Introduction to Cognitive Science
... Computations might still be sufficient for mentality even if some aspects of the human mind can only be explained neuro-physiologically. ...
... Computations might still be sufficient for mentality even if some aspects of the human mind can only be explained neuro-physiologically. ...
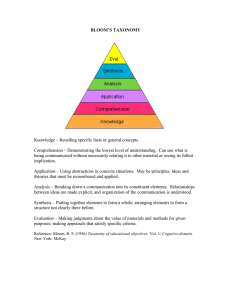
BLOOM`S TAXONOMY Knowledge – Recalling specific facts or
... Knowledge – Recalling specific facts or general concepts. Comprehension – Demonstrating the lowest level of understanding. Can use what is being communicated without necessarily relating it to other material or seeing its fullest implication. Application – Using abstractions in concrete situations. ...
... Knowledge – Recalling specific facts or general concepts. Comprehension – Demonstrating the lowest level of understanding. Can use what is being communicated without necessarily relating it to other material or seeing its fullest implication. Application – Using abstractions in concrete situations. ...
Thinking and Language Chapter 10
... Some thought does not need words to accomplish. When you think about how to turn on your faucet you do it through mental images. Mentally practicing things improves performance. Implicit memories and activities are thought about in pictures. Thinking affects our language which then affects our thoug ...
... Some thought does not need words to accomplish. When you think about how to turn on your faucet you do it through mental images. Mentally practicing things improves performance. Implicit memories and activities are thought about in pictures. Thinking affects our language which then affects our thoug ...
College Readiness David Conley`s Key Cognitive Strategies for
... College Readiness A university education is largely about learning how to think in particular ways. Content is a means to that end. That end is the ability to think about things differently and in deeper, more systematic and complex ways. For students who think about college strictly in terms of mas ...
... College Readiness A university education is largely about learning how to think in particular ways. Content is a means to that end. That end is the ability to think about things differently and in deeper, more systematic and complex ways. For students who think about college strictly in terms of mas ...
Заголовок слайда отсутствует
... of such language leads to the lack of understanding between representatives of different disciplines forming cognitive science. Underestimation of results obtained by collaborators, as well as their research efforts (“It’s trivial, isn’t it?”; “We could have done the same stuff much easier”); A ...
... of such language leads to the lack of understanding between representatives of different disciplines forming cognitive science. Underestimation of results obtained by collaborators, as well as their research efforts (“It’s trivial, isn’t it?”; “We could have done the same stuff much easier”); A ...
Cross-cultural Communication and Negotiation
... Time schedules are very important. Time is viewed as something that can be controlled and should be used wisely ...
... Time schedules are very important. Time is viewed as something that can be controlled and should be used wisely ...
Speech_Presentation
... “The purpose of Newspeak was not only to provide a medium of expression for the world-view and mental habits proper to the devotees of Ingsoc, but to make all other modes of thought impossible.” ...
... “The purpose of Newspeak was not only to provide a medium of expression for the world-view and mental habits proper to the devotees of Ingsoc, but to make all other modes of thought impossible.” ...