1.01 Remember structural organization
... Essential Questions How is the human body organized? What are the structural components of the body? How does the body’s structural organization relate to ...
... Essential Questions How is the human body organized? What are the structural components of the body? How does the body’s structural organization relate to ...
1. Anococcygeal liament 2. Deep transverse perineal muscle 3
... Origins : 2 bony structures & 1 tendineous structure Medial surface of body of pubis & Ischial spine Tendineous arch of levator ani (L. Arcus tendineus m. levatoris ani) Insertion : Perineal body (Centrum perinei- Corpus perineale) / Anal canal’s wall/ Anococcygeal ligament (Lig. anococcygeum) / Coc ...
... Origins : 2 bony structures & 1 tendineous structure Medial surface of body of pubis & Ischial spine Tendineous arch of levator ani (L. Arcus tendineus m. levatoris ani) Insertion : Perineal body (Centrum perinei- Corpus perineale) / Anal canal’s wall/ Anococcygeal ligament (Lig. anococcygeum) / Coc ...
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 3 of 37
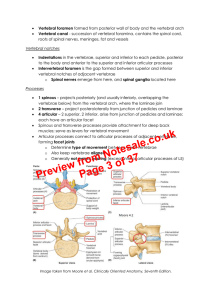
... o Later chondrify and cartilaginous vertebrae form Ossification begins at 8th week; 3 primary ossification centres in each vertebra o Endochondral centrum – will eventually constitute most of the body o 2 perichondiral centres – one each half of neural arch At birth, typical vertebra and the superio ...
... o Later chondrify and cartilaginous vertebrae form Ossification begins at 8th week; 3 primary ossification centres in each vertebra o Endochondral centrum – will eventually constitute most of the body o 2 perichondiral centres – one each half of neural arch At birth, typical vertebra and the superio ...
Kinesiology of Exercise Glossary
... PRONATED GRIP. A grip with the palms of the hands facing down or in. PRONATION. Rotating the forearm so that the hand is turned palm down. PRONE. Lying face downward. PROXIMAL RADIO-ULNAR JOINT. A radio-ulnar joint at the elbow that is a pivot joint between the head of the radius and the radial notc ...
... PRONATED GRIP. A grip with the palms of the hands facing down or in. PRONATION. Rotating the forearm so that the hand is turned palm down. PRONE. Lying face downward. PROXIMAL RADIO-ULNAR JOINT. A radio-ulnar joint at the elbow that is a pivot joint between the head of the radius and the radial notc ...
5-Thoacolumbar spine
... • The intervertebral discs are responsible for one fourth of the length of the vertebral column . • They are thickest in the cervical and lumbar regions, where the movements of the vertebral column are greatest unlike the thoracic region which is LESS THICK and has less movement . • Each disc consis ...
... • The intervertebral discs are responsible for one fourth of the length of the vertebral column . • They are thickest in the cervical and lumbar regions, where the movements of the vertebral column are greatest unlike the thoracic region which is LESS THICK and has less movement . • Each disc consis ...
Bodily Systems and the Spatial-Functional
... a reference ontology for the domain of biomedicine. [4] This ontology is not a computer application but a framework of axioms and definitions relating to general terms such as: organism, tissue, disease, therapy. In this paper we focus on the notion of bodily system, which we believe will serve as a ...
... a reference ontology for the domain of biomedicine. [4] This ontology is not a computer application but a framework of axioms and definitions relating to general terms such as: organism, tissue, disease, therapy. In this paper we focus on the notion of bodily system, which we believe will serve as a ...
Development of the mandible
... The lingual nerve passes forward, on the medial side of the cartilage, while the inferior alverolar lies lateral to its upper margins. ...
... The lingual nerve passes forward, on the medial side of the cartilage, while the inferior alverolar lies lateral to its upper margins. ...
Vertebras and Pelvic Girdle
... 1 facet on each transverse process T11 1 facet on each side of the body 1 facet on each transverse process T12 same as T11, but with widened inferior body to meet with L1 ...
... 1 facet on each transverse process T11 1 facet on each side of the body 1 facet on each transverse process T12 same as T11, but with widened inferior body to meet with L1 ...
UPPER LIMB
... segments from spine) • Dermatomes extend over limbs • Twisted orientation reflects twisting of limb during development • Named nerves generally innervate skin over muscles that they innervate Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb ...
... segments from spine) • Dermatomes extend over limbs • Twisted orientation reflects twisting of limb during development • Named nerves generally innervate skin over muscles that they innervate Frolich, Human Anatomy,UpprLimb ...
OTA Tip-of-the-Month: Medial Talar Pin Placement for Universal
... plane. The proximal pin is either in the proximal tibial metaphysis, posteriorly (for IM nailing) or in the meta-diaphysis for ORIF of pilon fractures. The distal Schantz pin may be placed in the posterior tibia, the talus, or the calcaneus... A distal pin in the tibia might interfere with the nail’ ...
... plane. The proximal pin is either in the proximal tibial metaphysis, posteriorly (for IM nailing) or in the meta-diaphysis for ORIF of pilon fractures. The distal Schantz pin may be placed in the posterior tibia, the talus, or the calcaneus... A distal pin in the tibia might interfere with the nail’ ...
Ventricles & CSF cisterns
... Ventricles • CSF filled spaces in the brain related to development of the nervous system as a tubular structure with central canal • Lined with ependyma • Plexuses of highly vascular pia mater form choroid plexuses which produce CSF ...
... Ventricles • CSF filled spaces in the brain related to development of the nervous system as a tubular structure with central canal • Lined with ependyma • Plexuses of highly vascular pia mater form choroid plexuses which produce CSF ...
Inferior division of 3 rd cranial n. Lateral Rectus Eye ball
... demonstration. Specimens were mounted by Kaiserlings technique in glass jars. Result: By this method ten specimens of eye were mounted showing all muscles with their origin and insertion, their nerve supply, optic nerve, ophthalmic artery and its branch entering into optic nerve in different views o ...
... demonstration. Specimens were mounted by Kaiserlings technique in glass jars. Result: By this method ten specimens of eye were mounted showing all muscles with their origin and insertion, their nerve supply, optic nerve, ophthalmic artery and its branch entering into optic nerve in different views o ...
Vertebral column and back Bony framework of the vertebral
... • Support/supporting axis – be able to move lower and upper limbs ...
... • Support/supporting axis – be able to move lower and upper limbs ...
Basic Human Anatomy - The Brookside Associates
... a. Fibroblasts. The characteristic cells of FCT are fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are able to form elongated fibers. b. Matrix. These fibers make up the matrix of FCT. c. Fibers. The fibers are either white or yellow. (1) White fibers are made from a protein called collagen. White fibers tend to have a f ...
... a. Fibroblasts. The characteristic cells of FCT are fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are able to form elongated fibers. b. Matrix. These fibers make up the matrix of FCT. c. Fibers. The fibers are either white or yellow. (1) White fibers are made from a protein called collagen. White fibers tend to have a f ...
full text
... One of the two specimens is sligthly smaller than the other, in other respects they are similar. The specimen from which sections have been made (the larger of the two) is represented in fig. 7 (the surface which was turned towards the thorax of the host) and fig. 8 (the surface facing the abdomen o ...
... One of the two specimens is sligthly smaller than the other, in other respects they are similar. The specimen from which sections have been made (the larger of the two) is represented in fig. 7 (the surface which was turned towards the thorax of the host) and fig. 8 (the surface facing the abdomen o ...
The vertebral column is 33 vertebrae held together by ligaments and
... The thorax creates a large compartment called the thoracic cavity (chest cavity), which houses the lungs and heart. The manubrium is the top upside-down shaped triangle of the sternum. The top notch of the top part of the manubrium is called the suprasternal notch (also called the jugular notch) an ...
... The thorax creates a large compartment called the thoracic cavity (chest cavity), which houses the lungs and heart. The manubrium is the top upside-down shaped triangle of the sternum. The top notch of the top part of the manubrium is called the suprasternal notch (also called the jugular notch) an ...
Body cavities and abdominal regions
... – A middle tissue mass diving the lungs into two cavities – Includes the pericardial cavity, esophagus, trachea, and large blood vessels. ...
... – A middle tissue mass diving the lungs into two cavities – Includes the pericardial cavity, esophagus, trachea, and large blood vessels. ...
use of quadruped models in thoraco- abdominal
... of necropsies performed on pigs and dogs. The results are summarized belo*. Emphasis is placed on specitic aspects which are felt to be important for impact biomechanics. In particular. emphasis is placed upon the effect oftethering structures because oftheir potential in explaining mechanisms of in ...
... of necropsies performed on pigs and dogs. The results are summarized belo*. Emphasis is placed on specitic aspects which are felt to be important for impact biomechanics. In particular. emphasis is placed upon the effect oftethering structures because oftheir potential in explaining mechanisms of in ...
Anterior cranial fossa
... 1. Body: short in height and square shaped. 2. Transverse process perforated by a round foramen transversarium (for a artery going into skull) 3. Spinous process: short and bifid ...
... 1. Body: short in height and square shaped. 2. Transverse process perforated by a round foramen transversarium (for a artery going into skull) 3. Spinous process: short and bifid ...
Body Worlds

Body Worlds (German title: Körperwelten) is a traveling exhibition of preserved human bodies and body parts that are prepared using a technique called plastination to reveal inner anatomical structures. The exhibition's developer and promoter is German anatomist Gunther von Hagens, who invented the plastination technique in the late 1970s at the University of Heidelberg.