Study Guide for Lab Practicals in Biol 241
... Study Guide for Lab Practicals in Biol 241 Four practical quizzes will be administered in the lab and will test your knowledge of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected Powerpoint slides, models, and fre ...
... Study Guide for Lab Practicals in Biol 241 Four practical quizzes will be administered in the lab and will test your knowledge of both gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy (histology). Each will be worth 50 points and may be made up of microscope slides, projected Powerpoint slides, models, and fre ...
Animal Evolution Assignment File
... mostly motile/non-motile Two unique tissues found only in animals are: muscle/epithelial/connective/nervous Most animals reproduce sexually/asexually. The diploid/haploid stage is usually dominant in their life cycle. Reproduction and Development Fertilization occurs when a small flagellated sperm ...
... mostly motile/non-motile Two unique tissues found only in animals are: muscle/epithelial/connective/nervous Most animals reproduce sexually/asexually. The diploid/haploid stage is usually dominant in their life cycle. Reproduction and Development Fertilization occurs when a small flagellated sperm ...
Lecture (3)
... • Oblique (Erect or Recumbent) • Position when the body is rotated so that the medial sagittal plane (MSP) is neither nor to the film but at an angle • Exact position is indicated by the surface closest to the film and the angle of rotation May be erect or recumbent • Abbreviations: (RPO,LPO, RAO, ...
... • Oblique (Erect or Recumbent) • Position when the body is rotated so that the medial sagittal plane (MSP) is neither nor to the film but at an angle • Exact position is indicated by the surface closest to the film and the angle of rotation May be erect or recumbent • Abbreviations: (RPO,LPO, RAO, ...
General motion - Northern Highlands
... decreases the angle between two parts. Bending the elbow, or clenching a hand into a fist, are examples of flexion. When sitting down, the knees are flexed. Flexion of the hip or shoulder moves the limb forward (towards the anterior side of the body). ...
... decreases the angle between two parts. Bending the elbow, or clenching a hand into a fist, are examples of flexion. When sitting down, the knees are flexed. Flexion of the hip or shoulder moves the limb forward (towards the anterior side of the body). ...
Body Planes, Directions, & Cavities
... Body Planes, Directions, & Cavities Med Terms & Principles of Health Science BECKY JACKSON, R.N. ...
... Body Planes, Directions, & Cavities Med Terms & Principles of Health Science BECKY JACKSON, R.N. ...
userfiles/140/my files/powerpoint presentations
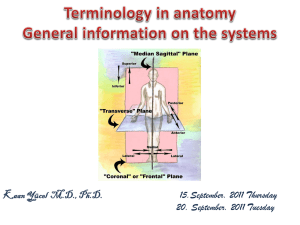
... Vertical plane from front to back Divides left and right ...
... Vertical plane from front to back Divides left and right ...
anatomical terms and terminoogy
... clavicle and the scapula are the bones of the shoulder girdle. It connects the upper limb to the trunk and transmits part of the weight of the upper limb to the sternum. It acts as a strut that allows the arm to swing away from the trunk. The clavicle is a long bone and has a shaft and two ends. The ...
... clavicle and the scapula are the bones of the shoulder girdle. It connects the upper limb to the trunk and transmits part of the weight of the upper limb to the sternum. It acts as a strut that allows the arm to swing away from the trunk. The clavicle is a long bone and has a shaft and two ends. The ...
POSITIONING TERMINOLOOGY - Community College of Philadelphia
... Dorsal decubitus position – Patient lying on back with the IR placed vertically adjacent to a side of the patient, and the x-ray beam horizontal. ...
... Dorsal decubitus position – Patient lying on back with the IR placed vertically adjacent to a side of the patient, and the x-ray beam horizontal. ...
Chapter 2
... articulate- To fit into each other fracture- A break in the bone skeletal (voluntary) muscle- Muscle that is under direct voluntary control of the brain smooth muscle- The muscles found in the walls of the internal organs and blood vessels, generally not under voluntary control involuntary muscle- S ...
... articulate- To fit into each other fracture- A break in the bone skeletal (voluntary) muscle- Muscle that is under direct voluntary control of the brain smooth muscle- The muscles found in the walls of the internal organs and blood vessels, generally not under voluntary control involuntary muscle- S ...
Chapter 2 38 Cha pter 2 The Thalamus is a sub
... The Thalamus is a sub-cortical, gray matter, oval or egg-shaped structure on either side of the Third ventricle. It is located at the top of the brainstem and superior to the hypothalamus. It is responsible for consciousness, sleep, wakefulness, motor control and all senses except olfactory. The fro ...
... The Thalamus is a sub-cortical, gray matter, oval or egg-shaped structure on either side of the Third ventricle. It is located at the top of the brainstem and superior to the hypothalamus. It is responsible for consciousness, sleep, wakefulness, motor control and all senses except olfactory. The fro ...
Document
... 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of most members of the phylum Annelida? a. hydrostatic skeleton b. segmentation c. pseudocoelom d. closed circulatory system e. all of the above are characteristics of Annelida 2. Which phylum is characterized by animals that have a segmented body? a ...
... 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of most members of the phylum Annelida? a. hydrostatic skeleton b. segmentation c. pseudocoelom d. closed circulatory system e. all of the above are characteristics of Annelida 2. Which phylum is characterized by animals that have a segmented body? a ...
Animal Quiz
... 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of most members of the phylum Annelida? a. hydrostatic skeleton b. segmentation c. pseudocoelom d. closed circulatory system e. all of the above are characteristics of Annelida 2. Which phylum is characterized by animals that have a segmented body? a ...
... 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of most members of the phylum Annelida? a. hydrostatic skeleton b. segmentation c. pseudocoelom d. closed circulatory system e. all of the above are characteristics of Annelida 2. Which phylum is characterized by animals that have a segmented body? a ...
PowerPoint Sunusu
... position, with movements occurring within, and around axes aligned with, specific anatomical planes. While most movements occur at joints where two or more bones or cartilages articulate with one another, several non-skeletal structures exhibit movement (e.g., tongue, lips, eyelids). ...
... position, with movements occurring within, and around axes aligned with, specific anatomical planes. While most movements occur at joints where two or more bones or cartilages articulate with one another, several non-skeletal structures exhibit movement (e.g., tongue, lips, eyelids). ...
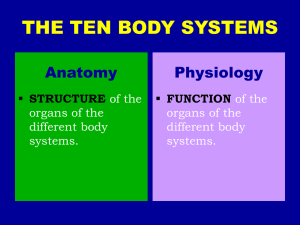
Ten Body Systems
... Hormones, released by endocrine glands, cause a particular changes in the body Maintains longterm homeostasis ...
... Hormones, released by endocrine glands, cause a particular changes in the body Maintains longterm homeostasis ...
Body Cavities
... defect but it does not arise from a failure in body wall closure. Instead, it originates when portions of the gut tube (the midgut), that normally herniates into the umbilical cord during the 6th to 10th weeks fails to return to the abdominal cavity. ...
... defect but it does not arise from a failure in body wall closure. Instead, it originates when portions of the gut tube (the midgut), that normally herniates into the umbilical cord during the 6th to 10th weeks fails to return to the abdominal cavity. ...
six key transitions in body plan
... • To judge which phyla are more closely related, taxonomists traditionally have compared anatomical features and aspects of embryological development. • The end result are phylogenies, which are basically like family trees. ...
... • To judge which phyla are more closely related, taxonomists traditionally have compared anatomical features and aspects of embryological development. • The end result are phylogenies, which are basically like family trees. ...
幻灯片 1
... For the purpose of description of various parts of body and their location, a body is assumed to be in erect position. It is essential to learn the anatomical position because most of the directional terminology used in anatomy refers to the body in this position. ...
... For the purpose of description of various parts of body and their location, a body is assumed to be in erect position. It is essential to learn the anatomical position because most of the directional terminology used in anatomy refers to the body in this position. ...
Lecture Chpt. 32 Intro Animals
... no body cavity between digestive cavity & outer body wall no tube outside of a tube ...
... no body cavity between digestive cavity & outer body wall no tube outside of a tube ...
Inverts
... 1. What word means that a sponge does not move? Sessile 2. How do sponges eat? By filtering the water around them 3. What tiny, hard particles make up the sponge skeleton? Spicules ...
... 1. What word means that a sponge does not move? Sessile 2. How do sponges eat? By filtering the water around them 3. What tiny, hard particles make up the sponge skeleton? Spicules ...
Body Worlds

Body Worlds (German title: Körperwelten) is a traveling exhibition of preserved human bodies and body parts that are prepared using a technique called plastination to reveal inner anatomical structures. The exhibition's developer and promoter is German anatomist Gunther von Hagens, who invented the plastination technique in the late 1970s at the University of Heidelberg.