Defence Against Disease
... As you will recognise when the second and third lines of defence are discussed, white blood cells play a vital role in both non-specific and specific defence. It is vitally important that, when defending the body against pathogens, the white blood cells are able to distinguish foreign cells and part ...
... As you will recognise when the second and third lines of defence are discussed, white blood cells play a vital role in both non-specific and specific defence. It is vitally important that, when defending the body against pathogens, the white blood cells are able to distinguish foreign cells and part ...
What is the basis of an allergic reaction
... An allergic reaction is a hypersensitivity reaction; an immune response to environmental antigens (allergens) (Rote, 2006). There are two steps to allergic reactions; formation of antibodies, and response to the allergen (Silverthorn, 1998). The first exposure to an allergen activates helper T-cells ...
... An allergic reaction is a hypersensitivity reaction; an immune response to environmental antigens (allergens) (Rote, 2006). There are two steps to allergic reactions; formation of antibodies, and response to the allergen (Silverthorn, 1998). The first exposure to an allergen activates helper T-cells ...
Chapter 20 The Lymphatic System, Nonspecific Resistance to
... • drains lymph from upper right side of body (arm & head) ...
... • drains lymph from upper right side of body (arm & head) ...
P-selective Sets and the Power of One Bit
... P-selective sets are immune to every subrecursive complexity class [this paper] ...
... P-selective sets are immune to every subrecursive complexity class [this paper] ...
Document
... Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) include dendritic cells, macrophages and B cells to… Ingest antigen, process, place next to MHC-II molecule in plasma membrane, and present to T cells ...
... Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) include dendritic cells, macrophages and B cells to… Ingest antigen, process, place next to MHC-II molecule in plasma membrane, and present to T cells ...
"Immune System Clues: Understanding Cold Virus Protein May Help Transplant Patients"
... member of the organ transplant team at the University of Maryland Medical Center who was not involved in the study. The report shows that carabin acts the same way as immunosuppressant drugs now on the market - inhibiting a pathway that activates the immune system, Cooper said. Researchers have know ...
... member of the organ transplant team at the University of Maryland Medical Center who was not involved in the study. The report shows that carabin acts the same way as immunosuppressant drugs now on the market - inhibiting a pathway that activates the immune system, Cooper said. Researchers have know ...
From Rome to Addis - Basic Science
... • Mucosal exposure in the context of PrEP influence immune response (animal models) ...
... • Mucosal exposure in the context of PrEP influence immune response (animal models) ...
Immuno-oncology Translational Research Initiative Planning
... oncolytic vaccinia virus was manufactured in Ottawa and clinically tested at the Juravinski Cancer Centre and Ottawa Regional Cancer Centre. The product was acquired by Transgene (France) and Sillajen (Korea) and is currently in phase III testing. Catalyst projects supported in Hamilton and Ottawa l ...
... oncolytic vaccinia virus was manufactured in Ottawa and clinically tested at the Juravinski Cancer Centre and Ottawa Regional Cancer Centre. The product was acquired by Transgene (France) and Sillajen (Korea) and is currently in phase III testing. Catalyst projects supported in Hamilton and Ottawa l ...
lymphmedterm - Weatherford High School
... •Lipids are transported from the small intestines to the blood stream by the lymph vessels Location of major groups of lymph nodes: ...
... •Lipids are transported from the small intestines to the blood stream by the lymph vessels Location of major groups of lymph nodes: ...
ALUM
... DT was administered locally via the intratracheal (i.t.) route, leading to a depletion of mediastinal-resident LN, as well as lung-derived migratory DCs, whereas leaving all other DCs unaffected T cell proliferation (measured 3 d after injection of OVA) was abolished in the MLN in mice receiving OVA ...
... DT was administered locally via the intratracheal (i.t.) route, leading to a depletion of mediastinal-resident LN, as well as lung-derived migratory DCs, whereas leaving all other DCs unaffected T cell proliferation (measured 3 d after injection of OVA) was abolished in the MLN in mice receiving OVA ...
Biomolecular chemistry 5. What proteins do: catalysts and binders
... system. An antigen is a substance capable of inducing a specific immune response. The term ‘antigen’ is derived from the generation of antibodies to such substances. • Often antigens are foreign proteins (or parts of them) that enter the body via an infection. Sometimes, however, the body's own prot ...
... system. An antigen is a substance capable of inducing a specific immune response. The term ‘antigen’ is derived from the generation of antibodies to such substances. • Often antigens are foreign proteins (or parts of them) that enter the body via an infection. Sometimes, however, the body's own prot ...
Adaptive Immune Response of V2V2 T Cells During Mycobacterial
... To examine the role of T cell receptor (TCR) in ␥␦ T cells in adaptive immunity, a macaque model was used to follow V␥2V␦2⫹ T cell responses to mycobacterial infections. These phosphoantigen-specific ␥␦ T cells displayed major expansion during Mycobacterium bovis Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) infec ...
... To examine the role of T cell receptor (TCR) in ␥␦ T cells in adaptive immunity, a macaque model was used to follow V␥2V␦2⫹ T cell responses to mycobacterial infections. These phosphoantigen-specific ␥␦ T cells displayed major expansion during Mycobacterium bovis Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) infec ...
Review on Immunomodulation and Immunomodulatory Activity of
... and surgery, investigation of their immune effects on these mechanisms of immune stimulation would seem prudent. The Adaptive Immune System Adaptive or acquired immunity differs from the innate response as it is specific, has an element of memory, and is unique to vertebrates. The humoral component ...
... and surgery, investigation of their immune effects on these mechanisms of immune stimulation would seem prudent. The Adaptive Immune System Adaptive or acquired immunity differs from the innate response as it is specific, has an element of memory, and is unique to vertebrates. The humoral component ...
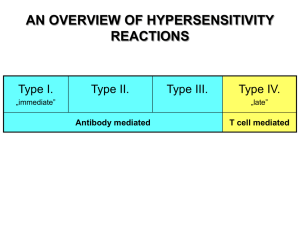
Hypersensitivity
... • Local vasculitis develops as a result of immune complex deposition • Inhaled antigens (fungi, animal feces) may induce similar reaction in the lung • IgG type antibody • ‘Farmers lung’ and ‘piegeon-breeder’s lung’ ...
... • Local vasculitis develops as a result of immune complex deposition • Inhaled antigens (fungi, animal feces) may induce similar reaction in the lung • IgG type antibody • ‘Farmers lung’ and ‘piegeon-breeder’s lung’ ...
Document
... a. Not quite clear on this part yet. Any suggestions on good sources? 7. Results: a. Mice – strong T cells-mediated immune responses, at least 155 days b. Rhesus macaques – prime-boost elicited HIV-specific T cell responsesiv c. Humans – Phase I and Phase II trials underway in Oxford and Nairobi i. ...
... a. Not quite clear on this part yet. Any suggestions on good sources? 7. Results: a. Mice – strong T cells-mediated immune responses, at least 155 days b. Rhesus macaques – prime-boost elicited HIV-specific T cell responsesiv c. Humans – Phase I and Phase II trials underway in Oxford and Nairobi i. ...
Curr Opin HIV AIDS
... Division of Experimental Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, USA. [email protected] ...
... Division of Experimental Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, USA. [email protected] ...
Accelerated Antigen Sampling and Transport by Airway Mucosal
... Virbac) during halothane anesthesia. Trachea was excised, flushed with PBS, opened longitudinally, cut finely transversely, and finally cut randomly. Tissue was transferred into GKN-10% FCS containing type IV collagenase (1.5 mg/ml) and type I DNase and incubated for 90 min at 37°C in a shaking wate ...
... Virbac) during halothane anesthesia. Trachea was excised, flushed with PBS, opened longitudinally, cut finely transversely, and finally cut randomly. Tissue was transferred into GKN-10% FCS containing type IV collagenase (1.5 mg/ml) and type I DNase and incubated for 90 min at 37°C in a shaking wate ...
File
... Gillepsie, S.L. (2011). Natural history and classification of pediatric HIV infection. Uptodate. Retrieved 9-22-11 at http://www.uptodate.com/contents/natural- historyand-classification- of- Pediatric-hiv-infection? Source =search _result&search=HIV+children&selectedTitle=3%7E150#H18840505.specificd ...
... Gillepsie, S.L. (2011). Natural history and classification of pediatric HIV infection. Uptodate. Retrieved 9-22-11 at http://www.uptodate.com/contents/natural- historyand-classification- of- Pediatric-hiv-infection? Source =search _result&search=HIV+children&selectedTitle=3%7E150#H18840505.specificd ...
Autoantibodies in systemic autoimmune diseases: specificity and
... In this Review we focus on the initiation of autoantibody production and autoantibody pathogenicity, with a special emphasis on the targeted antigens. Release of intracellular antigens due to excessive cell death or to ineffective clearance of apoptotic debris, modification of self-antigens during i ...
... In this Review we focus on the initiation of autoantibody production and autoantibody pathogenicity, with a special emphasis on the targeted antigens. Release of intracellular antigens due to excessive cell death or to ineffective clearance of apoptotic debris, modification of self-antigens during i ...
The Cell-Derived Mediators of Chemical Mediators of Inflammation
... Immune complexes Products of T-lymphocytes (adaptive immune response) ...
... Immune complexes Products of T-lymphocytes (adaptive immune response) ...
Louis Kock - TB-IPCP
... PD1 on both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and higher levels of HLA-DR+ CD4+ T cells in IRIS patients - high antigen load that may stimulate an activated phenotype. Elevated, Th1/Th17 production of IFN-γ, and other cytokines/chemokine’s. CD4+ T cells have a significant contribution to IRIS pathogenesis, ...
... PD1 on both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and higher levels of HLA-DR+ CD4+ T cells in IRIS patients - high antigen load that may stimulate an activated phenotype. Elevated, Th1/Th17 production of IFN-γ, and other cytokines/chemokine’s. CD4+ T cells have a significant contribution to IRIS pathogenesis, ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.