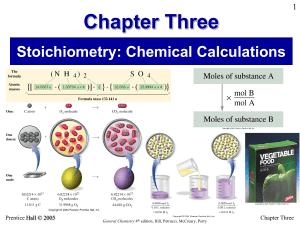
Conversion Problems
... simplest formula of the compound AND if it is known to have a molar mass of 181 g/mole, what is the molecular formula. strategy: (1) assume 100 g sample and convert % to grams, (2) convert the mass of each element to moles, and (3) divide by the smallest number of moles to get a whole number ratio. ...
... simplest formula of the compound AND if it is known to have a molar mass of 181 g/mole, what is the molecular formula. strategy: (1) assume 100 g sample and convert % to grams, (2) convert the mass of each element to moles, and (3) divide by the smallest number of moles to get a whole number ratio. ...
Chapter Three - CNG Chemistry
... In these examples, note the common practice of expressing molar mass and Avogadro’s number with at least one significant figure more than the number of significant figures in the least precisely known quantity. Doing this ensures that the precision of the calculated results is limited only by the le ...
... In these examples, note the common practice of expressing molar mass and Avogadro’s number with at least one significant figure more than the number of significant figures in the least precisely known quantity. Doing this ensures that the precision of the calculated results is limited only by the le ...
Organic and Bio-Molecular Chemistry
... Once we know the geometry of the three carbon atom building blocks, we can start to build and represent the organic molecules emphasizing their size and geometry. In order to do that we need a conventional method to draw the three-dimensional structures in two dimensions on a sheet of paper. 3.1. Gr ...
... Once we know the geometry of the three carbon atom building blocks, we can start to build and represent the organic molecules emphasizing their size and geometry. In order to do that we need a conventional method to draw the three-dimensional structures in two dimensions on a sheet of paper. 3.1. Gr ...
Chem 111 2:30p section Final Exam
... Ch 7.1 – wavelength & frequency 34a. What is the maximum number of orbitals that can be identified by the set of quantum numbers n=+5 l=+2 ? ...
... Ch 7.1 – wavelength & frequency 34a. What is the maximum number of orbitals that can be identified by the set of quantum numbers n=+5 l=+2 ? ...
chemistry
... 70 Explain why the radius of a positive ion of element M is smaller than the radius of an atom of element M. [1] 71 Using the symbol M for the element, write the chemical formula for the compound that forms when element M reacts with iodine. [1] ...
... 70 Explain why the radius of a positive ion of element M is smaller than the radius of an atom of element M. [1] 71 Using the symbol M for the element, write the chemical formula for the compound that forms when element M reacts with iodine. [1] ...
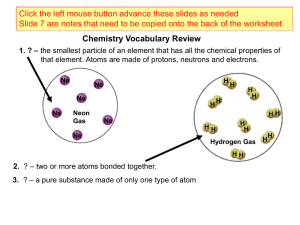
bond
... Organic Chemistry • Carbon-containing compounds were once considered “organ compounds” available only from living organisms. • The synthesis of the simple organic compound urea in 1828 showed that organic compounds can be prepared in the laboratory from non-living material. • Today, organic natural ...
... Organic Chemistry • Carbon-containing compounds were once considered “organ compounds” available only from living organisms. • The synthesis of the simple organic compound urea in 1828 showed that organic compounds can be prepared in the laboratory from non-living material. • Today, organic natural ...
____ 1. The energy required to convert a ground
... 51. In a qualitative analysis for the presence of Pb2+, Fe2+, and Cu2+ ions in aqueous solution, which of the following will allow the separation of Pb2+ from the other ions at room temperature? a. Adding dilute Na2S(aq) solution d. Adding dilute NH3(aq) solution b. Adding dilute HCl(aq) solution e. ...
... 51. In a qualitative analysis for the presence of Pb2+, Fe2+, and Cu2+ ions in aqueous solution, which of the following will allow the separation of Pb2+ from the other ions at room temperature? a. Adding dilute Na2S(aq) solution d. Adding dilute NH3(aq) solution b. Adding dilute HCl(aq) solution e. ...
Chapter 3: Formulae, Equations and Moles (Ch3 Chang, Ch3
... The empirical formula is the smallest whole number ratio of the elements present. It is consistent with the molecular formula, but does not have to be equal to it. E.g. hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, MF = H2O2 but EF = HO. ...
... The empirical formula is the smallest whole number ratio of the elements present. It is consistent with the molecular formula, but does not have to be equal to it. E.g. hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, MF = H2O2 but EF = HO. ...
Mendeleev`s Periodic Table
... in which he wrote: “If the elements are arranged in the order of their equivalents, with a few slight transpositions, as in the accompanying table, it will be observed that elements belonging to the same group usually appear on the same horizontal line. It will also be seen that the numbers of analo ...
... in which he wrote: “If the elements are arranged in the order of their equivalents, with a few slight transpositions, as in the accompanying table, it will be observed that elements belonging to the same group usually appear on the same horizontal line. It will also be seen that the numbers of analo ...
Mole/Stoich PowerPoint Notes
... • This is the exact formula of the molecule giving types of atoms and numbers of each type. This formula represents how the compound actually appears in nature. • You will need to be able to determine the molecular formula using data. ...
... • This is the exact formula of the molecule giving types of atoms and numbers of each type. This formula represents how the compound actually appears in nature. • You will need to be able to determine the molecular formula using data. ...
Chapter 2 slides
... Proposed by Joseph Proust between 1797 and 1804 A compound always has the same relative amounts of the elements that compose it. For example, when water is broken down by electrolysis into oxygen and hydrogen, the mass ratio is always 8 to 1. Figure 1.2 ...
... Proposed by Joseph Proust between 1797 and 1804 A compound always has the same relative amounts of the elements that compose it. For example, when water is broken down by electrolysis into oxygen and hydrogen, the mass ratio is always 8 to 1. Figure 1.2 ...
Dr David`s Chemistry Test Answers
... pressure would make the process less economic due to the increased costs of equipment and maintenance and a lower temperature would slow the reaction again reducing the overall economy. 2. Nitric acid the, Ostwald process: Ammonia is oxidised in air using a catalyst of rhodium and platinum at a temp ...
... pressure would make the process less economic due to the increased costs of equipment and maintenance and a lower temperature would slow the reaction again reducing the overall economy. 2. Nitric acid the, Ostwald process: Ammonia is oxidised in air using a catalyst of rhodium and platinum at a temp ...
CHAPTER 8 PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS AMONG THE ELEMENTS
... table, the ionization energies will continue to increase as we move to P. Continuing across to Cl and moving up the halogen group, F will have a higher ionization energy than P. Finally, Ne is to the right of F in period two, thus it will have a higher ionization energy. The correct order of increas ...
... table, the ionization energies will continue to increase as we move to P. Continuing across to Cl and moving up the halogen group, F will have a higher ionization energy than P. Finally, Ne is to the right of F in period two, thus it will have a higher ionization energy. The correct order of increas ...
Prospectus B.S. Chemistry 2014 Department of Chemistry
... Biochemistry (4 credits: 3 Lectures+ 3-hour Lab) Spring [REAL] Students in this course will apply principles from general and organic chemistry, as well as general biology, to understand the molecular processes that characterize life. The goal of this class will be to give students a solid backgroun ...
... Biochemistry (4 credits: 3 Lectures+ 3-hour Lab) Spring [REAL] Students in this course will apply principles from general and organic chemistry, as well as general biology, to understand the molecular processes that characterize life. The goal of this class will be to give students a solid backgroun ...
Unit 2: Atomic Concepts and Periodic Table (Level 1)
... the family. For the first two families (alkali metals and alkaline earth metals) it’s a single digit number, so there’s no confusion. Alkali metals are group 1, which means all elements in that family have 1 valence electron. The halogen family, on the other hand, is group 17, which means they have ...
... the family. For the first two families (alkali metals and alkaline earth metals) it’s a single digit number, so there’s no confusion. Alkali metals are group 1, which means all elements in that family have 1 valence electron. The halogen family, on the other hand, is group 17, which means they have ...
Follow this presentation to draw atoms 1-13
... strainer or filter can keep the pepper on top while the saltwater goes through. Heat can then be used to boil off the water leaving the salt in the pan. It takes too long to use tweezers to separate salt and pepper grains. ...
... strainer or filter can keep the pepper on top while the saltwater goes through. Heat can then be used to boil off the water leaving the salt in the pan. It takes too long to use tweezers to separate salt and pepper grains. ...
NCERT Solution - Mywayteaching
... Lattice energy is directly proportional to the charge carried by an ion. When a metal combines with oxygen, the lattice energy of the oxide involving O2− ion is much more than the oxide involving O− ion. Hence, the oxide having O2− ions are more stable than oxides having O−. Hence, we can say that f ...
... Lattice energy is directly proportional to the charge carried by an ion. When a metal combines with oxygen, the lattice energy of the oxide involving O2− ion is much more than the oxide involving O− ion. Hence, the oxide having O2− ions are more stable than oxides having O−. Hence, we can say that f ...
this PDF file
... Teaching atomic structure within a history and philosophy of chemistry perspective has been recognized by researchers in science education. The present study aimed at evaluation of the presentation of chemistry textbooks used in secondary schools in Tanzania. The criteria used for evaluation were th ...
... Teaching atomic structure within a history and philosophy of chemistry perspective has been recognized by researchers in science education. The present study aimed at evaluation of the presentation of chemistry textbooks used in secondary schools in Tanzania. The criteria used for evaluation were th ...
Answers - University of Waterloo
... Use the following information and diagram to answer questions 7-10. A galvanic cell is constructed by placing a strip of zinc into a 1.0 mol L−1 solution of zinc nitrate and a strip of aluminum into a 1.0 mol L−1 solution of aluminum nitrate. The two metal strips are connected to a voltmeter by wire ...
... Use the following information and diagram to answer questions 7-10. A galvanic cell is constructed by placing a strip of zinc into a 1.0 mol L−1 solution of zinc nitrate and a strip of aluminum into a 1.0 mol L−1 solution of aluminum nitrate. The two metal strips are connected to a voltmeter by wire ...
Atomic Structure
... What is the atomic number (Z) and the mass number (A) of an isotope of lithium containing 4 neutrons? A lithium atom contains 3 protons in its nucleus. atomic number Z = number of protons = 3 number of neutrons = 4 mass number A = (number of protons) + (number of neutrons) mass number A = (3) + (4) ...
... What is the atomic number (Z) and the mass number (A) of an isotope of lithium containing 4 neutrons? A lithium atom contains 3 protons in its nucleus. atomic number Z = number of protons = 3 number of neutrons = 4 mass number A = (number of protons) + (number of neutrons) mass number A = (3) + (4) ...
Chemistry HSC - The Bored of Studies Community
... Polymerisation is the process of bonding monomers together to form long chains. Polymers are macromolecules consisting of small repeating units called monomers joined by covalent chemical bonds. Polymers can be divided into two categories: 1. Natural polymers – naturally occurring polymers used by h ...
... Polymerisation is the process of bonding monomers together to form long chains. Polymers are macromolecules consisting of small repeating units called monomers joined by covalent chemical bonds. Polymers can be divided into two categories: 1. Natural polymers – naturally occurring polymers used by h ...
Explained answers - Admissions Testing Service
... Bile is alkaline and neutralises the acid material released from the stomach into the small intestine. This will increase the pH rather than reduce it. Therefore statement 2 is incorrect. Lipase is not present in human bile. Therefore statement 3 is incorrect. The answer is B ...
... Bile is alkaline and neutralises the acid material released from the stomach into the small intestine. This will increase the pH rather than reduce it. Therefore statement 2 is incorrect. Lipase is not present in human bile. Therefore statement 3 is incorrect. The answer is B ...
Chapter
... • Structural Formula describe the kinds of elements found in the compound, the numbers of their atoms, order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment they do not directly describe the 3-dimensional shape, but an experienced chemist can make a good guess at it use lines to represent covalen ...
... • Structural Formula describe the kinds of elements found in the compound, the numbers of their atoms, order of atom attachment, and the kind of attachment they do not directly describe the 3-dimensional shape, but an experienced chemist can make a good guess at it use lines to represent covalen ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Change
... Marie began to test about matter were various substances based on the ideas for radioactivity. of the ancient Analyzing a mineral Greek philosopher composite called Aristotle. He postupitchblende, a lated that all matter known source of consisted of four uranium, she was elements: earth, startled to ...
... Marie began to test about matter were various substances based on the ideas for radioactivity. of the ancient Analyzing a mineral Greek philosopher composite called Aristotle. He postupitchblende, a lated that all matter known source of consisted of four uranium, she was elements: earth, startled to ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.