Simulating the thermochemical magmatic and tectonic evolution of
... inference from crater counting of a relatively uniform surface age of 300–700 Ma [Herrick, 1994; Schaber et al., 1992; Strom et al., 1994], although the crater distribution could instead be explained by an equilibrium “random resurfacing” model [Bjonnes et al., 2012; Hauck et al., 1998; Phillips et ...
... inference from crater counting of a relatively uniform surface age of 300–700 Ma [Herrick, 1994; Schaber et al., 1992; Strom et al., 1994], although the crater distribution could instead be explained by an equilibrium “random resurfacing” model [Bjonnes et al., 2012; Hauck et al., 1998; Phillips et ...
GEOLOGY OF THE BUCHANS–ROBERTS ARM VOLCANIC BELT
... tectonic strike, drawn from the eastern shore of Great Gull Lake to the vicinity of Kippens Pond, southwest of Badger Bay (Figure 3). Here, the Baker Brook, Burnt Pond and Powderhorn Lake tracts occur on the southwest flank of a regional antiformal thrust stack cored by the Middle Ordovician and old ...
... tectonic strike, drawn from the eastern shore of Great Gull Lake to the vicinity of Kippens Pond, southwest of Badger Bay (Figure 3). Here, the Baker Brook, Burnt Pond and Powderhorn Lake tracts occur on the southwest flank of a regional antiformal thrust stack cored by the Middle Ordovician and old ...
Mercury - GEOCITIES.ws
... The craters on Mercury are very much like those on the Moon. The smallest craters are bowl-shaped, with raised rims and blankets of ejecta surrounding these rims and thinning rapidly away from the crater. At about 10 kilometres in diameter, craters begin to show interior complexities (slumping, ter ...
... The craters on Mercury are very much like those on the Moon. The smallest craters are bowl-shaped, with raised rims and blankets of ejecta surrounding these rims and thinning rapidly away from the crater. At about 10 kilometres in diameter, craters begin to show interior complexities (slumping, ter ...
Balestro et al., 2011
... WGS 1984 UTM Zone 32N). The overall dataset includes i) lithological and petrological data collected in three Master’s Degree theses (Arduino,1986; Brasher, 1985; Rattalino, 1985), ii) new lithological and structural field information, and iii) new remotely sensed morpho-structural features. The fou ...
... WGS 1984 UTM Zone 32N). The overall dataset includes i) lithological and petrological data collected in three Master’s Degree theses (Arduino,1986; Brasher, 1985; Rattalino, 1985), ii) new lithological and structural field information, and iii) new remotely sensed morpho-structural features. The fou ...
Major Land Form Features
... to disintegration caused by mechanical (physical) weathering in the hot desert areas. Strong winds pick up these weathered and communited fine particles and deposite them else where. The repetition of this process over longer period of time results in the transformation of stony areas into plains. S ...
... to disintegration caused by mechanical (physical) weathering in the hot desert areas. Strong winds pick up these weathered and communited fine particles and deposite them else where. The repetition of this process over longer period of time results in the transformation of stony areas into plains. S ...
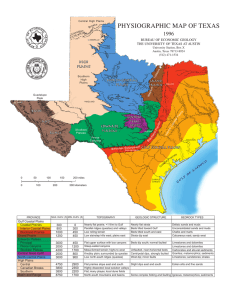
Physiographic Map of Texas - Bureau of Economic Geology
... draws forming narrow blind canyons with nearly vertical walls. The Pecos Canyons include the major river and its side streams. Vegetation is sparse, even near springs and streams. Central Texas Uplift. The most characteristic feature of this province is a central basin having a rolling floor studded ...
... draws forming narrow blind canyons with nearly vertical walls. The Pecos Canyons include the major river and its side streams. Vegetation is sparse, even near springs and streams. Central Texas Uplift. The most characteristic feature of this province is a central basin having a rolling floor studded ...
A105 Stars and Galaxies
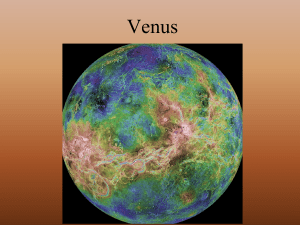
... Ground features can be mapped with radar from Earth and spacecraft orbiting Venus, since radar can penetrate the Venusian clouds Venus’s surface is less mountainous and rugged than Earth, with most of its surface low, gently rolling plains ...
... Ground features can be mapped with radar from Earth and spacecraft orbiting Venus, since radar can penetrate the Venusian clouds Venus’s surface is less mountainous and rugged than Earth, with most of its surface low, gently rolling plains ...
Venus pdf
... • Dense atmosphere prevents studying the surface from orbit. • Craters and “pristine” appearance suggest young surface. • No plate tectonics • No true continents or ocean basins • We do not know the range of ages of the rocks on the surface • We do not know how the surface changed with time ...
... • Dense atmosphere prevents studying the surface from orbit. • Craters and “pristine” appearance suggest young surface. • No plate tectonics • No true continents or ocean basins • We do not know the range of ages of the rocks on the surface • We do not know how the surface changed with time ...