Immune system and Cancer
... defense antigens - large complex molecules not normally in the body - "non-self" - self-antigens - protein molecules on your cells that mark them as "yours"; these are antigens to other people - MHC (major histocompatibility proteins) ...
... defense antigens - large complex molecules not normally in the body - "non-self" - self-antigens - protein molecules on your cells that mark them as "yours"; these are antigens to other people - MHC (major histocompatibility proteins) ...
DEFINITIONS - Tehran University of Medical Sciences
... – Some glycolipids and phosopholipids can be immunogenic for T cells and illicit a cell mediated immune response ...
... – Some glycolipids and phosopholipids can be immunogenic for T cells and illicit a cell mediated immune response ...
Interferon Type II & III - Bite
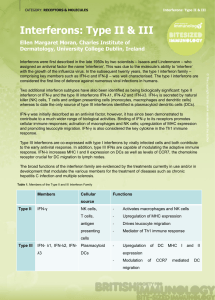
... interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic c ...
... interferon or IFN-γ and the type III interferons IFN-λ1, IFN-λ2 and IFN-λ3. IFN-γ is secreted by natural killer (NK) cells, T cells and antigen presenting cells (monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells) whereas to date the only source of type III interferons identified is plasmacytoid dendritic c ...
lesson-1-active
... • Immunisation is the process by which a person develops immunity to a pathogen • Active Immunity is when the protection is gained as a result of a person producing ...
... • Immunisation is the process by which a person develops immunity to a pathogen • Active Immunity is when the protection is gained as a result of a person producing ...
Read More - Division of Rheumatology
... examples of the acquisition and loss of differentiation antigens with developmental stage. Several aspects of the expression of HLA-DR were found relevant to rheumatic diseases, including the first demonstration that fibroblastoid lineage lining cells in the rheumatoid synovium expressed HLA-DR mole ...
... examples of the acquisition and loss of differentiation antigens with developmental stage. Several aspects of the expression of HLA-DR were found relevant to rheumatic diseases, including the first demonstration that fibroblastoid lineage lining cells in the rheumatoid synovium expressed HLA-DR mole ...
Chapter 24 - Teacher Pages
... 24.4 The adaptive immune response counters specific invaders Our immune system responds to foreign molecules called antigens, which elicit the adaptive immune response. The adaptive immune system – is found only in the vertebrates, – reacts to specific pathogens, and ...
... 24.4 The adaptive immune response counters specific invaders Our immune system responds to foreign molecules called antigens, which elicit the adaptive immune response. The adaptive immune system – is found only in the vertebrates, – reacts to specific pathogens, and ...
What Happens When the Immune System Attacks Itself?
... When the immune system malfunctions, it can affect the skin, heart, central nervous system, and almost any structure in the body. There are two types of autoimmune diseases: localized and systemic. Localized diseases slowly destroy a specific type of organ or tissue, make an organ grow excessively, ...
... When the immune system malfunctions, it can affect the skin, heart, central nervous system, and almost any structure in the body. There are two types of autoimmune diseases: localized and systemic. Localized diseases slowly destroy a specific type of organ or tissue, make an organ grow excessively, ...
Vitamin A Quercetin Vitamin C Goldenseal Echinacea Ginseng Did
... optimal hydrolysis of food proteins to reduce food intolerances and allergies. Additionally, when taken between meals they impart numerous systemic benefits. Proteolytic enzymes have fibrinolytic activity which reduces inflammation and may help attenuate and/or prevent tumor cell growth. With respec ...
... optimal hydrolysis of food proteins to reduce food intolerances and allergies. Additionally, when taken between meals they impart numerous systemic benefits. Proteolytic enzymes have fibrinolytic activity which reduces inflammation and may help attenuate and/or prevent tumor cell growth. With respec ...
Modulation of Inflammatory Genes in Immune Cells by miR-150
... included a general exam for height, weight, BMI, serum inflammatory markers, and body composition (DXA), as well as a breathing test to measure lung inflammation (exhaled nitric oxide, eNO) and a complete laboratory metabolic panel (glucose, insulin, serum lipids). MicroRNAs were detected in serum b ...
... included a general exam for height, weight, BMI, serum inflammatory markers, and body composition (DXA), as well as a breathing test to measure lung inflammation (exhaled nitric oxide, eNO) and a complete laboratory metabolic panel (glucose, insulin, serum lipids). MicroRNAs were detected in serum b ...
- Abdel Hamid Derm Atlas
... Langerhans' cells may be processing antigen prior to their presentation to lymphocytes. Immune histochemistry of T lymphocytes bound in epidermis by anti CD2 monoclonal antibody are shown to be in close contact with epidermal cells and Langerhans' cells .Could this mean that keratinocytes and Langer ...
... Langerhans' cells may be processing antigen prior to their presentation to lymphocytes. Immune histochemistry of T lymphocytes bound in epidermis by anti CD2 monoclonal antibody are shown to be in close contact with epidermal cells and Langerhans' cells .Could this mean that keratinocytes and Langer ...
T cell
... 1. For cytotoxic CD8 T-cells, ligation of the TCR by MHC I/peptide + co-stimulation results in release of granzymes and perforin and/or FasL, leading to apoptosis of the target cells. 2. Viruses evade host defense, in part, by down-regulating MHC Class I. Uninfected dendritic cells circumvent this b ...
... 1. For cytotoxic CD8 T-cells, ligation of the TCR by MHC I/peptide + co-stimulation results in release of granzymes and perforin and/or FasL, leading to apoptosis of the target cells. 2. Viruses evade host defense, in part, by down-regulating MHC Class I. Uninfected dendritic cells circumvent this b ...
Central nervous system control and coordination
... They do not adapt and improve their effectiveness against previously encountered antigens. Nonspecific components include: Physical Barriers: skin, mucosa, stomach acid Chemical Agents: lysozymes complement Effector Cells: macrophages, natural killer cells Specific: also referred to as acquired imm ...
... They do not adapt and improve their effectiveness against previously encountered antigens. Nonspecific components include: Physical Barriers: skin, mucosa, stomach acid Chemical Agents: lysozymes complement Effector Cells: macrophages, natural killer cells Specific: also referred to as acquired imm ...
File
... production of IL-12 by the APC then the T cell itself secretes IL-4 inducing its differentiation into the Th2 phenotype. – This is what happens in infections by helminths which are too big to be phagocytosed. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-11B ...
... production of IL-12 by the APC then the T cell itself secretes IL-4 inducing its differentiation into the Th2 phenotype. – This is what happens in infections by helminths which are too big to be phagocytosed. Abbas & Lichtman’s Basic Immunology 5-11B ...
Immunol-mol-med-5-2010-Prof
... • “white pulp” - 20% of spleen • Distinct T and B follicular areas • Respond to circulating antigen - important in response to certain bacteria* • “Red pulp” area - phagocytic cells, storage of other cell types ...
... • “white pulp” - 20% of spleen • Distinct T and B follicular areas • Respond to circulating antigen - important in response to certain bacteria* • “Red pulp” area - phagocytic cells, storage of other cell types ...
Chapter 18
... presence or absence of antigens (agglutinogens) on RBCs – type A person has A antigens – type B person has B antigens – type AB has both antigens – type O has neither antigen • most common - type O • rarest - type AB ...
... presence or absence of antigens (agglutinogens) on RBCs – type A person has A antigens – type B person has B antigens – type AB has both antigens – type O has neither antigen • most common - type O • rarest - type AB ...
Microbiology
... Allograft: use of tissue from another person Xenotransplantation product: use of nonhuman tissue Hyperacute rejection: response to nonhuman Ag ...
... Allograft: use of tissue from another person Xenotransplantation product: use of nonhuman tissue Hyperacute rejection: response to nonhuman Ag ...
understanding the Immune System and AIDS Vaccine Strategies
... Humans are repeatedly exposed to various disease-causing organisms known as pathogens, including viruses and bacteria, which pose a threat to their health. The body defends itself against these foreign invaders using an incredibly complex network of cells, molecules, tissues, and organs, which toget ...
... Humans are repeatedly exposed to various disease-causing organisms known as pathogens, including viruses and bacteria, which pose a threat to their health. The body defends itself against these foreign invaders using an incredibly complex network of cells, molecules, tissues, and organs, which toget ...
S. Typhi-specific CD8+ T EM responses
... Uncovered, for the first time, that S. Typhi-specific CD8 T cell baseline responses correlate significantly with clinical outcome after infection Revealed some of the immunological mechanisms responsible for delayed time to disease onset Demonstrated that multifunctional T cells appear to play ...
... Uncovered, for the first time, that S. Typhi-specific CD8 T cell baseline responses correlate significantly with clinical outcome after infection Revealed some of the immunological mechanisms responsible for delayed time to disease onset Demonstrated that multifunctional T cells appear to play ...
Main Differences Between IgE and IgG Allergies
... After the exposure to peanuts, IgE antibodies can also attach themselves to mast cells. There the IgE antibodies wait until the next peanut exposure. When the next peanut exposure occurs the IgE antibodies signal the mast cells to release histamine and other compounds. Histamine and these other comp ...
... After the exposure to peanuts, IgE antibodies can also attach themselves to mast cells. There the IgE antibodies wait until the next peanut exposure. When the next peanut exposure occurs the IgE antibodies signal the mast cells to release histamine and other compounds. Histamine and these other comp ...
1 ANTIBIOTIC THERAPY Antibiotics and their MOA
... Avoid PCNs entirely In cases of a mild allergy, a cephalosporin could be used; if anaphylaxis or severe allergy, avoid a ceph (5-10% cross-sensitivity) Vancomycin and Erythromycin may be alternatives In life-threatening infections when no alternative will do, give PCN according to a desensitization ...
... Avoid PCNs entirely In cases of a mild allergy, a cephalosporin could be used; if anaphylaxis or severe allergy, avoid a ceph (5-10% cross-sensitivity) Vancomycin and Erythromycin may be alternatives In life-threatening infections when no alternative will do, give PCN according to a desensitization ...
Genetically Engineered Multivalent Proteins for Targeted
... toxicity with the retention of therapeutic activity. Mechanistically, mAbs utilize a variety of strategies to mediate antitumor activity (2). One such mechanism, antibodydependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), involves an interaction between the antibody Fc region and Fc receptors on immune cells, i ...
... toxicity with the retention of therapeutic activity. Mechanistically, mAbs utilize a variety of strategies to mediate antitumor activity (2). One such mechanism, antibodydependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), involves an interaction between the antibody Fc region and Fc receptors on immune cells, i ...
Cytotoxic T Cells
... and blocks an active site, preventing antigen binding to receptors on tissue cells Agglutination: antibodies are divalent (have more than one binding site); they can bind to more than one antigen at a time, forming cross linked clumps of antigen/antibody complexes Precipitation: same as agglutinatio ...
... and blocks an active site, preventing antigen binding to receptors on tissue cells Agglutination: antibodies are divalent (have more than one binding site); they can bind to more than one antigen at a time, forming cross linked clumps of antigen/antibody complexes Precipitation: same as agglutinatio ...
35-2 PowerPoint
... Cell-Mediated Immunity Although cytotoxic T cells are helpful in the immune system, they make the acceptance of organ transplants difficult. When an organ is transplanted from one person to another, the normal response of the recipient’s immune system would be to recognize it as nonself. T cells and ...
... Cell-Mediated Immunity Although cytotoxic T cells are helpful in the immune system, they make the acceptance of organ transplants difficult. When an organ is transplanted from one person to another, the normal response of the recipient’s immune system would be to recognize it as nonself. T cells and ...