A vaccine for malaria?
... for destruction by white blood cells and making it difficult for them to cause disease. However, because the malaria parasite spends a lot of its life cycle hiding inside human liver cells, antibodies alone may not be protective against malaria. More recent approaches aim to use a different group of ...
... for destruction by white blood cells and making it difficult for them to cause disease. However, because the malaria parasite spends a lot of its life cycle hiding inside human liver cells, antibodies alone may not be protective against malaria. More recent approaches aim to use a different group of ...
Immune homeostasis in the respiratory tract and its impact on
... evidence to suggest that TLRs prevent inflammation [53] by increasing epithelial integrity [54] and promoting B cell responses and IgA production [55]. In the colon suppression of TLR responses is mediated by an increase of negative regulators such as IRAKM [56], SIGIRR [57] and Tollip [58]. In the l ...
... evidence to suggest that TLRs prevent inflammation [53] by increasing epithelial integrity [54] and promoting B cell responses and IgA production [55]. In the colon suppression of TLR responses is mediated by an increase of negative regulators such as IRAKM [56], SIGIRR [57] and Tollip [58]. In the l ...
Proceedings Template - WORD
... reason to believe that they will also hold for immune systems that are either autoreactive, or immunodeficient. In particular, a possible route to autoimmunity would be a significant reversal in one or more of the above inequalities, while immunodeficiency could be induced by increasing the same par ...
... reason to believe that they will also hold for immune systems that are either autoreactive, or immunodeficient. In particular, a possible route to autoimmunity would be a significant reversal in one or more of the above inequalities, while immunodeficiency could be induced by increasing the same par ...
Aalborg Universitet Molecular Pathogenesis of Spondyloarthritis Carlsen, Thomas Gelsing
... predominantly of the IgG3 subclass, antibodies against bacterial HSP60 are predominantly of the IgG1 subclass. Therefore, based on the ELISA results, crossreaction between bacterial and human HSP60 could not be supported as a pathogenic mechanism for SpA disease in our study. However, a weak correl ...
... predominantly of the IgG3 subclass, antibodies against bacterial HSP60 are predominantly of the IgG1 subclass. Therefore, based on the ELISA results, crossreaction between bacterial and human HSP60 could not be supported as a pathogenic mechanism for SpA disease in our study. However, a weak correl ...
Secretion Induces Hormone, Chemokine, and Defensin Activation of
... needs of nutrient absorption and host defense meet. Because nutrient absorption requires a large surface area and a thin epithelium, features that potentially compromise host defense, it is not surprising that the gastrointestinal tract has evolved an elaborate network of surveillance systems compri ...
... needs of nutrient absorption and host defense meet. Because nutrient absorption requires a large surface area and a thin epithelium, features that potentially compromise host defense, it is not surprising that the gastrointestinal tract has evolved an elaborate network of surveillance systems compri ...
Adoptive cell transfer: a clinical path to effective cancer
... further enhance the effectiveness of these IL2-dependent cells in vivo20. The need for immunization of lymphocyte donors limited the application of this approach until 1986 when it was shown that tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) from non-immunized mice bearing sarcomas or melanomas could be exp ...
... further enhance the effectiveness of these IL2-dependent cells in vivo20. The need for immunization of lymphocyte donors limited the application of this approach until 1986 when it was shown that tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) from non-immunized mice bearing sarcomas or melanomas could be exp ...
Autoimmunity and Apoptosis – Therapeutic Implications Iran Rashedi , Soumya Panigrahi
... countering the antigen cannot be completely activated and are called anergic [17, 18]. Some of these anergic T-cells produce IL10, which suppresses the activation of T-cells [19]. Reduction in the number of these anergic cells in the peripheral repertoire confers the susceptibility to autoimmune dis ...
... countering the antigen cannot be completely activated and are called anergic [17, 18]. Some of these anergic T-cells produce IL10, which suppresses the activation of T-cells [19]. Reduction in the number of these anergic cells in the peripheral repertoire confers the susceptibility to autoimmune dis ...
Development of biochemical assays for immunotherapy drug
... Immunotherapy has become an important approach for the treatment of numerous diseases including cancer. A number of immunotherapies target one or more co-stimulatory or co-inhibitory pathways regulating immune activation such as cell surface receptors and enzymes like IDO1 and TDO. Reliable high thr ...
... Immunotherapy has become an important approach for the treatment of numerous diseases including cancer. A number of immunotherapies target one or more co-stimulatory or co-inhibitory pathways regulating immune activation such as cell surface receptors and enzymes like IDO1 and TDO. Reliable high thr ...
DNA vaccines
... important cell types: the B-cell and the T-cell. The B-cell is responsible for the production of antibodies, and the T-cell (two types) is responsible either for helping the B-cell to make antibodies, or for the killing of damaged or "different" cells within the body. The two main types of T-cells a ...
... important cell types: the B-cell and the T-cell. The B-cell is responsible for the production of antibodies, and the T-cell (two types) is responsible either for helping the B-cell to make antibodies, or for the killing of damaged or "different" cells within the body. The two main types of T-cells a ...
Th2-type immune response induced by a phage clone displaying a
... Thus, it is still unclear if there is any difference in the role of CD80 as opposed to CD86 on the interaction with CTLA4. In our case, we have shown here that the selective inhibitor of CD80-binding, F2-g3p induced the skewing toward a Th2-type response when administered in mice in vivo. The influe ...
... Thus, it is still unclear if there is any difference in the role of CD80 as opposed to CD86 on the interaction with CTLA4. In our case, we have shown here that the selective inhibitor of CD80-binding, F2-g3p induced the skewing toward a Th2-type response when administered in mice in vivo. The influe ...
Effects of Mold Exposure on Immune Cells
... immune response to them. The exact mechanisms of many types of allergies are not fully understood. Typically, immune responses involve cell to cell communication via cytokines – chemicals secreted by immune cells that illicit some type of response in other cells. Chemokines are chemo-attractant cyto ...
... immune response to them. The exact mechanisms of many types of allergies are not fully understood. Typically, immune responses involve cell to cell communication via cytokines – chemicals secreted by immune cells that illicit some type of response in other cells. Chemokines are chemo-attractant cyto ...
Transplantation Immunology
... Basically, self MHC molecule recognizes the structure of an intact allogeneic MHC molecule ...
... Basically, self MHC molecule recognizes the structure of an intact allogeneic MHC molecule ...
PDF - The Journal of Immunology
... system. For example, the MHC class I-like molecule MIC is induced on the surface of heat-shocked or otherwise stressed cells, and has been shown to bind to an activating receptor called NKG2D, which is expressed by ␥␦ T cells, CD8⫹ T cells, and NK cells (37). Heat shock proteins themselves appear to ...
... system. For example, the MHC class I-like molecule MIC is induced on the surface of heat-shocked or otherwise stressed cells, and has been shown to bind to an activating receptor called NKG2D, which is expressed by ␥␦ T cells, CD8⫹ T cells, and NK cells (37). Heat shock proteins themselves appear to ...
Disorders NK Cells in Central Nervous System
... and CD11bhighCD272 NK cells present lower rates of proliferation and are found in spleen and peripheral blood (8). In humans, NK cells can be subdivided into different populations based on the relative expression of the surface markers CD16 and CD56. The mature subtype CD56dimCD16+, found mainly in ...
... and CD11bhighCD272 NK cells present lower rates of proliferation and are found in spleen and peripheral blood (8). In humans, NK cells can be subdivided into different populations based on the relative expression of the surface markers CD16 and CD56. The mature subtype CD56dimCD16+, found mainly in ...
Catabolic Cytokine Expressions in Patients with Degenerative Disc
... reactions could play a key role in lumbar DDD. Although there are several studies in relation to the lumbar disc herniation, no study has yet attempted to ...
... reactions could play a key role in lumbar DDD. Although there are several studies in relation to the lumbar disc herniation, no study has yet attempted to ...
Slide
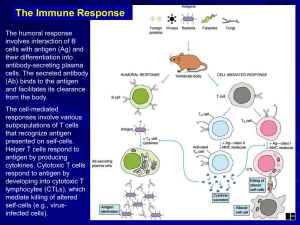
... The Immune Response The humoral response involves interaction of B cells with antigen (Ag) and their differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells. The secreted antibody (Ab) binds to the antigen and facilitates its clearance from the body. The cell-mediated responses involve various subpopul ...
... The Immune Response The humoral response involves interaction of B cells with antigen (Ag) and their differentiation into antibody-secreting plasma cells. The secreted antibody (Ab) binds to the antigen and facilitates its clearance from the body. The cell-mediated responses involve various subpopul ...
CD4 and CD8 T Cells Are - The Journal of Immunology
... (LM),3 is a Gram-positive bacterium that invades host cells, escapes from the endosome, and replicates within the host cell cytosol (2). LM proteins are presented by both MHC class I and class II pathways and stimulate strong CD8 and CD4 T cell responses (1, 3). The in vivo dynamics of the CD8 T cel ...
... (LM),3 is a Gram-positive bacterium that invades host cells, escapes from the endosome, and replicates within the host cell cytosol (2). LM proteins are presented by both MHC class I and class II pathways and stimulate strong CD8 and CD4 T cell responses (1, 3). The in vivo dynamics of the CD8 T cel ...
Sensing of pathogen-induced F-actin
... this process. Moreover, NOD1 localizes at F-actin rich structures at the cell cortex and at the site of bacterial invasion (Kufer et al., 2008). Recent evidence now links GEF-H1 to NOD1-mediated detection of the Shigella effector proteins (Fukazawa et al., 2008). Notably, induction of inflammatory r ...
... this process. Moreover, NOD1 localizes at F-actin rich structures at the cell cortex and at the site of bacterial invasion (Kufer et al., 2008). Recent evidence now links GEF-H1 to NOD1-mediated detection of the Shigella effector proteins (Fukazawa et al., 2008). Notably, induction of inflammatory r ...
Transplantation Immunology
... CTL mediated cytotoxicity lyse graft endothelial and parenchymal cells directly ...
... CTL mediated cytotoxicity lyse graft endothelial and parenchymal cells directly ...
The viral manipulation of the host cellular and immune environments
... Inhibition of cytokine action Cytokines are the messenger molecules that play an important role in inflammation, cellular activation, proliferation, and differentiation [12]. Their effects involve a wide range of mechanisms including alteration of the expression of MHC molecules, adhesion molecules, ...
... Inhibition of cytokine action Cytokines are the messenger molecules that play an important role in inflammation, cellular activation, proliferation, and differentiation [12]. Their effects involve a wide range of mechanisms including alteration of the expression of MHC molecules, adhesion molecules, ...
Thai Journal of Veterinary Medicine
... proPO granules and their transformation (cascade reaction) ...
... proPO granules and their transformation (cascade reaction) ...
Role of Regulatory T-cells in Oral Tolerance and Immunotherapy
... properties against effector cells, mainly through the production of IL10 [25]. IL-10 is the only detectable cytokine produced by NO-Tregs. It has been repeatedly shown that all subsets of Tregs coexist and overlap in many immune tolerance-related situations in humans, ...
... properties against effector cells, mainly through the production of IL10 [25]. IL-10 is the only detectable cytokine produced by NO-Tregs. It has been repeatedly shown that all subsets of Tregs coexist and overlap in many immune tolerance-related situations in humans, ...
Evaluation of the Cell-mediated Immune
... assay was useful in detecting cell-mediated immunity in the mouse MSV system, we performed preliminary ex periments testing the cytotoxicity of lymphocytes from some MSV-infected animals, at different times after virus inoculation, against MSB and MSC target cells. As shown in Chart 1, cellular acti ...
... assay was useful in detecting cell-mediated immunity in the mouse MSV system, we performed preliminary ex periments testing the cytotoxicity of lymphocytes from some MSV-infected animals, at different times after virus inoculation, against MSB and MSC target cells. As shown in Chart 1, cellular acti ...
Adaptive immune system

The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune or, more rarely, as the specific immune system, is a subsystem of the overall immune system that is composed of highly specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate or prevent pathogen growth. The adaptive immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, leads to an enhanced response to subsequent encounters with that pathogen. This process of acquired immunity is the basis of vaccination. Like the innate system, the adaptive system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components.Unlike the innate immune system, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to a specific pathogen. Adaptive immunity can also provide long-lasting protection: for example; someone who recovers from measles is now protected against measles for their lifetime but in other cases it does not provide lifetime protection: for example; chickenpox. The adaptive system response destroys invading pathogens and any toxic molecules they produce. Sometimes the adaptive system is unable to distinguish foreign molecules, the effects of this may be hayfever, asthma or any other allergies. Antigens are any substances that elicit the adaptive immune response. The cells that carry out the adaptive immune response are white blood cells known as lymphocytes. Two main broad classes—antibody responses and cell mediated immune response—are also carried by two different lymphocytes (B cells and T cells). In antibody responses, B cells are activated to secrete antibodies, which are proteins also known as immunoglobulins. Antibodies travel through the bloodstream and bind to the foreign antigen causing it to inactivate, which does not allow the antigen to bind to the host.In acquired immunity, pathogen-specific receptors are ""acquired"" during the lifetime of the organism (whereas in innate immunity pathogen-specific receptors are already encoded in the germline). The acquired response is called ""adaptive"" because it prepares the body's immune system for future challenges (though it can actually also be maladaptive when it results in autoimmunity).The system is highly adaptable because of somatic hypermutation (a process of accelerated somatic mutations), and V(D)J recombination (an irreversible genetic recombination of antigen receptor gene segments). This mechanism allows a small number of genes to generate a vast number of different antigen receptors, which are then uniquely expressed on each individual lymphocyte. Because the gene rearrangement leads to an irreversible change in the DNA of each cell, all progeny (offspring) of that cell inherit genes that encode the same receptor specificity, including the memory B cells and memory T cells that are the keys to long-lived specific immunity.A theoretical framework explaining the workings of the acquired immune system is provided by immune network theory. This theory, which builds on established concepts of clonal selection, is being applied in the search for an HIV vaccine.