Chapter 5.3 - Isotopes of Elements
... 6. Below the diagram, write the mass number found in the mass number box. 7. Drag one neutron towards the center. 8. Draw your diagram in the second box including symbol and mass number. 9. Drag another neutron towards the center. 10. Draw your diagram in the third box including symbol and mass numb ...
... 6. Below the diagram, write the mass number found in the mass number box. 7. Drag one neutron towards the center. 8. Draw your diagram in the second box including symbol and mass number. 9. Drag another neutron towards the center. 10. Draw your diagram in the third box including symbol and mass numb ...
Workshop material for week 2 Homework assigned
... • Summarize these findings with the expression and explain that the second power was discovered by Coulomb using a torsion balance • Go back in time to the 1700s and ask what are the units of charge? • Explain that it is a new property of matter and cannot be measure in the usual units (m or s); Cou ...
... • Summarize these findings with the expression and explain that the second power was discovered by Coulomb using a torsion balance • Go back in time to the 1700s and ask what are the units of charge? • Explain that it is a new property of matter and cannot be measure in the usual units (m or s); Cou ...
Rutherford`s Gold-Foil Experiment In 1911, Rutherford and his
... massive alpha particles, which are helium atoms that have lost their two electrons and have a double positive charge because of the two remaining protons. In the experiment, illustrated in Figure 4.7, a narrow beam of alpha particles was directed at a very thin sheet of gold foil. According to the p ...
... massive alpha particles, which are helium atoms that have lost their two electrons and have a double positive charge because of the two remaining protons. In the experiment, illustrated in Figure 4.7, a narrow beam of alpha particles was directed at a very thin sheet of gold foil. According to the p ...
(+) emitter super thin gold foil
... Early History of Atomic Theory According to Dalton’s theory, atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. Dalton’s theory CAN explain how elements and compounds have an exact composition. Dalton’s theory can NOT explain ... ... what atoms are made of or ... ... how atoms are structured (put to ...
... Early History of Atomic Theory According to Dalton’s theory, atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. Dalton’s theory CAN explain how elements and compounds have an exact composition. Dalton’s theory can NOT explain ... ... what atoms are made of or ... ... how atoms are structured (put to ...
Ch 3 Outline- Intro to Atom and Periodic Table
... a. Democratus-proposed that matter was formed from small pieces that couldn’t be cut into smaller parts. (439 BC) b. Used the word atomos, which means “un-cuttable”. c. The idea of an “atom” being the smallest particle of matter developed in 1600s as more scientists experimented and gathered evidenc ...
... a. Democratus-proposed that matter was formed from small pieces that couldn’t be cut into smaller parts. (439 BC) b. Used the word atomos, which means “un-cuttable”. c. The idea of an “atom” being the smallest particle of matter developed in 1600s as more scientists experimented and gathered evidenc ...
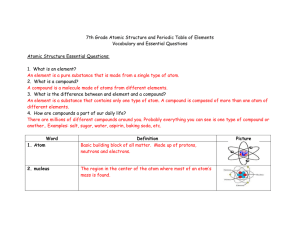
7th Grade Atomic Structure and Periodic Table of Elements
... An element is a pure substance that is made from a single type of atom. 2. What is a compound? A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is co ...
... An element is a pure substance that is made from a single type of atom. 2. What is a compound? A compound is a molecule made of atoms from different elements. 3. What is the difference between and element and a compound? An element is a substance that contains only one type of atom. A compound is co ...
Atoms, Molecules and Periodic Table
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Atoms
... • Help make up the nucleus of the atom • Help identify the atom (could be considered an atom’s DNA) • Equal to the atomic number of the atom • Contribute to the atomic mass • Equal to the number of electrons ...
... • Help make up the nucleus of the atom • Help identify the atom (could be considered an atom’s DNA) • Equal to the atomic number of the atom • Contribute to the atomic mass • Equal to the number of electrons ...
What is Organic Chemistry?
... removing an electron from an orbital closer to the nucleus. Electrons in the closer orbitals experience greater forces of electrostatic attraction; thus, their removal requires increasingly more energy.) ...
... removing an electron from an orbital closer to the nucleus. Electrons in the closer orbitals experience greater forces of electrostatic attraction; thus, their removal requires increasingly more energy.) ...
Worksheet 2 Structure of matter Task 2.1.
... A. Read the text provided and underline in red the sentences, which state what makes the atoms of two different elements different from each other. B. Underline in blue the sentences, which state why all atoms of an element do not have the same number of neutrons All matter, such as solids, liquids ...
... A. Read the text provided and underline in red the sentences, which state what makes the atoms of two different elements different from each other. B. Underline in blue the sentences, which state why all atoms of an element do not have the same number of neutrons All matter, such as solids, liquids ...
Unit3IonsEtc - Montville.net
... • Matter is composed of atoms – moving around in empty space • Atoms are solid homogeneous, indestructible and indivisible • Different size and shape • Size shape & movement determine the properties of matter Aristotle – ( 384 322 B.C.) • Empty space cannot exist • Matter is made of earth, fire air ...
... • Matter is composed of atoms – moving around in empty space • Atoms are solid homogeneous, indestructible and indivisible • Different size and shape • Size shape & movement determine the properties of matter Aristotle – ( 384 322 B.C.) • Empty space cannot exist • Matter is made of earth, fire air ...
Chem BIG REVIEW - Jones-wiki
... A. Electrons absorb energy as they move to an excited state. B. Electrons release energy as they move to an excited state. C. Electrons absorb energy as they return to the ground state. D. Electrons release energy as they return to the ground state. 6. Which statement regarding red and green visible ...
... A. Electrons absorb energy as they move to an excited state. B. Electrons release energy as they move to an excited state. C. Electrons absorb energy as they return to the ground state. D. Electrons release energy as they return to the ground state. 6. Which statement regarding red and green visible ...
LESSON PLAN Subject: Chemistry Topic: Matter matters!
... A. Read the text provided and underline in red the sentences, which state what makes the atoms of two different elements different from each other. B. Underline in blue the sentences, which state why all atoms of an element do not have the same number of neutrons All matter, such as solids, liquids ...
... A. Read the text provided and underline in red the sentences, which state what makes the atoms of two different elements different from each other. B. Underline in blue the sentences, which state why all atoms of an element do not have the same number of neutrons All matter, such as solids, liquids ...
Atomic Masses
... Dalton’s atomic theory. Identify the parts of an atom, their location, charge, and relative mass. Determine the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom. ...
... Dalton’s atomic theory. Identify the parts of an atom, their location, charge, and relative mass. Determine the numbers of subatomic particles in an atom. ...
Ch 2 Test
... b. All the protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. c. Electrons travel in definite circular pathways around the nucleus. d. All atomic nuclei are positively charged. 2. In _____, the atomic number decreases by two. a. alpha decay b. beta decay c. gamma decay d. omega decay 3. Which of the f ...
... b. All the protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus. c. Electrons travel in definite circular pathways around the nucleus. d. All atomic nuclei are positively charged. 2. In _____, the atomic number decreases by two. a. alpha decay b. beta decay c. gamma decay d. omega decay 3. Which of the f ...
Subatomic Particles
... atomic number =# of p+, this is the only number that cannot change for an element. electrons- if the atom is neutral then # of p+= # of e-. If it has a charge change this number to agree. neutrons- mass number – atomic number = # of no Do not use the mass number from the ...
... atomic number =# of p+, this is the only number that cannot change for an element. electrons- if the atom is neutral then # of p+= # of e-. If it has a charge change this number to agree. neutrons- mass number – atomic number = # of no Do not use the mass number from the ...
Midterm Review
... Define the law of multiple proportions and provide examples of two compounds that illustrate the concept. ...
... Define the law of multiple proportions and provide examples of two compounds that illustrate the concept. ...
APS Practice Final 2011
... ____ 102. If you are given the mass of an object in pounds, the time in seconds, and the distance in feet, what must you do before you can calculate the momentum in SI units? a. convert the mass to kilograms c. Both (a) and (b) b. convert the distance to meters d. None of the above ____ 103. Weight ...
... ____ 102. If you are given the mass of an object in pounds, the time in seconds, and the distance in feet, what must you do before you can calculate the momentum in SI units? a. convert the mass to kilograms c. Both (a) and (b) b. convert the distance to meters d. None of the above ____ 103. Weight ...
Practice exam Part 3 Name 1) A Ca 2+ ion differs from a Ca0 atom in
... 2) Which particles are referred to as nucleons (subatomic particles located in the nucleus)? a) protons and neutrons c) neutrons, only b) protons and electrons d) neutrons and electrons 3) What is the mass number of an atom that contains 19 protons, 19 electrons, and 20 neutrons? a) 39 b) 19 ...
... 2) Which particles are referred to as nucleons (subatomic particles located in the nucleus)? a) protons and neutrons c) neutrons, only b) protons and electrons d) neutrons and electrons 3) What is the mass number of an atom that contains 19 protons, 19 electrons, and 20 neutrons? a) 39 b) 19 ...
Notes - The Models of the Atom
... A model is a visual, verbal or mathematical explanation of how phenomena occur or how data and events are related. Because atoms are so small, models are helpful to explain their structure. As we have learned more about the atom, we have had to update our models of it. This outline traces the atomic ...
... A model is a visual, verbal or mathematical explanation of how phenomena occur or how data and events are related. Because atoms are so small, models are helpful to explain their structure. As we have learned more about the atom, we have had to update our models of it. This outline traces the atomic ...
atomic mass - Belle Vernon Area School District
... composed of tiny electrically charged particles He designed an experiment to demonstrate this by measuring the amount of force it took to deflect the particles path a given amount A force was exerted by placing a charged electric field around the CRT 1. charged matter is attracted to an electric f ...
... composed of tiny electrically charged particles He designed an experiment to demonstrate this by measuring the amount of force it took to deflect the particles path a given amount A force was exerted by placing a charged electric field around the CRT 1. charged matter is attracted to an electric f ...
1. Base your answer to the following question - Trupia
... Elements with atomic numbers 112 and 114 have been produced and their IUPAC names are pending approval. However, an element that would be put between these two elements on the Periodic Table has not yet been produced. If produced, this element will be identified by the symbol Uut until an IUPAC name ...
... Elements with atomic numbers 112 and 114 have been produced and their IUPAC names are pending approval. However, an element that would be put between these two elements on the Periodic Table has not yet been produced. If produced, this element will be identified by the symbol Uut until an IUPAC name ...
History of molecular theory
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more atoms.The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific Greek philosophers such as Leucippus who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles imagined fundamental elements (fire (20px), earth (20px), air (20px), and water (20px)) and ""forces"" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this, Heraclitus had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus, Plato, following Pythagoras, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical substances such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.