Types of White Blood Cells WBCs.
... T cells come from PHSC and maturate in the thymus. B cells originate from bone marrow PHSC and maturate in the liver and bone marrow. T lymphocytes called the cell-mediated immunity B lymphocytes are known as humoral immunity because they produce anti bodies from plasma cells. ...
... T cells come from PHSC and maturate in the thymus. B cells originate from bone marrow PHSC and maturate in the liver and bone marrow. T lymphocytes called the cell-mediated immunity B lymphocytes are known as humoral immunity because they produce anti bodies from plasma cells. ...
No T cells
... an identical MHC gene locus T-cells recognize products of MHC genes as self or non-self If any cell of an individual starts to produce foreign (viral or bacterial) or abnormal (tumor associated) proteins, the T-cells recognize these antigen presenting cells as altered self cells and respond against ...
... an identical MHC gene locus T-cells recognize products of MHC genes as self or non-self If any cell of an individual starts to produce foreign (viral or bacterial) or abnormal (tumor associated) proteins, the T-cells recognize these antigen presenting cells as altered self cells and respond against ...
Exam 1 Exam 2 - Sinoe Medical Association
... receptor for an antigen on its cell surface, it is said to be immunocompetent. B. some lymphocytes will never encounter an antigen, to which they are capable of responding. C. an antigen only determines which existing lymphocytes will be stimulated to proliferate. ...
... receptor for an antigen on its cell surface, it is said to be immunocompetent. B. some lymphocytes will never encounter an antigen, to which they are capable of responding. C. an antigen only determines which existing lymphocytes will be stimulated to proliferate. ...
B Cells and Antibodies
... a B cell that cannot express a receptor is totally useless. If the heavy chain rearrangement is productive, the baby B cell proliferates for a bit, and then the light chain players step up to the table. The rules of their game are similar to those of the heavy chain game, but there is a second test ...
... a B cell that cannot express a receptor is totally useless. If the heavy chain rearrangement is productive, the baby B cell proliferates for a bit, and then the light chain players step up to the table. The rules of their game are similar to those of the heavy chain game, but there is a second test ...
Microbial Cell Wall Oligomannan Inhibits
... However this accounts for only a proportion of the heritability, and it is likely that other non-HLA genes are involved in disease development. Association of CD with a locus on chromosome 2q33, which contains the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated (CTLA-4)gene and the CD28 gene has been demonstrated ...
... However this accounts for only a proportion of the heritability, and it is likely that other non-HLA genes are involved in disease development. Association of CD with a locus on chromosome 2q33, which contains the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated (CTLA-4)gene and the CD28 gene has been demonstrated ...
Cytotoxic CD8 T
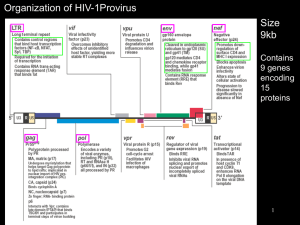
... • The sequence of a given viral envelope is specific for one of the chemokine receptor types • The main two chemokine receptors are CCR5 and CXCR4 that are distributed on different cell lineages • Strains that bind to CCR5 are termed “R5” tropic and those that bind CXCR4 are termed “R4” tropic ...
... • The sequence of a given viral envelope is specific for one of the chemokine receptor types • The main two chemokine receptors are CCR5 and CXCR4 that are distributed on different cell lineages • Strains that bind to CCR5 are termed “R5” tropic and those that bind CXCR4 are termed “R4” tropic ...
European Respiratory Society Annual Congress 2013
... commenced from day 3 of life. We hypothesised that age at first allergen exposure is critical in determining development of allergic immune responses and aimed to investigate disease progression when allergen exposure is commenced at different ages. Intranasal HDM or saline was administered intermit ...
... commenced from day 3 of life. We hypothesised that age at first allergen exposure is critical in determining development of allergic immune responses and aimed to investigate disease progression when allergen exposure is commenced at different ages. Intranasal HDM or saline was administered intermit ...
Three major uncertainties in the antibody therapy
... Antibodies against surface molecules of human tumors are now frequently administered in combination with strong chemotherapy, increasing therapeutic efficacy but making the task of elucidating immunological events more difficult. Experiments on genetically manipulated mice indicate that antibody eff ...
... Antibodies against surface molecules of human tumors are now frequently administered in combination with strong chemotherapy, increasing therapeutic efficacy but making the task of elucidating immunological events more difficult. Experiments on genetically manipulated mice indicate that antibody eff ...
PPoint - Doctor of the Future
... asthma Juvenile Diabetes has risen 5 fold in developed world – no increase in developing world Environmental pollution has been eliminated as the suspected cause Children with juvenile diabetes had fewer childhood infections Children with no infections during the first year of life are 5 tim ...
... asthma Juvenile Diabetes has risen 5 fold in developed world – no increase in developing world Environmental pollution has been eliminated as the suspected cause Children with juvenile diabetes had fewer childhood infections Children with no infections during the first year of life are 5 tim ...
ELISA technique
... cells are called hybridomas, and will continually grow and secrete antibody in culture. Single hybridoma cells are isolated by dilution cloning to generate cell clones that all produce the same antibody; these antibodies are called monoclonal antibodies ...
... cells are called hybridomas, and will continually grow and secrete antibody in culture. Single hybridoma cells are isolated by dilution cloning to generate cell clones that all produce the same antibody; these antibodies are called monoclonal antibodies ...
SWR Tatort Mensch
... molecules of the types MHC-I and MHC-II. The abbreviation MHC stands for major histocompatibility complex. All of the body's cells bear MHC-I molecules on their surface. In a manner of speaking, the MHC molecules serve as identification papers. They vary from one individual to the next and help the ...
... molecules of the types MHC-I and MHC-II. The abbreviation MHC stands for major histocompatibility complex. All of the body's cells bear MHC-I molecules on their surface. In a manner of speaking, the MHC molecules serve as identification papers. They vary from one individual to the next and help the ...
Cytokines and Chemokines
... • Some cytokines may also be associated with the extracellular matrix • Switching between soluble and membrane bound forms of cytokines may be an important immunoregulatory event • Most Cytokines are not stored inside cells (exceptions are, for example TGF-b and PDGF which are stored in platelets) ...
... • Some cytokines may also be associated with the extracellular matrix • Switching between soluble and membrane bound forms of cytokines may be an important immunoregulatory event • Most Cytokines are not stored inside cells (exceptions are, for example TGF-b and PDGF which are stored in platelets) ...
Ch18_Lecture - Ms. Lee`s Classes @ JICHS
... bile salts in the small intestine. Small intestine lining is not normally penetrated by pathogens. ...
... bile salts in the small intestine. Small intestine lining is not normally penetrated by pathogens. ...
Cells, Tissues and Organs of the Immune System
... Discovered receptor proteins that can recognize bacteria and other microorganisms as they enter the body, and activate the first line of defense in the immune system, known as innate immunity. ...
... Discovered receptor proteins that can recognize bacteria and other microorganisms as they enter the body, and activate the first line of defense in the immune system, known as innate immunity. ...
Course 24: Psychoneuroimmunology and neuroendocrinimmunology
... greatest on CD8+ cells, followed by macrophages, B cells, and CD4+ cells. By binding to these receptors on immune cells, NE is able to modulate their ability to function. The modulatory effect induced by NE on immune cells is usually inhibitory, but this inhibition may be dependent on the way cells ...
... greatest on CD8+ cells, followed by macrophages, B cells, and CD4+ cells. By binding to these receptors on immune cells, NE is able to modulate their ability to function. The modulatory effect induced by NE on immune cells is usually inhibitory, but this inhibition may be dependent on the way cells ...
Bones can be described on the basis of their overall macroscopic
... B and T cells originate in bone marrow B cells remain in bone marrow for maturation T cells leave bone marrow, and migrate to thymus gland for maturation Lymphocyte Activation All lymphocytes originate in bone marrow B lymphocytes remain in bone marrow for maturation T lymphocytes leave bone marrow, ...
... B and T cells originate in bone marrow B cells remain in bone marrow for maturation T cells leave bone marrow, and migrate to thymus gland for maturation Lymphocyte Activation All lymphocytes originate in bone marrow B lymphocytes remain in bone marrow for maturation T lymphocytes leave bone marrow, ...
immediate hypersensitivity
... The effects of these mediators become apparent about 6 hours after antigen contact and are marked by an infiltration of eosinophils and neutrophils. Clinical features of the late phase include erythema, induration, warmth, pruritus, and a burning sensation at the affected site. Fibrin deposition ...
... The effects of these mediators become apparent about 6 hours after antigen contact and are marked by an infiltration of eosinophils and neutrophils. Clinical features of the late phase include erythema, induration, warmth, pruritus, and a burning sensation at the affected site. Fibrin deposition ...
1 THE LAUGHTER: IMMUNE CONNECTION
... immunoregulator. IFN is a lymphokine, a soluble product produced by some lymphocytes that exert numerous biological functions including a variety of specific and nonspecific effects on other cells. IFN is produced by activated T cells and natural killer cells. It is active in fighting viruses and re ...
... immunoregulator. IFN is a lymphokine, a soluble product produced by some lymphocytes that exert numerous biological functions including a variety of specific and nonspecific effects on other cells. IFN is produced by activated T cells and natural killer cells. It is active in fighting viruses and re ...
Antigen-Antibody Interaction
... organism are called pathogens. Pathogens are typically microorganisms like viral, bacterial, and parasite antigens. Auto-antigens or self-antigens are tissues of the host that trigger an immune response and may be a signal of autoimmune disease. Tumour antigens are selfantigens that can cause harm t ...
... organism are called pathogens. Pathogens are typically microorganisms like viral, bacterial, and parasite antigens. Auto-antigens or self-antigens are tissues of the host that trigger an immune response and may be a signal of autoimmune disease. Tumour antigens are selfantigens that can cause harm t ...
05070302
... Fas ligand by tumor cells has been suggested as a tumor escape mechanism, how tumor cells kill activated cytotoxic T cells and thus avoid an antitumor immune response. ...
... Fas ligand by tumor cells has been suggested as a tumor escape mechanism, how tumor cells kill activated cytotoxic T cells and thus avoid an antitumor immune response. ...
Hemolytic disease of the newborn - Easymed.club
... that an infant is affected by HDN both in the fetus and newborn. State the treatment options for intrauterine treatment of HDN. State the treatment options for HDN in the moderately and severely affected newborn. State the requirements of blood to be used for transfusion of the fetus and newborn. ...
... that an infant is affected by HDN both in the fetus and newborn. State the treatment options for intrauterine treatment of HDN. State the treatment options for HDN in the moderately and severely affected newborn. State the requirements of blood to be used for transfusion of the fetus and newborn. ...
the emergence of immuno-oncology in clinical cancer research
... is suppressed for a number of cogent reasons. Cancer itself suppresses T-cell function as does prior anticancer therapy, especially chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Immune function decreases with age as the incidence of cancer increases with this demographic. Finally, upregulation and increased e ...
... is suppressed for a number of cogent reasons. Cancer itself suppresses T-cell function as does prior anticancer therapy, especially chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Immune function decreases with age as the incidence of cancer increases with this demographic. Finally, upregulation and increased e ...
Protein-energy malnutrition and wounds: nutritional
... Smaller serum pool Binds and transports Is affected by inflammation Less affected by hydration status Used to monitor current nutrition status ...
... Smaller serum pool Binds and transports Is affected by inflammation Less affected by hydration status Used to monitor current nutrition status ...