Lecture 2
... Ancient Greek philosophers proposed that all matter consisted of some combination of four elements: air, earth, fire, water. Democritus (~460-370 B.C.) disagreed, proposing that all matter could be repeatedly subdivided until an indivisible particle was reached. He called this the atom (Greek: a = n ...
... Ancient Greek philosophers proposed that all matter consisted of some combination of four elements: air, earth, fire, water. Democritus (~460-370 B.C.) disagreed, proposing that all matter could be repeatedly subdivided until an indivisible particle was reached. He called this the atom (Greek: a = n ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... He asked: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided? ...
... He asked: Could matter be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever, or was there a limit to the number of times a piece of matter could be divided? ...
Document
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory - Summary 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new comp ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory - Summary 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical 3. different elements have different atoms 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new comp ...
Atoms and Isotopes Worksheet
... 7. The # of protons in the nucleus of an atom is also known as the atomic _________ (mass/ number/ weight/ charge) 8. Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus? ____________________ ...
... 7. The # of protons in the nucleus of an atom is also known as the atomic _________ (mass/ number/ weight/ charge) 8. Which subatomic particles are found in the nucleus? ____________________ ...
Atomic Structure - Miami East Schools
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. Matter is composed of tiny indivisible atoms 2. All atoms of a given element are exactly the same 3. Different elements are made of different atoms 4. Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory 1. Matter is composed of tiny indivisible atoms 2. All atoms of a given element are exactly the same 3. Different elements are made of different atoms 4. Atoms of different elements can combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds ...
Name__________________________________________ Answers to Sample Exam Questions #1 Chemistry 112
... b) Atoms of the same element can be different. c) Compounds form when atoms combine in whole number ratios. d) A chemical reaction involves rearrangement of atoms. 3. Which of the following pairs of compounds illustrates the law of multiple proportions? a) Fe, FeO3 b) Cl, Cl2 c) H2SO4, NaOH d) H2O, ...
... b) Atoms of the same element can be different. c) Compounds form when atoms combine in whole number ratios. d) A chemical reaction involves rearrangement of atoms. 3. Which of the following pairs of compounds illustrates the law of multiple proportions? a) Fe, FeO3 b) Cl, Cl2 c) H2SO4, NaOH d) H2O, ...
Ch 3 Notes Atoms
... History lesson - originally H was the basis of all atomic masses and was given the mass of 1.0. Later, chemists changed the standard to oxygen being 16.000 (which left H = 1.008). In 1961, chemists agreed that 12C is the standard upon which all other masses are based. ...
... History lesson - originally H was the basis of all atomic masses and was given the mass of 1.0. Later, chemists changed the standard to oxygen being 16.000 (which left H = 1.008). In 1961, chemists agreed that 12C is the standard upon which all other masses are based. ...
Elements, Atomic Structure, and Atomic Models
... • Mixture of science and mysticism. • Lab procedures were developed, but alchemists did not perform controlled experiments like true scientists. ...
... • Mixture of science and mysticism. • Lab procedures were developed, but alchemists did not perform controlled experiments like true scientists. ...
5.1 section summary
... electrons within atoms. The chemical properties of atoms are related to the arrangement of the electrons within them. John Dalton proposed the first modern atomic theory. He portrayed the atom as a solid, indivisible mass. Next, J. J. Thomson discovered the electron and proposed the plum-pudding mod ...
... electrons within atoms. The chemical properties of atoms are related to the arrangement of the electrons within them. John Dalton proposed the first modern atomic theory. He portrayed the atom as a solid, indivisible mass. Next, J. J. Thomson discovered the electron and proposed the plum-pudding mod ...
Electron
... The first discovery of a subatomic particle resulted from investigating the relationship between electricity and matter Cathode Rays & Electrons In 1897, J.J. Thomson used a cathode ray tube to deduce (reason) the presence of a negatively charged particle Cathode ray tubes pass electricity t ...
... The first discovery of a subatomic particle resulted from investigating the relationship between electricity and matter Cathode Rays & Electrons In 1897, J.J. Thomson used a cathode ray tube to deduce (reason) the presence of a negatively charged particle Cathode ray tubes pass electricity t ...
Atoms and the Periodic Table Test
... How can you use the periodic table to tell you how many valence electrons an element has? How can you use the periodic table to tell how many energy levels an element has? ...
... How can you use the periodic table to tell you how many valence electrons an element has? How can you use the periodic table to tell how many energy levels an element has? ...
Hydrogen Bonding
... It is the cardinal rule of bonding. It is the gain in stability when atoms have a full complement of eight electrons in their valence shells. The bonding in carbon dioxide (CO2): all atoms are surrounded by 8 electrons, fulfilling the octet rule http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Octet_rule ...
... It is the cardinal rule of bonding. It is the gain in stability when atoms have a full complement of eight electrons in their valence shells. The bonding in carbon dioxide (CO2): all atoms are surrounded by 8 electrons, fulfilling the octet rule http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Octet_rule ...
ATOMIC THEORY
... about the men whose quests for knowledge about the fundamental nature of the universe helped define our views. ...
... about the men whose quests for knowledge about the fundamental nature of the universe helped define our views. ...
The structure of atoms
... answer, is: what is the world composed of? The greek philosopher Democritus is considered the first who proposed the existence of atoms. He argued that the world is made up of indivisible particles (atomos = indivisible, greek), and the vaccum inbetween. The real turn in this view was brought by the ...
... answer, is: what is the world composed of? The greek philosopher Democritus is considered the first who proposed the existence of atoms. He argued that the world is made up of indivisible particles (atomos = indivisible, greek), and the vaccum inbetween. The real turn in this view was brought by the ...
Unit 2 * Chapter 11 - Dr. Wall`s Science
... – 440 BCE – Idea that cutting something until it cannot be cut anymore ...
... – 440 BCE – Idea that cutting something until it cannot be cut anymore ...
CHAPTER 18 NOTES
... • Area around the nucleus of an atom where its electrons are most likely found • Farther an electron is from the nucleus, the more energy • Electrons with lower amount of energy are in the first level • 1st – 2 electrons 2nd – 8 electrons 3rd – 18 electrons 4th – 32 electrons ...
... • Area around the nucleus of an atom where its electrons are most likely found • Farther an electron is from the nucleus, the more energy • Electrons with lower amount of energy are in the first level • 1st – 2 electrons 2nd – 8 electrons 3rd – 18 electrons 4th – 32 electrons ...
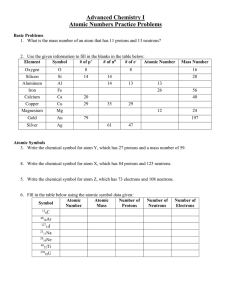
Atomic Numbers Practice Problems
... 7. With respect to the three fundamental particles of atoms, which numbers of particles are the same between two isotopes, and which ones are different? ...
... 7. With respect to the three fundamental particles of atoms, which numbers of particles are the same between two isotopes, and which ones are different? ...
study guide - atomic srtucture/_classification of matter
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
... idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still believed today. They are: 1. All matter is composed of extremely small particles too small to see 2. In reactio ...
Chp 4 slideshow notes - Lower Cape May Regional School District
... Our understanding of atoms took many centuries. The 4th century Greek philosopher, Democritus, suggested that the universe was made of invisible units called “atoms”. The word atom means “that which cannot be divided”. The Greek idea of atoms had to wait 2000 years before it became accepted. ...
... Our understanding of atoms took many centuries. The 4th century Greek philosopher, Democritus, suggested that the universe was made of invisible units called “atoms”. The word atom means “that which cannot be divided”. The Greek idea of atoms had to wait 2000 years before it became accepted. ...
Science 9 Topic 3 What Are Elements Name:
... An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of particle, or atom. Each element has its own unique set of distinguishing properties and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by means of a chemical change. A compound is a pure substance made up of 2 or more elements chemically comb ...
... An element is a pure substance made up of only one type of particle, or atom. Each element has its own unique set of distinguishing properties and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by means of a chemical change. A compound is a pure substance made up of 2 or more elements chemically comb ...
Review Packet
... After much observation and questioning, Democritus concluded that matter could not be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. Eventually the smallest possible piece would be obtained. All elements are composed of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible particles. Atoms of the sam ...
... After much observation and questioning, Democritus concluded that matter could not be divided into smaller and smaller pieces forever. Eventually the smallest possible piece would be obtained. All elements are composed of atoms. Atoms are indivisible and indestructible particles. Atoms of the sam ...
The Chemistry of Life
... Combining of elements involving interactions In order to achieve stability, an atom will either gain, lose, or share electrons. ...
... Combining of elements involving interactions In order to achieve stability, an atom will either gain, lose, or share electrons. ...
PowerPoint - Models of the Atom
... B.C. - Democritus thought matter could not be divided indefinitely. ...
... B.C. - Democritus thought matter could not be divided indefinitely. ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.