, express heterodimeric (αβ or γδ) cell surface receptors (T-cell receptors, or TCRs). The vast majority of ...
Hepatocytes: a key cell type for innate immunity
... rapidly synthesize and secrete a large amount of CRP into the blood, reaching levels 1000 times higher than basal levels.19 This effect is executed by IL-6 and enhanced by IL-1b. Downstream signals, including STAT3, C/EBPs, and NF-kB, are responsible for the increased transcription.19–21CRP is a str ...
... rapidly synthesize and secrete a large amount of CRP into the blood, reaching levels 1000 times higher than basal levels.19 This effect is executed by IL-6 and enhanced by IL-1b. Downstream signals, including STAT3, C/EBPs, and NF-kB, are responsible for the increased transcription.19–21CRP is a str ...
The Role of Autoantibodies in Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis
... complexes were detected in foamy macrophages in active lesion areas.[9] These observations provide further evidence on the role of antibodies, complement and macrophages in plaque development, which strongly suggest that they can induce axonal injury, an important cause of disability in MS. They may ...
... complexes were detected in foamy macrophages in active lesion areas.[9] These observations provide further evidence on the role of antibodies, complement and macrophages in plaque development, which strongly suggest that they can induce axonal injury, an important cause of disability in MS. They may ...
Bovine mammary gland
... 2) The contents of the gland are no longer being removed at regular intervals. 3) Teat end disinfection is stopped. 4) The factors of natural defense are only marginally elevated over normal milk levels during this potentially vulnerable period (first 3 d). 5) The phagocytic cells are occupied in th ...
... 2) The contents of the gland are no longer being removed at regular intervals. 3) Teat end disinfection is stopped. 4) The factors of natural defense are only marginally elevated over normal milk levels during this potentially vulnerable period (first 3 d). 5) The phagocytic cells are occupied in th ...
Peptides in Neurons and Microglia Inducing the Synthesis of
... immunological reaction that encompasses both neural components and peripheral immune system cells. Within the mammalian CNS, resident glial cells, including astrocytes and microglia, have been shown to initiate a characteristic innate immune response by producing and releasing antimicrobial peptides ...
... immunological reaction that encompasses both neural components and peripheral immune system cells. Within the mammalian CNS, resident glial cells, including astrocytes and microglia, have been shown to initiate a characteristic innate immune response by producing and releasing antimicrobial peptides ...
Foxp3+ regulatory T cells: differentiation, specification, subphenotypes
... single-positive lineage. CD8+ Foxp3+ cells are normally very rare but IL-2 signal transducers Jak3 or STAT5 (ref. 2). However, most evidence can be observed in experimental conditions of thwarted selection of indicates that transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is not required the CD4+ lineage16,28,2 ...
... single-positive lineage. CD8+ Foxp3+ cells are normally very rare but IL-2 signal transducers Jak3 or STAT5 (ref. 2). However, most evidence can be observed in experimental conditions of thwarted selection of indicates that transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) is not required the CD4+ lineage16,28,2 ...
An essential role for decorin in bladder cancer invasiveness
... labelled with the probe (Fig 3C). Altogether these data demonstrate that MB49‐I has lost expression of antigens present on the Y chromosome, and thus does not activate adaptive immune responses elicited to the male antigen in female hosts. To determine whether loss of H‐Y antigens fully explains the ...
... labelled with the probe (Fig 3C). Altogether these data demonstrate that MB49‐I has lost expression of antigens present on the Y chromosome, and thus does not activate adaptive immune responses elicited to the male antigen in female hosts. To determine whether loss of H‐Y antigens fully explains the ...
No Slide Title
... Immune responses initially form IgM with IgG later as B-cell maturation proceeds & somatic mutation causes chain switching. Late clonal responses & boosters favor high affinity antibodies. Immune Response System: http://www.people.virginia.edu/~rjh9u/imresp.html ...
... Immune responses initially form IgM with IgG later as B-cell maturation proceeds & somatic mutation causes chain switching. Late clonal responses & boosters favor high affinity antibodies. Immune Response System: http://www.people.virginia.edu/~rjh9u/imresp.html ...
Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors: Positioning Cells for Host
... CXCL12/CXCR4 interactions are necessary for normal bone marrow development of multiple immune cell lineages, including B cells, monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer (NK) cells, and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) (11). CXCL12/CXCR4 interactions promote the retention of both develo ...
... CXCL12/CXCR4 interactions are necessary for normal bone marrow development of multiple immune cell lineages, including B cells, monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer (NK) cells, and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) (11). CXCL12/CXCR4 interactions promote the retention of both develo ...
Are Targeted by NK Cells Hematopoietic Progenitors Express H60
... Students t test to evaluate experimental data for significant differences; p ⬍ 0.05 was considered significant. ...
... Students t test to evaluate experimental data for significant differences; p ⬍ 0.05 was considered significant. ...
Antibody response to DBY minor histocompatibility antigen is
... men. Antibody responses were directed primarily against areas of amino acid disparity between DBY and DBX. These studies demonstrate that the immune response to mHA includes the generation of specific antibodies and suggests that the serologic response to these antigens may also be useful in the ide ...
... men. Antibody responses were directed primarily against areas of amino acid disparity between DBY and DBX. These studies demonstrate that the immune response to mHA includes the generation of specific antibodies and suggests that the serologic response to these antigens may also be useful in the ide ...
The Injectable-Only Contraceptive
... [18,19]. Norethisterone enanthate (NET-EN) is a 200 mg twomonthly injectable with less widespread use than MPA, although its usage is high in some regions of South Africa [20]. In most studies the adjusted hazard ratio for HIV-1 acquisition by DMPA, or injectable contraceptives users where the major ...
... [18,19]. Norethisterone enanthate (NET-EN) is a 200 mg twomonthly injectable with less widespread use than MPA, although its usage is high in some regions of South Africa [20]. In most studies the adjusted hazard ratio for HIV-1 acquisition by DMPA, or injectable contraceptives users where the major ...
Dual role for B-1a cells in immunity to influenza virus infection
... studies demonstrated that immunization led B-1a cells to generate the robust and dominant T15 idiotype antibody response to phosphocholine (20, 21), which provides immune protection against reinfection with S. pneumoniae (22). Furthermore, although B-1a cells do not respond to BCR-mediated signals t ...
... studies demonstrated that immunization led B-1a cells to generate the robust and dominant T15 idiotype antibody response to phosphocholine (20, 21), which provides immune protection against reinfection with S. pneumoniae (22). Furthermore, although B-1a cells do not respond to BCR-mediated signals t ...
Bivalve immunity and response to infections: Are we
... investigations. During the last few decades, the acknowledgment of infectious diseases as a major driver for bivalve population dynamics also fueled interest in the immunity of these animals. Currently, there are seven infectious diseases impacting mollusks that are listed by the Office International ...
... investigations. During the last few decades, the acknowledgment of infectious diseases as a major driver for bivalve population dynamics also fueled interest in the immunity of these animals. Currently, there are seven infectious diseases impacting mollusks that are listed by the Office International ...
Cells Injury of Transplanted Liver Parenchymal Mediating CD4
... cell dependent, B cell dependent, and allospecific (22). The histology associated with alloantibody-mediated hepatocellular allograft rejection is remarkable for absence of injury to the native liver tissue. Hepatocellular allografts are distinguished from solid organ allografts by the absence of do ...
... cell dependent, B cell dependent, and allospecific (22). The histology associated with alloantibody-mediated hepatocellular allograft rejection is remarkable for absence of injury to the native liver tissue. Hepatocellular allografts are distinguished from solid organ allografts by the absence of do ...
Olive oil and immune system functions: potential
... protection of the host from infectious agents. Hence, immune system should recognise the self from non-self and to eliminate non-self, which constitutes a critical function of this system. The innate arm of immunity prevents the entry of infectious agents into the body. It plays a crucial role in th ...
... protection of the host from infectious agents. Hence, immune system should recognise the self from non-self and to eliminate non-self, which constitutes a critical function of this system. The innate arm of immunity prevents the entry of infectious agents into the body. It plays a crucial role in th ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.