Chapter 8 Periodic Properties of the Element
... 2 electrons. p sublevel has 3 orbitals; therefore, it can hold 6 electrons. d sublevel has 5 orbitals; therefore, it can hold 10 electrons. f sublevel has 7 orbitals; therefore, it can hold 14 electrons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... 2 electrons. p sublevel has 3 orbitals; therefore, it can hold 6 electrons. d sublevel has 5 orbitals; therefore, it can hold 10 electrons. f sublevel has 7 orbitals; therefore, it can hold 14 electrons. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
key for Unit 1 pp 21
... simplest formula of the compound AND if it is known to have a molar mass of 181 g/mole, what is the molecular formula. strategy: (1) assume 100 g sample and convert % to grams, (2) convert the mass of each element to moles, and (3) divide by the smallest number of moles to get a whole number ratio. ...
... simplest formula of the compound AND if it is known to have a molar mass of 181 g/mole, what is the molecular formula. strategy: (1) assume 100 g sample and convert % to grams, (2) convert the mass of each element to moles, and (3) divide by the smallest number of moles to get a whole number ratio. ...
THE ATOM AND THE QUANTUM
... more complex model in which the electrons are represented as clouds spread throughout the interior of the atom, as shown in Figure 38.2. We will see that the planetary model of the atom is still useful for understanding the emission of light. Models are assessed not in terms of their “truthfulness,” ...
... more complex model in which the electrons are represented as clouds spread throughout the interior of the atom, as shown in Figure 38.2. We will see that the planetary model of the atom is still useful for understanding the emission of light. Models are assessed not in terms of their “truthfulness,” ...
Lecture Notes
... Moreover, we will describe the following properties of charge: g - Types of electric charge - Forces among two charges (Coulomb’s (Coulomb s law) - Charge quantization - Charge g conservation ...
... Moreover, we will describe the following properties of charge: g - Types of electric charge - Forces among two charges (Coulomb’s (Coulomb s law) - Charge quantization - Charge g conservation ...
Chemistry 101L
... Draw a straight line that best fits your data. The line does not have to pass through all data points, or through any of them, but it should pass as closely as possible to all of them. There should be about the same number of points above the line as below the line. Do not connect the dots. You shou ...
... Draw a straight line that best fits your data. The line does not have to pass through all data points, or through any of them, but it should pass as closely as possible to all of them. There should be about the same number of points above the line as below the line. Do not connect the dots. You shou ...
Atomic Model Timeline
... they are eternal, and always moving. He made a theory on this to explain why and how atoms were so small, and what they were about. He proposed a more advance atomic theory. http://www.philosophyprofessor.com/images/philosophers/democritus.jpg ...
... they are eternal, and always moving. He made a theory on this to explain why and how atoms were so small, and what they were about. He proposed a more advance atomic theory. http://www.philosophyprofessor.com/images/philosophers/democritus.jpg ...
Department of Chemistry First Year Syllabus
... Summary of Content The first year consists of 153 hours of chemistry lectures (plus approximately 50, maximum 60, hours of ancillary courses), 230 hours of practical work (one laboratory course each term) including a maths laboratory (24 hours) and three tutorials a week (in small groups of 4 to 6 s ...
... Summary of Content The first year consists of 153 hours of chemistry lectures (plus approximately 50, maximum 60, hours of ancillary courses), 230 hours of practical work (one laboratory course each term) including a maths laboratory (24 hours) and three tutorials a week (in small groups of 4 to 6 s ...
Atomic Model Timeline - Lewiston School District
... they are eternal, and always moving. He made a theory on this to explain why and how atoms were so small, and what they were about. He proposed a more advance atomic theory. http://www.philosophyprofessor.com/images/philosophers/democritus.jpg ...
... they are eternal, and always moving. He made a theory on this to explain why and how atoms were so small, and what they were about. He proposed a more advance atomic theory. http://www.philosophyprofessor.com/images/philosophers/democritus.jpg ...
File
... If you have 55.0g of C5H12, how many grams of water could you make? If you start with 6.0 liters of oxygen, what mass of carbon dioxide could you make? If you end up with 17 liters of CO2, what volume of oxygen would you have started ...
... If you have 55.0g of C5H12, how many grams of water could you make? If you start with 6.0 liters of oxygen, what mass of carbon dioxide could you make? If you end up with 17 liters of CO2, what volume of oxygen would you have started ...
ZOONO TECHNICAL OVERVIEW
... Note: This material is classified as an organ functional trihydroxysilane as it contains a functional organic group (quaternary nitrogen) covalently bound to a silicon atom. Organosilane denotes a minimum of one carbon-silicon bond. Trihydroxy describes the number of hydroxy groups bound to the sili ...
... Note: This material is classified as an organ functional trihydroxysilane as it contains a functional organic group (quaternary nitrogen) covalently bound to a silicon atom. Organosilane denotes a minimum of one carbon-silicon bond. Trihydroxy describes the number of hydroxy groups bound to the sili ...
Quantization of the Atom plus Attempting to
... an epochal moment in modern physics, it spot-lighted the conundrum posed by the new theory of radiation and the concept of the quantum. Nineteen extant experts from six European nations examined the most pressing problems of that era. In particular, Sommerfeld’s theory of X-ray waves, as well as the ...
... an epochal moment in modern physics, it spot-lighted the conundrum posed by the new theory of radiation and the concept of the quantum. Nineteen extant experts from six European nations examined the most pressing problems of that era. In particular, Sommerfeld’s theory of X-ray waves, as well as the ...
Chapter 17 Green chemistry
... account when deciding which method of production should be used. A4. Some factors would include: • The difference between the atom economies of each process • The degree of hazard of the starting material • Whether the hazardous material in the second method can be degraded into a benign compound Q5 ...
... account when deciding which method of production should be used. A4. Some factors would include: • The difference between the atom economies of each process • The degree of hazard of the starting material • Whether the hazardous material in the second method can be degraded into a benign compound Q5 ...
ch6 - ChemistryVCE
... a Metals and ionic solids both contain positive ions in a regular arrangement. b In metals and ionic solids, there is attraction between one particle and all the neighbouring particles of opposite charge. c In metals and ionic solids, there will be forces of repulsion between particles with like cha ...
... a Metals and ionic solids both contain positive ions in a regular arrangement. b In metals and ionic solids, there is attraction between one particle and all the neighbouring particles of opposite charge. c In metals and ionic solids, there will be forces of repulsion between particles with like cha ...
17 ADSORPTION AND CATALYSIS S MODULE - 5
... S urface of solids plays a crucial role in many physical and chemical phenomena. There are two main reasons for this special role. Firstly, the surface of a substance interacts first with its surroundings. Secondly, the surface molecules are in a different state as compared to the molecules in the i ...
... S urface of solids plays a crucial role in many physical and chemical phenomena. There are two main reasons for this special role. Firstly, the surface of a substance interacts first with its surroundings. Secondly, the surface molecules are in a different state as compared to the molecules in the i ...
Chapter 4 Power Point Quiz
... volume of 3.50 M H2SO4 is required to prepare 250.0 mL of 1.25 M H2SO4? a) b) c) d) ...
... volume of 3.50 M H2SO4 is required to prepare 250.0 mL of 1.25 M H2SO4? a) b) c) d) ...
Discover Chemical Changes - gk-12
... This lesson should be an open inquiry-based lesson where you have many stations set up with before and after chemical changes so that students can make the chemical changes happen themselves or at least make observations of chemical changes that have happened at each station. I have listed above 9 p ...
... This lesson should be an open inquiry-based lesson where you have many stations set up with before and after chemical changes so that students can make the chemical changes happen themselves or at least make observations of chemical changes that have happened at each station. I have listed above 9 p ...
Wizard Test Maker
... 56. When heat energy is lost by a pure substance at its freezing point, its potential energy 1) decreases 3) remains the same 2) increases 57. At STP, which of the following gases will diffuse most rapidly? 1) hydrogen 3) fluorine 2) nitrogen 4) oxygen ...
... 56. When heat energy is lost by a pure substance at its freezing point, its potential energy 1) decreases 3) remains the same 2) increases 57. At STP, which of the following gases will diffuse most rapidly? 1) hydrogen 3) fluorine 2) nitrogen 4) oxygen ...
Periodic table Periodic Trends
... electron. Remember that the atomic radius increases down a group. The atomic radius of chlorine (100pm) is smaller than that of bromine (117pm) so chlorine has a stronger attraction for a valence electron than does bromine. Therefore chlorine forms the chloride anion, Cl- more readily than bromine f ...
... electron. Remember that the atomic radius increases down a group. The atomic radius of chlorine (100pm) is smaller than that of bromine (117pm) so chlorine has a stronger attraction for a valence electron than does bromine. Therefore chlorine forms the chloride anion, Cl- more readily than bromine f ...
4.2 Structure of the Nuclear Atom
... If cathode rays are electrons given off by atoms, what remains of the atoms that have lost the electrons? • For example, after a hydrogen atom (the lightest kind of atom) loses an electron, what is left? ...
... If cathode rays are electrons given off by atoms, what remains of the atoms that have lost the electrons? • For example, after a hydrogen atom (the lightest kind of atom) loses an electron, what is left? ...
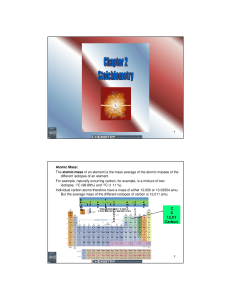
Atomic Mass: The atomic mass of an element is the mass average of
... Second: to determine the Empirical formula for ethanol: ...
... Second: to determine the Empirical formula for ethanol: ...
Atoms, Isotopes and Relative Atomic Masses
... Antimony, Sb, is a metal used in alloys to make lead harder. Bullets contain about 1% of antimony for this reason. Antimony has two main isotopes. (i) ...
... Antimony, Sb, is a metal used in alloys to make lead harder. Bullets contain about 1% of antimony for this reason. Antimony has two main isotopes. (i) ...
Changes in Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes
... How are you going to know if the equation is balanced if you don't actually make a list of how many of each atom you have? You won't. You have to make an inventory of how many atoms of each element you have, and then you have to keep it current throughout the whole problem. 4. Write numbers in front ...
... How are you going to know if the equation is balanced if you don't actually make a list of how many of each atom you have? You won't. You have to make an inventory of how many atoms of each element you have, and then you have to keep it current throughout the whole problem. 4. Write numbers in front ...
Unit 2 - Solon City Schools
... 19)______________________ A scientist whose research lead to the discovery that the nucleus is small, dense, and positively charged. The electrons orbit around the nucleus. The experiment he used is known as the gold foil experiment. 20)______________________ Smallest particle of an element that ret ...
... 19)______________________ A scientist whose research lead to the discovery that the nucleus is small, dense, and positively charged. The electrons orbit around the nucleus. The experiment he used is known as the gold foil experiment. 20)______________________ Smallest particle of an element that ret ...
GROUP 13 ELEMENTS -THE BORON FAMILY -
... do not shield the nuclear very effectively, so that the orbital electrons are more firmly or tightly held and the metal are less electropositive. This is evidenced by the increase of ionization energy between Al and Ga even though the large atom would be expected to have a lower value ...
... do not shield the nuclear very effectively, so that the orbital electrons are more firmly or tightly held and the metal are less electropositive. This is evidenced by the increase of ionization energy between Al and Ga even though the large atom would be expected to have a lower value ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.