Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Membranes and Their
... can be used, however, to compare the relative effectiveness of different filters in a given application. The true pore size distribution of an air filter does not by itself determine the capture efficiency versus particle size curve, because most particles that can fit through the pores are still ca ...
... can be used, however, to compare the relative effectiveness of different filters in a given application. The true pore size distribution of an air filter does not by itself determine the capture efficiency versus particle size curve, because most particles that can fit through the pores are still ca ...
Filtration Methods - Wiley Online Library
... Filtration is the separation process of removing solid particles, microorganisms or droplets from a liquid or a gas by depositing them on a filter medium also called a septum, which is essentially permeable to only the fluid phase of the mixture being separated. The particles are deposited either at ...
... Filtration is the separation process of removing solid particles, microorganisms or droplets from a liquid or a gas by depositing them on a filter medium also called a septum, which is essentially permeable to only the fluid phase of the mixture being separated. The particles are deposited either at ...
F_b_word
... Intensity of the heat transfer process can also greatly differ along the furnace height. In fluidized beds, heat transfer coefficients to the immersed surfaces range from 250 to 700 W/m2K . In the freeboard heat transfer coefficients are less than 100 W/m2K. When considering heat transfer processes ...
... Intensity of the heat transfer process can also greatly differ along the furnace height. In fluidized beds, heat transfer coefficients to the immersed surfaces range from 250 to 700 W/m2K . In the freeboard heat transfer coefficients are less than 100 W/m2K. When considering heat transfer processes ...
Stoke`s Law of Settling
... chemical used in coagulation or in other treatment processes, such as lime softening. • Sedimentation is accomplished by decreasing the velocity of the water being treated to a point below which the particles will no longer remain in suspension. • When the velocity no longer supports the transport o ...
... chemical used in coagulation or in other treatment processes, such as lime softening. • Sedimentation is accomplished by decreasing the velocity of the water being treated to a point below which the particles will no longer remain in suspension. • When the velocity no longer supports the transport o ...
Mechanism for clogging of micro-channels
... of any kind of blockage. However, despite their importance, the physical mechanisms that lead to clogging of porous media are still not well understood. Physically, filters are porous media with a distribution of pore sizes that determines the smallest filtrate to be removed from suspension. The sim ...
... of any kind of blockage. However, despite their importance, the physical mechanisms that lead to clogging of porous media are still not well understood. Physically, filters are porous media with a distribution of pore sizes that determines the smallest filtrate to be removed from suspension. The sim ...
Nonequilibrium translational effects in evaporation and condensation
... maximum in the interfacial region and that the velocity component normal to the interface is important for the likelihood of condensation. It is also known that the energy flux across the interface has maximum contribution from potential energy in the interface.12 In order to describe this, we intro ...
... maximum in the interfacial region and that the velocity component normal to the interface is important for the likelihood of condensation. It is also known that the energy flux across the interface has maximum contribution from potential energy in the interface.12 In order to describe this, we intro ...
Section 13.1
... Kinetic Theory and a Model for Gases The word kinetic refers to motion. The energy an object has because of its motion is called kinetic energy. According to the kinetic theory, all matter consists of tiny particles that are in constant motion. The particles in a gas are usually molecules or atoms. ...
... Kinetic Theory and a Model for Gases The word kinetic refers to motion. The energy an object has because of its motion is called kinetic energy. According to the kinetic theory, all matter consists of tiny particles that are in constant motion. The particles in a gas are usually molecules or atoms. ...
Fluidized Bed Characteristics
... fluidization. With a gas, uniform fluidization is frequently observed only at low velocities. At high velocities, non uniform or “aggregative” fluidization will be observed with large bubbling and the bed is then often referred to as a “boiling” bed. In long, narrow fluidized beds, coalescence of th ...
... fluidization. With a gas, uniform fluidization is frequently observed only at low velocities. At high velocities, non uniform or “aggregative” fluidization will be observed with large bubbling and the bed is then often referred to as a “boiling” bed. In long, narrow fluidized beds, coalescence of th ...
MECHANICAL SEPARATIONS Read or print this Chapter as a
... surface by the use of air bubbles. This technique is known as flotation and it depends upon the relative tendency of air and water to adhere to the particle surface. The water at the particle surface must be displaced by air, after which the buoyancy of the air is sufficient to carry both the partic ...
... surface by the use of air bubbles. This technique is known as flotation and it depends upon the relative tendency of air and water to adhere to the particle surface. The water at the particle surface must be displaced by air, after which the buoyancy of the air is sufficient to carry both the partic ...
Rigid body constraints realized in massively
... One such extension is SHAKE [8]. The SHAKE algorithm enforces fixed bond distances between two particles. Via an iterative method, any number of bonds in the system can be constrained. A set of particles may be combined into a single rigid body with an appropriate choice of bond constraints while tak ...
... One such extension is SHAKE [8]. The SHAKE algorithm enforces fixed bond distances between two particles. Via an iterative method, any number of bonds in the system can be constrained. A set of particles may be combined into a single rigid body with an appropriate choice of bond constraints while tak ...
SIMULATION OF FLUID FLOW WITH INTERACTING PARTICLES
... closer to one another than ¦red . Below this critical distance the lubrication force Filrj starts to attract particles. This is in order to model the process of attraction of the particles due to lower pressure between them, caused by higher velocity of liquid flowing through the gap. When an overla ...
... closer to one another than ¦red . Below this critical distance the lubrication force Filrj starts to attract particles. This is in order to model the process of attraction of the particles due to lower pressure between them, caused by higher velocity of liquid flowing through the gap. When an overla ...
Computer simulation of air filtration including electric
... The first ingredient in the simulation of air filtration is a three-dimensional representation of the filter media in the computer. We use a voxel model, where a large enough cutout of the media is discretized by a uniform Cartesian grid with edge-length h . This h has to be chosen in such a way tha ...
... The first ingredient in the simulation of air filtration is a three-dimensional representation of the filter media in the computer. We use a voxel model, where a large enough cutout of the media is discretized by a uniform Cartesian grid with edge-length h . This h has to be chosen in such a way tha ...
8.1 – Viscosity and the effects of temperature
... The distance between the particles will increase and the forces of attraction between the particles decreases as well after heating. 3) Draw a diagram to show what happens to the particles when a gas is heated. The particles in the gas will move faster when heated and collide more often causing m ...
... The distance between the particles will increase and the forces of attraction between the particles decreases as well after heating. 3) Draw a diagram to show what happens to the particles when a gas is heated. The particles in the gas will move faster when heated and collide more often causing m ...
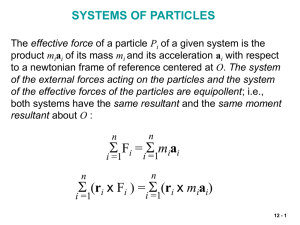
Lec12
... momentum is applied to a system S of particles during a time interval Dt, including particles which enter the system at A during that time interval and those (of the same mass Dm) which leave the system at B. The system formed by the momentum (Dm)vA of the particles entering S in the time Dt and the ...
... momentum is applied to a system S of particles during a time interval Dt, including particles which enter the system at A during that time interval and those (of the same mass Dm) which leave the system at B. The system formed by the momentum (Dm)vA of the particles entering S in the time Dt and the ...
Particle Consistency of Microscopic and Macroscopic
... theory of vitreous and resinous electricity, but in 1839 Michael Faraday believed the division of static electricity, current electricity, and bioelectricity to be only a consequence of the behavior of a single kind of electricity appearing in opposite polarities. It is not certain which polarity is ...
... theory of vitreous and resinous electricity, but in 1839 Michael Faraday believed the division of static electricity, current electricity, and bioelectricity to be only a consequence of the behavior of a single kind of electricity appearing in opposite polarities. It is not certain which polarity is ...
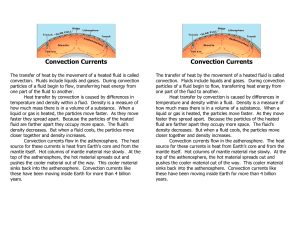
Convection Currents The transfer of heat by the movement of a
... mantle itself. Hot columns of mantle material rise slowly. At the top of the asthenosphere, the hot material spreads out and pushes the cooler material out of the way. This cooler material sinks back into the asthenosphere. Convection currents like these have been moving inside Earth for more than 4 ...
... mantle itself. Hot columns of mantle material rise slowly. At the top of the asthenosphere, the hot material spreads out and pushes the cooler material out of the way. This cooler material sinks back into the asthenosphere. Convection currents like these have been moving inside Earth for more than 4 ...
Numerical Simulation of Blood Flow in Centrifugal Heart
... damages by determining theareas of circulation flow and high pressure gradient and shear stress, although the amount of damage is not realized. Therefore, the possible damages can be reduced by evaluating the locations in which return flow or vertex occurs or disturbance is higher than other areas a ...
... damages by determining theareas of circulation flow and high pressure gradient and shear stress, although the amount of damage is not realized. Therefore, the possible damages can be reduced by evaluating the locations in which return flow or vertex occurs or disturbance is higher than other areas a ...
Topic 7 Section 2 Liquids and solids
... Any liquid gradually diffuses throughout any other liquid in which it can dissolve. The constant, random motion of particles causes diffusion in liquids. ...
... Any liquid gradually diffuses throughout any other liquid in which it can dissolve. The constant, random motion of particles causes diffusion in liquids. ...
S2 File.
... aerodynamically smaller particle than it appears geometrically. Also, where the density of the particle is less than 1, the particle will behave as an aerodynamically smaller particle than it appears geometrically. In addition, if the particle is smaller than 1m, it will ‘slip’ between gas molecule ...
... aerodynamically smaller particle than it appears geometrically. Also, where the density of the particle is less than 1, the particle will behave as an aerodynamically smaller particle than it appears geometrically. In addition, if the particle is smaller than 1m, it will ‘slip’ between gas molecule ...
Section 13.2 Forces Within Liquids
... drops the bead up on a freshly washed and waxed car. Why does surface tension produce spherical drops? The force pulling the surface particles into a liquid causes the surface to become as small as possible, and the shape that has the least surface for a given volume is a sphere. The higher the surf ...
... drops the bead up on a freshly washed and waxed car. Why does surface tension produce spherical drops? The force pulling the surface particles into a liquid causes the surface to become as small as possible, and the shape that has the least surface for a given volume is a sphere. The higher the surf ...
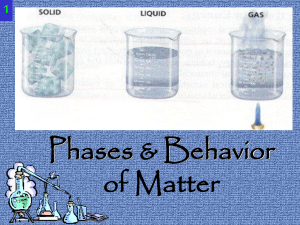
Phases and Behavior of Matter ppt
... observed that the amount of water which flowed outside the pool was equal to the amount of his body that was immersed. Since this fact indicated the method of explaining the case, he did not linger, but moved with delight, he leapt out of the pool, and going home naked, cried aloud that he had found ...
... observed that the amount of water which flowed outside the pool was equal to the amount of his body that was immersed. Since this fact indicated the method of explaining the case, he did not linger, but moved with delight, he leapt out of the pool, and going home naked, cried aloud that he had found ...
Course Syllabus
... Deliberate plagiarism is a serious act of academic misconduct. Students may be suspended from the University if they are found to have plagiarized their course work. Whether inadvertent or deliberate, plagiarism includes the following: (a) word-for-word copying of sentences or whole paragraphs or pr ...
... Deliberate plagiarism is a serious act of academic misconduct. Students may be suspended from the University if they are found to have plagiarized their course work. Whether inadvertent or deliberate, plagiarism includes the following: (a) word-for-word copying of sentences or whole paragraphs or pr ...
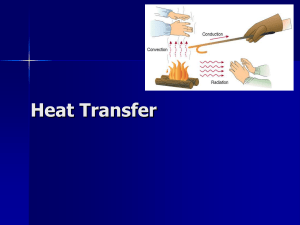
Heat Transfer - Cobb Learning
... moving faster, they spread out more. So they are less dense and rise. After giving their energy to the cooler fluid at the top, they are now cooler and more dense. More dense fluids sink. ...
... moving faster, they spread out more. So they are less dense and rise. After giving their energy to the cooler fluid at the top, they are now cooler and more dense. More dense fluids sink. ...
Mushroom cloud

A mushroom cloud is a distinctive pyrocumulus mushroom-shaped cloud of debris/smoke and usually condensed water vapor resulting from a large explosion. The effect is most commonly associated with a nuclear explosion (and sometimes referred to in this context as a thunderball), but any sufficiently energetic detonation or deflagration will produce the same sort of effect. They can be caused by powerful conventional weapons, like vacuum bombs, including the ATBIP and GBU-43/B Massive Ordnance Air Blast. Some volcanic eruptions and impact events can produce natural mushroom clouds.Mushroom clouds result from the sudden formation of a large volume of lower-density gases at any altitude, causing a Rayleigh–Taylor instability. The buoyant mass of gas rises rapidly, resulting in turbulent vortices curling downward around its edges, forming a temporary vortex ring that draws up a central column, possibly with smoke, debris, or/and condensed water vapor to form the ""mushroom stem"". The mass of gas plus entrained moist air eventually reaches an altitude where it is no longer of lower density than the surrounding air; at this point, it disperses, any debris drawn upward from the ground scattering and drifting back down (see fallout). The stabilization altitude depends strongly on the profiles of the temperature, dew point, and wind shear in the air at and above the starting altitude.