NASA Workshop on Scientific Requirements for Mitigation of
... objects by 2008. While no known asteroid is on collision course with Earth, ongoing detection should alert us to serious threats. Significant topics of discussion at the workshop included large uncertainties in the state of scientific knowledge of asteroid surfaces, despite great advances in recent ...
... objects by 2008. While no known asteroid is on collision course with Earth, ongoing detection should alert us to serious threats. Significant topics of discussion at the workshop included large uncertainties in the state of scientific knowledge of asteroid surfaces, despite great advances in recent ...
KeplerandtheHeavenly.. - How It Began - A Time
... names in European astronomy. [1] His greatest achievement was the formulation of the Laws of Planetary Motion which made a fundamental break with astronomical tradition in describing the orbits of the planets as elliptical rather than circular and in recognising that a planet's speed is not uniform ...
... names in European astronomy. [1] His greatest achievement was the formulation of the Laws of Planetary Motion which made a fundamental break with astronomical tradition in describing the orbits of the planets as elliptical rather than circular and in recognising that a planet's speed is not uniform ...
Attitude and Orbit Control for small satellites
... To explore space is still many peoples dream. But before mankind can enter space themselves, investigating probes have to be sent out in advance. Their missions are many, such as communication, global surveillance or planetary research. With a combined name, these probes are often called arti cial s ...
... To explore space is still many peoples dream. But before mankind can enter space themselves, investigating probes have to be sent out in advance. Their missions are many, such as communication, global surveillance or planetary research. With a combined name, these probes are often called arti cial s ...
Galileo and Kepler: breaking away from the ancients
... 3. The square of the period of the orbit is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis. Reception of Kepler’s astronomy The agreement of Kepler’s three laws with the most precise data of the time, including subsequent telescopic data, was so spectacular that one might suppose that astronomers we ...
... 3. The square of the period of the orbit is proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis. Reception of Kepler’s astronomy The agreement of Kepler’s three laws with the most precise data of the time, including subsequent telescopic data, was so spectacular that one might suppose that astronomers we ...
Binary Pulsar, Neutron Star, Asteroid, Gravity, Jefimenko, Rotation
... clear focus in the present. Unfortunately only our imagination could pred ict a future event in our wo rld but such a prediction would be fraught with huge uncertainties. 3.2. Jefimenko’s Conjecture Jefimenko’s notions[e.g., 7] are contrary to Newtonian gravitation, wh ich is considered only as an a ...
... clear focus in the present. Unfortunately only our imagination could pred ict a future event in our wo rld but such a prediction would be fraught with huge uncertainties. 3.2. Jefimenko’s Conjecture Jefimenko’s notions[e.g., 7] are contrary to Newtonian gravitation, wh ich is considered only as an a ...
PowerPoint file: Higher Physics: Gravitation
... that these things, which now seem to us so mysterious, will be no mysteries at all; that the scales will fall from our eyes; that we shall learn to look on things in a different way—when that which is now a difficulty will be the only commonsense and intelligible way of looking at the subject.' ©Hun ...
... that these things, which now seem to us so mysterious, will be no mysteries at all; that the scales will fall from our eyes; that we shall learn to look on things in a different way—when that which is now a difficulty will be the only commonsense and intelligible way of looking at the subject.' ©Hun ...
chapter7 - People Server at UNCW
... moving about the earth in a circular orbit and in an elliptical orbit. The only external force that acts on the satellite is the gravitational force. For these two orbits, determine whether the kinetic energy of the satellite changes during the motion. ...
... moving about the earth in a circular orbit and in an elliptical orbit. The only external force that acts on the satellite is the gravitational force. For these two orbits, determine whether the kinetic energy of the satellite changes during the motion. ...
Does the Galaxy need guarding
... the ‘RNA world’ in which RNA did everything and was a precursor to DNA. RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a nucleic acid (like DNA) that is present in all living cells. It acts as a messager, carrying instructions from DNA, controlling protein synthesis. Some viruses still use RNA rather than DNA to carry t ...
... the ‘RNA world’ in which RNA did everything and was a precursor to DNA. RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a nucleic acid (like DNA) that is present in all living cells. It acts as a messager, carrying instructions from DNA, controlling protein synthesis. Some viruses still use RNA rather than DNA to carry t ...
Visualization of Planetesimal Close Encounters with Jovian Planets
... the Solar System (1). It employed a total of 40,000 massless particles having both inclined and eccentric orbits. 10,000 were placed in each of the inter-Jovian planet gaps, and another 10,000 in the Kuiper belt. The planetesimal’s orbits will destabilize due to close approaches to the Jovian planet ...
... the Solar System (1). It employed a total of 40,000 massless particles having both inclined and eccentric orbits. 10,000 were placed in each of the inter-Jovian planet gaps, and another 10,000 in the Kuiper belt. The planetesimal’s orbits will destabilize due to close approaches to the Jovian planet ...
PHY101_Lec_Sept12 - MSU Physics and Astronomy Department
... To draw an ellipse: Take a string. Tack down the two ends. Put a pencil in the string and pull the string taut. Move the pencil around keeping the string taut. An ellipse is the locus of points for which the sum of the distances to two fixed points is fixed. ...
... To draw an ellipse: Take a string. Tack down the two ends. Put a pencil in the string and pull the string taut. Move the pencil around keeping the string taut. An ellipse is the locus of points for which the sum of the distances to two fixed points is fixed. ...
Satellite Communication
... Here’s the Math… • Gravity depends on the mass of the earth, the mass of the satellite, and the distance between the center of the earth and the satellite • For a satellite traveling in a circle, the speed of the satellite and the radius of the circle determine the force (of gravity) needed to main ...
... Here’s the Math… • Gravity depends on the mass of the earth, the mass of the satellite, and the distance between the center of the earth and the satellite • For a satellite traveling in a circle, the speed of the satellite and the radius of the circle determine the force (of gravity) needed to main ...
5050_Rsrch - Colorado Center for Astrodynamics Research
... starts to "roll-off the hill" it picks up speed, but the Coriolis force sends the satellite into a stable orbit around the Lagrange point (Cornish). ...
... starts to "roll-off the hill" it picks up speed, but the Coriolis force sends the satellite into a stable orbit around the Lagrange point (Cornish). ...
planet problem set
... ball. Since you can’t actually measure the diameter of a tennis ball (why not?) you manage to meaure the circumference, which is 19.0 cm. Find the diameter of the tennis ball. Use 3.14 for an approximation for π and give your answer to the nearest .1cm. Show how you arrived at the following answers. ...
... ball. Since you can’t actually measure the diameter of a tennis ball (why not?) you manage to meaure the circumference, which is 19.0 cm. Find the diameter of the tennis ball. Use 3.14 for an approximation for π and give your answer to the nearest .1cm. Show how you arrived at the following answers. ...
to see a sample homework problem set from Dynamics
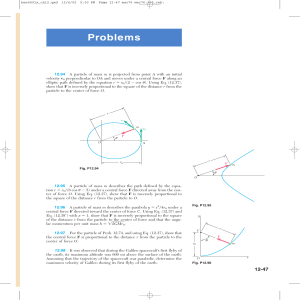
... 12.103 The Chandra X-ray observatory, launched in 1999, achieved an elliptical orbit of minimum altitude 6200 mi and maximum altitude 86,900 mi above the surface of the earth. Assuming that the observatory was transferred to this orbit from a circular orbit of altitude 6200 mi at point A, determine ...
... 12.103 The Chandra X-ray observatory, launched in 1999, achieved an elliptical orbit of minimum altitude 6200 mi and maximum altitude 86,900 mi above the surface of the earth. Assuming that the observatory was transferred to this orbit from a circular orbit of altitude 6200 mi at point A, determine ...
Comparative Planetology
... inclinations of more than 90° of their rotation axes to their orbital plane normals. Another exemption is Triton, whose retrograde orbital motion about Neptune is unusual. Triton, like Pluto, is speculated to have originated in the Kuiper belt and to have been captured into its retrograde orbit by N ...
... inclinations of more than 90° of their rotation axes to their orbital plane normals. Another exemption is Triton, whose retrograde orbital motion about Neptune is unusual. Triton, like Pluto, is speculated to have originated in the Kuiper belt and to have been captured into its retrograde orbit by N ...
Note Taking Worksheet Forces
... 2. Gravity is a long range force that gives the universe its structure. ...
... 2. Gravity is a long range force that gives the universe its structure. ...
The Helen Sharman Space Club Programme
... messenger to the gods. Mercury is one of the rocky planets, and is made mostly from metals. Its surface is heavily cratered, like the Moon, which means that any geological activity stopped billions of years ago. As Mercury is so close to the Sun, and has very little atmosphere to retain heat, temper ...
... messenger to the gods. Mercury is one of the rocky planets, and is made mostly from metals. Its surface is heavily cratered, like the Moon, which means that any geological activity stopped billions of years ago. As Mercury is so close to the Sun, and has very little atmosphere to retain heat, temper ...
Newton’s Laws of Force
... is this law different from the other two? Forces don’t cancel each other out even if they are equal and opposite. There are always two objects involved If forces are equal then how can a swimmer move through the water? Newton’s second law determines the acceleration of an object ...
... is this law different from the other two? Forces don’t cancel each other out even if they are equal and opposite. There are always two objects involved If forces are equal then how can a swimmer move through the water? Newton’s second law determines the acceleration of an object ...
WhatNewPlanets
... • Simplest Strategy: Detection + Diversion • Destruction too unpredictable – Can object be destroyed? – “Cookie crumbs have no calories” – In real life, the pieces matter ...
... • Simplest Strategy: Detection + Diversion • Destruction too unpredictable – Can object be destroyed? – “Cookie crumbs have no calories” – In real life, the pieces matter ...
Page 434
... Why did many people not like him? He challenged the Christian teaching that the universe revolved around the earth What happened to him? Tried and put under house arrest; he said he was wrong under the threat of death Would you do what everyone else did and doubt him? Bacon/Descartes both tried to u ...
... Why did many people not like him? He challenged the Christian teaching that the universe revolved around the earth What happened to him? Tried and put under house arrest; he said he was wrong under the threat of death Would you do what everyone else did and doubt him? Bacon/Descartes both tried to u ...
Orbit

In physics, an orbit is the gravitationally curved path of an object around a point in space, for example the orbit of a planet around the center of a star system, such as the Solar System. Orbits of planets are typically elliptical, but unlike the ellipse followed by a pendulum or an object attached to a spring, the central object is at a focal point of the ellipse and not at its center.Current understanding of the mechanics of orbital motion is based on Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, which accounts for gravity as due to curvature of space-time, with orbits following geodesics. For ease of calculation, relativity is commonly approximated by the force-based theory of universal gravitation based on Kepler's laws of planetary motion.