p68/DDX5 DEAD-box RNA helicase gene encodes a novel miRNA
... Rossler et al. 2000). Inclusion of the intron introduces a stop codon, but, to date, there is no evidence for the presence of a truncated protein. In yeast, the p68 RNA that contains this large intron can negatively regulate expression of p68 protein levels (Barta and Iggo 1995), again suggesting th ...
... Rossler et al. 2000). Inclusion of the intron introduces a stop codon, but, to date, there is no evidence for the presence of a truncated protein. In yeast, the p68 RNA that contains this large intron can negatively regulate expression of p68 protein levels (Barta and Iggo 1995), again suggesting th ...
Computational Identification of Plant MicroRNAs and
... plant miRNAs have a strong propensity to target genes controlling development, particularly those of transcription factors and F-box proteins. However, plant miRNAs have conserved regulatory functions extending beyond development, in that they also target superoxide dismutases, laccases, and ATP sul ...
... plant miRNAs have a strong propensity to target genes controlling development, particularly those of transcription factors and F-box proteins. However, plant miRNAs have conserved regulatory functions extending beyond development, in that they also target superoxide dismutases, laccases, and ATP sul ...
Bayesian Learning of MicroRNA Targets from Sequence
... takes into account the down-regulation of target mRNAs subject to the action of multiple miRNAs. Each miRNA can reduce the expression of its targets by some fixed amount: given high expression of one or many miRNAs, the expression of a targeted transcript is negatively shifted with respect to a back ...
... takes into account the down-regulation of target mRNAs subject to the action of multiple miRNAs. Each miRNA can reduce the expression of its targets by some fixed amount: given high expression of one or many miRNAs, the expression of a targeted transcript is negatively shifted with respect to a back ...
2. Ischemic heart disease and limited cardiac regeneration
... proliferation remain unclear, which may be due to the complexity of the different stages in cardiogenesis and the other Wnt pathways, as well as other factors involving β-catenin regulation (Tzahor, 2007). Nonetheless, it is clear that the Wnt/β-catenin pathway plays an important role in cardiac cel ...
... proliferation remain unclear, which may be due to the complexity of the different stages in cardiogenesis and the other Wnt pathways, as well as other factors involving β-catenin regulation (Tzahor, 2007). Nonetheless, it is clear that the Wnt/β-catenin pathway plays an important role in cardiac cel ...
The microRNAs of Caenorhabditis elegans
... diverse biological processes, from skin cell differentiation [1], to the timing of flowering in plants [2], to the response to osmotic stress [3] or DNA damage [4], to name but a few examples. The miRNA biogenesis pathway is summarized in Fig. 1. Generally, miRNAs are derived from capped and polyaden ...
... diverse biological processes, from skin cell differentiation [1], to the timing of flowering in plants [2], to the response to osmotic stress [3] or DNA damage [4], to name but a few examples. The miRNA biogenesis pathway is summarized in Fig. 1. Generally, miRNAs are derived from capped and polyaden ...
Identification of novel micro RNAs and their targets in Cocos
... omotic stress. As exemplified, CDPKs (Calcium dependent protein kinases) play major roles in development for recycling transcription to hormone levels and are known to function in abiotic stress response and ABA signaling through phosphorylation activity(Ishida et al., 2008; Mori et al., 2006). On t ...
... omotic stress. As exemplified, CDPKs (Calcium dependent protein kinases) play major roles in development for recycling transcription to hormone levels and are known to function in abiotic stress response and ABA signaling through phosphorylation activity(Ishida et al., 2008; Mori et al., 2006). On t ...
RNA Genes: Retroelements and Virally Retroposable microRNAs in
... from both coding and non-coding regions of genomic DNA [2, 3]. The small RNAs are functional and their sizes fall within a range of 19 to 31 nucleotides (nts). The most common small RNAs are miRNAs, which consist of genomic and resident miRNA genes, which are subsequently produced by digestions on t ...
... from both coding and non-coding regions of genomic DNA [2, 3]. The small RNAs are functional and their sizes fall within a range of 19 to 31 nucleotides (nts). The most common small RNAs are miRNAs, which consist of genomic and resident miRNA genes, which are subsequently produced by digestions on t ...
miRNA pptx - NUS School of Computing
... Improving miRNA Target Genes Prediction Rikky Wenang Purbojati ...
... Improving miRNA Target Genes Prediction Rikky Wenang Purbojati ...
Polymorphic miRNA-mediated gene regulation: contribution to
... miRNA precursor hairpins do not have specific consensus sequences. It is their secondary structure that positions the double-stranded RNA-binding protein DGCR8 (known as Pasha in Drosophila) such that its ribonuclease III partner Drosha cleaves the stem at approximately one helical turn from the bas ...
... miRNA precursor hairpins do not have specific consensus sequences. It is their secondary structure that positions the double-stranded RNA-binding protein DGCR8 (known as Pasha in Drosophila) such that its ribonuclease III partner Drosha cleaves the stem at approximately one helical turn from the bas ...
MicroRNA Analysis
... • synthetic RNAi and siRNA duplexes • vectors carrying RNAi cassette expressing shRNA or artificial miRNAs • in vitro transcription and dicing of dsRNA to generate pools of siRNA. •SILAC studies - Although miRNA profiling can show changes based on miRNA activity, it is not always indicative of trans ...
... • synthetic RNAi and siRNA duplexes • vectors carrying RNAi cassette expressing shRNA or artificial miRNAs • in vitro transcription and dicing of dsRNA to generate pools of siRNA. •SILAC studies - Although miRNA profiling can show changes based on miRNA activity, it is not always indicative of trans ...
MiRNA_GO_Meeting_August2015
... Capturing physiological effects of silencing Important for functional analysis of miRNAs ...
... Capturing physiological effects of silencing Important for functional analysis of miRNAs ...
Distinct Roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer
... dsRNA processing depletion of dicer results in reduced effectiveness of injected siRNA Dicer binds to components of RISC (R2D2) & binds tightly to siRNA Role of Dicer in siRISC is not well characterized… The authors took a genetic approach to study Dicer function in Drosophila ...
... dsRNA processing depletion of dicer results in reduced effectiveness of injected siRNA Dicer binds to components of RISC (R2D2) & binds tightly to siRNA Role of Dicer in siRISC is not well characterized… The authors took a genetic approach to study Dicer function in Drosophila ...
Role of microRNA in Skeleton Development
... the upregulation of osteogenic genes. In this context, it may be useful to look at the two roles played by the muscle-specific miR-133 in myocyte and osteoblast differentiation. In myocyte differentiation, miR-133 is up regulated downstream of the transcription factors myogenin, MyoD, SRF, and Mef2 ...
... the upregulation of osteogenic genes. In this context, it may be useful to look at the two roles played by the muscle-specific miR-133 in myocyte and osteoblast differentiation. In myocyte differentiation, miR-133 is up regulated downstream of the transcription factors myogenin, MyoD, SRF, and Mef2 ...
miRNA
... expressed genes (DEGs) or clusters of similarly expressed genes Generation from these analyses of new hypotheses about the underlying biological processes stimulates new hypotheses that in turn should be tested in follow-up experiments ...
... expressed genes (DEGs) or clusters of similarly expressed genes Generation from these analyses of new hypotheses about the underlying biological processes stimulates new hypotheses that in turn should be tested in follow-up experiments ...
View Poster - Technology Networks
... Micro (mi)RNAs are short (mostly 21-23nt) RNAs with the ability to regulate target genes post-transcriptionally. Many known miRNAs are involved in tissue development and maintenance and, until now, miRNAs appeared to be absent altogether from unicellular organisms. This has often led to the speculat ...
... Micro (mi)RNAs are short (mostly 21-23nt) RNAs with the ability to regulate target genes post-transcriptionally. Many known miRNAs are involved in tissue development and maintenance and, until now, miRNAs appeared to be absent altogether from unicellular organisms. This has often led to the speculat ...
Poster Patrocles_V3
... Using positional cloning, we have recently identified the mutation responsible for muscular phenotype of the Texel sheep. It is located in the 3’UTR of the GDF8 gene - a known developmental repressor of muscle growth - and creates an illegitimate target site for miRNA expressed in the same tissue. T ...
... Using positional cloning, we have recently identified the mutation responsible for muscular phenotype of the Texel sheep. It is located in the 3’UTR of the GDF8 gene - a known developmental repressor of muscle growth - and creates an illegitimate target site for miRNA expressed in the same tissue. T ...
emboj200858-sup
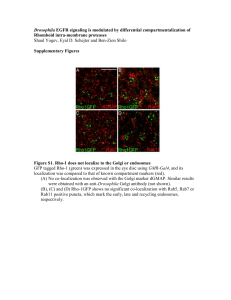
... Activation of EGFR was monitored by induction of pointedP1 expression. Normally, pntP1 is expressed in two cell rows on each side of the midline. Upon expression of Rhomboid proteins by prd-Gal4, the pattern of ectopic pntP1 expression was monitored within the stripes, and adjacent to them. (A) Rho- ...
... Activation of EGFR was monitored by induction of pointedP1 expression. Normally, pntP1 is expressed in two cell rows on each side of the midline. Upon expression of Rhomboid proteins by prd-Gal4, the pattern of ectopic pntP1 expression was monitored within the stripes, and adjacent to them. (A) Rho- ...
microRNA: microRNA
... initial treatment in CLL Alterations in genomic DNA encoding miRNA exist in CLL pts, and in 16-1 causes decreased miRNA miR-15a and miR-16-1 directly target bcl2, and their absence may contribute to the pathogenesis of CLL miRNA or miRNA-like sequences may be used therapeutically to target bcl2 or o ...
... initial treatment in CLL Alterations in genomic DNA encoding miRNA exist in CLL pts, and in 16-1 causes decreased miRNA miR-15a and miR-16-1 directly target bcl2, and their absence may contribute to the pathogenesis of CLL miRNA or miRNA-like sequences may be used therapeutically to target bcl2 or o ...
Nature Rev.Genet
... lin-4 encodes the precursor to a 22 ntlong microRNA that is partially complementary to sites in the 3’UTR of lin-14 mRNA ...
... lin-4 encodes the precursor to a 22 ntlong microRNA that is partially complementary to sites in the 3’UTR of lin-14 mRNA ...
Text S1.
... a luciferase construct containing two perfect complementary target sites for the endogenous miR2 in its 3’UTR (data not shown) [7]. In addition, transgenic flies expressing VP1 driven ...
... a luciferase construct containing two perfect complementary target sites for the endogenous miR2 in its 3’UTR (data not shown) [7]. In addition, transgenic flies expressing VP1 driven ...
Example 2. - the Gene Ontology Consortium Wiki
... by repressing the opposing TH2 programs. (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UL17). In this example we are interested in how you would annotate the regulation of expression of targets of T-box protein 21 (T-bet). Abstract Upon detection of antigen, CD4+ T helper (Th) cells can differentiate into a num ...
... by repressing the opposing TH2 programs. (http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9UL17). In this example we are interested in how you would annotate the regulation of expression of targets of T-box protein 21 (T-bet). Abstract Upon detection of antigen, CD4+ T helper (Th) cells can differentiate into a num ...
MiR-155

MiR-155 is a microRNA that in humans is encoded by the MIR155 host gene or MIR155HG. MiR-155 plays a role in various physiological and pathological processes. Exogenous molecular control in vivo of miR-155 expression may inhibit malignant growth, viral infections, and enhance the progression of cardiovascular diseases.