chapter 2 - Columbia University
... •The shape, size, location, and movement of these particles make up literally all of the qualities, relations, and other features of the natural world. 384 - 270 BC ...
... •The shape, size, location, and movement of these particles make up literally all of the qualities, relations, and other features of the natural world. 384 - 270 BC ...
Ch 2 notes
... 1. qualitative…what does it contain, and 2. quantitative…how much of everything does it contain B) Stoichiometry – composition stoichiometry (this chapter) and reaction stoichiometry (ch 3) 2-1 Atoms and Molecules A) Aristotle v Democritus 1. Early scientists – philosophers/thinkers – NOT experiment ...
... 1. qualitative…what does it contain, and 2. quantitative…how much of everything does it contain B) Stoichiometry – composition stoichiometry (this chapter) and reaction stoichiometry (ch 3) 2-1 Atoms and Molecules A) Aristotle v Democritus 1. Early scientists – philosophers/thinkers – NOT experiment ...
Stoichiometry
... an Avogadro’s number of softdrink cans would cover the surface of the earth to a depth of over 200 miles if we were able to count atoms at the rate of 10 million per second, it would take about 2 billion years to count an Avogadro’s number of atoms ...
... an Avogadro’s number of softdrink cans would cover the surface of the earth to a depth of over 200 miles if we were able to count atoms at the rate of 10 million per second, it would take about 2 billion years to count an Avogadro’s number of atoms ...
CHEM 1411 CHAPTER 2
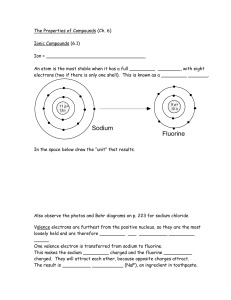
... Ions An ion is an atom or a group of atoms with positive or negative charges. The losing of electrons forms positive ions. They are also called cations. The gaining of electrons forms negative ions. They are also called anions. Molecular Formula and Empirical formula. The formula that gives the actu ...
... Ions An ion is an atom or a group of atoms with positive or negative charges. The losing of electrons forms positive ions. They are also called cations. The gaining of electrons forms negative ions. They are also called anions. Molecular Formula and Empirical formula. The formula that gives the actu ...
Atoms, and Elements
... 1. For main group elements, the charges of the ions formed by the atoms can be predicted by applying this principle: Atoms that are close to a noble gas( the nonmetals) form ions that contain the same number of electrons as the neighboring noble gas atom. 2. Metals of group 1A –3A form positive ions ...
... 1. For main group elements, the charges of the ions formed by the atoms can be predicted by applying this principle: Atoms that are close to a noble gas( the nonmetals) form ions that contain the same number of electrons as the neighboring noble gas atom. 2. Metals of group 1A –3A form positive ions ...
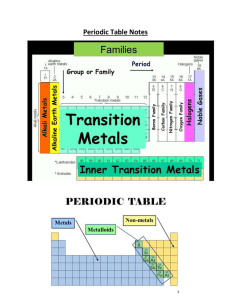
Period Table, valence Electrons and Ion Notes
... Example: Na = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Add up the e-‘s found in the last energy level, in this case there is only 1 so Na has 1 valence e**You have to do this for the Transition metal every time** ...
... Example: Na = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 Add up the e-‘s found in the last energy level, in this case there is only 1 so Na has 1 valence e**You have to do this for the Transition metal every time** ...
Understanding the Properties of Elements – Chapter 5
... 5. Compare the electrical conductivity of pure water, tap water, and salt water. ...
... 5. Compare the electrical conductivity of pure water, tap water, and salt water. ...
Chapter 2
... • Atoms of same element same; different element different • Compounds form from combinations of elements in definite proportions. • Chemical reactions involve rearrangements of atoms. ...
... • Atoms of same element same; different element different • Compounds form from combinations of elements in definite proportions. • Chemical reactions involve rearrangements of atoms. ...
Build an Atom
... of adding more of each particle. When the subatomic particles in an atom change, an ion, isotope or different element will be created. Procedure: Play with the Sims Chemistry Build An Atom Begin by playing with the simulation for a while. Become familiar with the interface. What happens when you ...
... of adding more of each particle. When the subatomic particles in an atom change, an ion, isotope or different element will be created. Procedure: Play with the Sims Chemistry Build An Atom Begin by playing with the simulation for a while. Become familiar with the interface. What happens when you ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... – Cations have lost one or more electrons giving them a positive charge(+) • Typically occur between elements on opposite sides of the periodic table. ...
... – Cations have lost one or more electrons giving them a positive charge(+) • Typically occur between elements on opposite sides of the periodic table. ...
Structure of the Nuclear Atom
... Structure of the Nuclear Atom Electrons Section 5.2 Electrons Remember Dalton? Most of his atomic theory is still accepted. Most !! Atoms are known to be divisible. Atoms are composed of smaller particles. These are the subatomic particles. Like… Electrons An electron is a negatively charged s ...
... Structure of the Nuclear Atom Electrons Section 5.2 Electrons Remember Dalton? Most of his atomic theory is still accepted. Most !! Atoms are known to be divisible. Atoms are composed of smaller particles. These are the subatomic particles. Like… Electrons An electron is a negatively charged s ...
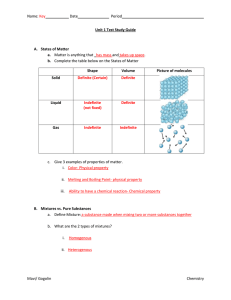
1 Unit 3 Notepack – Atomic Structure Unit 3 Objectives: 1. Describe
... In nature carbon is composed of 98.89% 12C atoms and 1.11% 13C atoms. 12C has a mass of 12 amu and 13C has a mass of 13.0034 amu. What is the average atomic mass of carbon? ...
... In nature carbon is composed of 98.89% 12C atoms and 1.11% 13C atoms. 12C has a mass of 12 amu and 13C has a mass of 13.0034 amu. What is the average atomic mass of carbon? ...
Bio_130_files/Chemistry Review
... – Cations have lost one or more electrons giving them a positive charge(+) • Typically occur between elements on opposite sides of the periodic table. ...
... – Cations have lost one or more electrons giving them a positive charge(+) • Typically occur between elements on opposite sides of the periodic table. ...
Topics for Final
... Amplitude, wavelength, frequency Electromagnetic radiation, atomic emission spectrum Planck’s Constant = h (E= hv) Photons, photoelectric effect, ground state ...
... Amplitude, wavelength, frequency Electromagnetic radiation, atomic emission spectrum Planck’s Constant = h (E= hv) Photons, photoelectric effect, ground state ...
Chapter 2 Test Review - Mercer Island School District
... 12. What evidence told scientists that electrons were located on specific energy levels, rather than being scattered randomly around the nucleus? • The emission spectrum. Specific Frequencies of light are observed. The light is emitted from electrons when they return to the ground state energy level ...
... 12. What evidence told scientists that electrons were located on specific energy levels, rather than being scattered randomly around the nucleus? • The emission spectrum. Specific Frequencies of light are observed. The light is emitted from electrons when they return to the ground state energy level ...
Discovery of electrons The size of an atom
... Nitrogen is to the left, so elements are in order: Nitrogen fluoride Add prefixes: dinitrogen trifluoride ...
... Nitrogen is to the left, so elements are in order: Nitrogen fluoride Add prefixes: dinitrogen trifluoride ...
Document
... 74. A column of elements in the periodic table is known as a ___________________. 75. What type of ions have names ending in –ide? ...
... 74. A column of elements in the periodic table is known as a ___________________. 75. What type of ions have names ending in –ide? ...
Matter Test: Review
... 28. What did Democritus call the particles? 29. What were Aristotle’s four elements? 30. What were Aristotle’s four properties which the elements were combinations of? ...
... 28. What did Democritus call the particles? 29. What were Aristotle’s four elements? 30. What were Aristotle’s four properties which the elements were combinations of? ...
Chemistry (B) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is the electron configuration of potassium? a. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s c. 1s 2s 3s 3p 3d b. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p d. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s ____ 53. Which of the following electromagnetic wav ...
... ____ 51. What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital? a. sphere c. bar b. dumbbell d. two perpendicular dumbbells ____ 52. What is the electron configuration of potassium? a. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s c. 1s 2s 3s 3p 3d b. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p d. 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s ____ 53. Which of the following electromagnetic wav ...
Study Guide Answer Key
... The mass doesn’t change in chemical reactions because the atoms only rearrange in the reaction, nothing is added or removed from the system. ...
... The mass doesn’t change in chemical reactions because the atoms only rearrange in the reaction, nothing is added or removed from the system. ...
Unit 01 Qual Chem
... Law of Conservation of Energy = energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Only transferred. ...
... Law of Conservation of Energy = energy can neither be created nor destroyed. Only transferred. ...
Bohr Models and Lewis Dot Structures
... 2-8-8 RULE!! Must fill an energy level to capacity before moving to the next energy level ...
... 2-8-8 RULE!! Must fill an energy level to capacity before moving to the next energy level ...
Chemistry Terms
... atomic number The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. chemical reaction A process in which atoms and molecules interact, resulting in the alteration of their molecular structures. covalent bond An atomic bond in which an electron is a resident of the out ...
... atomic number The atomic number of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom. chemical reaction A process in which atoms and molecules interact, resulting in the alteration of their molecular structures. covalent bond An atomic bond in which an electron is a resident of the out ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.