Elements of Adaptive Immunity
... Elements of Adaptive Immunity • T Lymphocytes (T Cells) – Produced in the red bone marrow and mature in the thymus – Circulate in the lymph and blood and migrate to the lymph nodes, spleen, and Peyer’s patches – Antigen-binding sites are complementary to epitopes – Have T cell receptors (TCRs) on t ...
... Elements of Adaptive Immunity • T Lymphocytes (T Cells) – Produced in the red bone marrow and mature in the thymus – Circulate in the lymph and blood and migrate to the lymph nodes, spleen, and Peyer’s patches – Antigen-binding sites are complementary to epitopes – Have T cell receptors (TCRs) on t ...
Immunology
... stem cells differentiates to lymphocytes which acquire several surface markers and become able to discriminate between self and non self. In secondary lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, MALT), there are the environments in which the lymphocytes can interact with immunogens to induce an immune res ...
... stem cells differentiates to lymphocytes which acquire several surface markers and become able to discriminate between self and non self. In secondary lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, MALT), there are the environments in which the lymphocytes can interact with immunogens to induce an immune res ...
Lymphatic/Immune Power Point
... • Allergic reactions: immune system forms antibodies to substances not usually recognized as foreign ...
... • Allergic reactions: immune system forms antibodies to substances not usually recognized as foreign ...
Title page Immunological reconstitution in children after completing
... including the subclasses according to the time (0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 24 months after cessation of ...
... including the subclasses according to the time (0, 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, and 24 months after cessation of ...
Blood
... or hemosiderin Heme is degraded to bilirubin (yellow) Bilirubin is secreted by the liver into the intestine as bile The intestines metabolize it into urobilinogen (green) then to stercobilin (brown) Globin portion is metabolized into amino acids & is released into the circulation ...
... or hemosiderin Heme is degraded to bilirubin (yellow) Bilirubin is secreted by the liver into the intestine as bile The intestines metabolize it into urobilinogen (green) then to stercobilin (brown) Globin portion is metabolized into amino acids & is released into the circulation ...
Chapter40_Section02_edit
... Injection of a weakened or mild form of a pathogen to produce immunity is known as a vaccination. Vaccines stimulate the immune system to create millions of plasma cells ready to produce specific types of antibodies. Immunity produced by the body's reaction to a vaccine is known as active immunity. ...
... Injection of a weakened or mild form of a pathogen to produce immunity is known as a vaccination. Vaccines stimulate the immune system to create millions of plasma cells ready to produce specific types of antibodies. Immunity produced by the body's reaction to a vaccine is known as active immunity. ...
Lo et al. Supplementary Materials
... All tumor specimens and clinical information were obtained with informed consent (or a formal waiver of consent) with approval by the Research Ethics Boards of the BC Cancer Agency, University of British Columbia, and University Health Network. Three retrospective cohorts of HGSC cases were evaluate ...
... All tumor specimens and clinical information were obtained with informed consent (or a formal waiver of consent) with approval by the Research Ethics Boards of the BC Cancer Agency, University of British Columbia, and University Health Network. Three retrospective cohorts of HGSC cases were evaluate ...
A Mathematical Model for within-host Toxoplasma gondii Invasion
... from a PV into the organ, we assume the parasite may interact with 10 host cells and the probability of invasion of individual host is 2%. It follows that βT = 8.889 × 10−10 h−1 and βB = 8.533 × 10−9 h−1 . Since tachyzoites can convert to bradyzoites after about 20 generations of reproduction [17], ...
... from a PV into the organ, we assume the parasite may interact with 10 host cells and the probability of invasion of individual host is 2%. It follows that βT = 8.889 × 10−10 h−1 and βB = 8.533 × 10−9 h−1 . Since tachyzoites can convert to bradyzoites after about 20 generations of reproduction [17], ...
LECTURE 3. BLOOD AND LYMPH Of all the derivatives of the
... Heparin, histamine and several other inflammatory substances are contained in the granules, closely resembling those of labrocytes. These substances are associated with polysaccharides. Since granules are positive to carbohydrate stains e.g. azure A and PAS stain with which they are metachromatic i. ...
... Heparin, histamine and several other inflammatory substances are contained in the granules, closely resembling those of labrocytes. These substances are associated with polysaccharides. Since granules are positive to carbohydrate stains e.g. azure A and PAS stain with which they are metachromatic i. ...
Document
... cell suppression to Der p 1 and Bet v 1 was observed. • This was characterized by: - suppressed proliferative T cell, (Th1) INF-, and (Th2) IL-5, IL-13 responses - increased IL-10 and TGF- secretion by allergen-specific T cells. ...
... cell suppression to Der p 1 and Bet v 1 was observed. • This was characterized by: - suppressed proliferative T cell, (Th1) INF-, and (Th2) IL-5, IL-13 responses - increased IL-10 and TGF- secretion by allergen-specific T cells. ...
lecture # 2 blood - Dr. Justo Lopez Website
... (B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, and NK lymphocytes) They are the largest WBCs, often two or three times the diameter of an RBC. They are about 3% to 8% of WBC count. The nucleus is large and clearly visible, often light violet. It is typically ovoid, kidney-shaped, or horseshoe-shaped. The cytoplasm ...
... (B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes, and NK lymphocytes) They are the largest WBCs, often two or three times the diameter of an RBC. They are about 3% to 8% of WBC count. The nucleus is large and clearly visible, often light violet. It is typically ovoid, kidney-shaped, or horseshoe-shaped. The cytoplasm ...
Non-Specific Defense
... are activated when a host cell is invaded by a virus • Interferon molecules leave the infected cell and enter neighboring cells • Interferon stimulates the neighboring cells to activate genes for PKR (an antiviral ...
... are activated when a host cell is invaded by a virus • Interferon molecules leave the infected cell and enter neighboring cells • Interferon stimulates the neighboring cells to activate genes for PKR (an antiviral ...
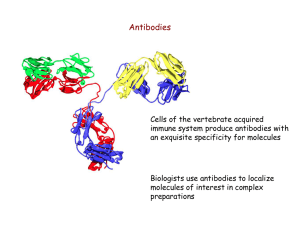
antibodies
... What is the relationship between antibodies, antigens and epitopes? What happens during an immune response? ...
... What is the relationship between antibodies, antigens and epitopes? What happens during an immune response? ...
Acemannan - Symmetry Global
... Monosaccharaides can be covalently linked together through glycosidic bonds to form complex polymeric structures. There are four types of glycosidic bonds, O-glycosidic, S-glycosidic, N-glycosidic or C-glycosidic, depending upon whether oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen or carbon is used as the central link ...
... Monosaccharaides can be covalently linked together through glycosidic bonds to form complex polymeric structures. There are four types of glycosidic bonds, O-glycosidic, S-glycosidic, N-glycosidic or C-glycosidic, depending upon whether oxygen, sulfur, nitrogen or carbon is used as the central link ...
the_large_1 - Salk Institute
... either NTBR or TBR. NTBR-antigens are composed uniquely of NTBR-epitopes; TBR-antigens are of two types, those made up of TBR-epitopes only and those which share epitopes with NTBR-antigens. While one might guess that the immune system can either define NTBRepitopes and leave all else as TBR-epitope ...
... either NTBR or TBR. NTBR-antigens are composed uniquely of NTBR-epitopes; TBR-antigens are of two types, those made up of TBR-epitopes only and those which share epitopes with NTBR-antigens. While one might guess that the immune system can either define NTBRepitopes and leave all else as TBR-epitope ...
immunology – introduction - 1
... - NK cells, mast cells, activated T cells also - Recruit and activate neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages to sites - Induce macrophages to secrete chemokines - Stimulate vascular endothelial cells to express adhesion molecules ...
... - NK cells, mast cells, activated T cells also - Recruit and activate neutrophils and monocytes/macrophages to sites - Induce macrophages to secrete chemokines - Stimulate vascular endothelial cells to express adhesion molecules ...
7_Chronic Inflammation - V14-Study
... o Mutation of the AIRE gene results in autoimmunity and an inflammatory condition known as autoimmune-polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (affects various tissues) AIRE cannot account for the expression of all thymic self-antigens (there are other AIRE-like factors) - Self reactive ...
... o Mutation of the AIRE gene results in autoimmunity and an inflammatory condition known as autoimmune-polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (affects various tissues) AIRE cannot account for the expression of all thymic self-antigens (there are other AIRE-like factors) - Self reactive ...
Glycolipid Immunology: NKT cells
... utilization of receptors that recognizes structures common to pathogens (i.e., pattern recognition receptors). Once the innate immune system is activated, the adaptive immune system is induced by T as well as B cells bearing receptors that have higher specificity and affinity for antigens. Natural k ...
... utilization of receptors that recognizes structures common to pathogens (i.e., pattern recognition receptors). Once the innate immune system is activated, the adaptive immune system is induced by T as well as B cells bearing receptors that have higher specificity and affinity for antigens. Natural k ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿
... APSGN in a matter of weeks or months. In those who do not recover fully, chronic or progressive problems of kidney function may occur. Kidney failure may result in some patients. ...
... APSGN in a matter of weeks or months. In those who do not recover fully, chronic or progressive problems of kidney function may occur. Kidney failure may result in some patients. ...
The predominant surface glycoproteins of thymocytes and
... Simple inspection of Table 1 shows that the different lymphoid cell types are very different in their major cell surface constituents. The only molecule in Table 1 which may be identical on any two cell types is the Class-I histocompatibility antigen on T and B lymphocytes. Thymocytes and T l y m p ...
... Simple inspection of Table 1 shows that the different lymphoid cell types are very different in their major cell surface constituents. The only molecule in Table 1 which may be identical on any two cell types is the Class-I histocompatibility antigen on T and B lymphocytes. Thymocytes and T l y m p ...
18 AIDS
... CTL escape mutants (peptide epitopes) always arise during HIV infection • Since T cells cannot undergo affinity maturation, like B cells, these escape mutants evade the CTL response ...
... CTL escape mutants (peptide epitopes) always arise during HIV infection • Since T cells cannot undergo affinity maturation, like B cells, these escape mutants evade the CTL response ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.