Diapositive 1 - indico in2p3
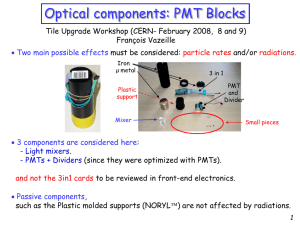
... Warning: Current simulations gave 576 nA as maximum current for Layer 1 There would be an additional safety factor of about 4. • Rule 2: Intense pulses Storage capacitors in the last stages to balance the voltage drop due to large current flow. - Performances: from the study of a set of 250 PMTs o ...
... Warning: Current simulations gave 576 nA as maximum current for Layer 1 There would be an additional safety factor of about 4. • Rule 2: Intense pulses Storage capacitors in the last stages to balance the voltage drop due to large current flow. - Performances: from the study of a set of 250 PMTs o ...
doc
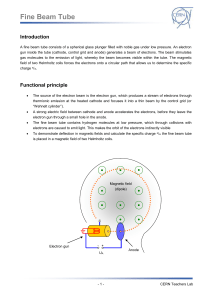
... measured, we can calculate the impulse of the electrons. In particle detectors the deflection within magnetic fields is used to determine the impulse of particles in the same way as in the fine beam tube. That’s why particle detectors need strong magnetic fields – at the CMS detectors this is a 13m ...
... measured, we can calculate the impulse of the electrons. In particle detectors the deflection within magnetic fields is used to determine the impulse of particles in the same way as in the fine beam tube. That’s why particle detectors need strong magnetic fields – at the CMS detectors this is a 13m ...
Charge mass ratio
... in a glass tube which has been evacuated and filled with a very small amount of background gas. One plate is heated (by passing a current through it) and “particles” boil off of the cathode and accelerate towards the other plate which is held at a positive potential. The gas in between the plates in ...
... in a glass tube which has been evacuated and filled with a very small amount of background gas. One plate is heated (by passing a current through it) and “particles” boil off of the cathode and accelerate towards the other plate which is held at a positive potential. The gas in between the plates in ...
Measurement of Charge-to-Mass (e/m) Ratio for the Electron
... ray tube in 1897. A cathode ray tube basically consists of two metallic plates in a glass tube which has been evacuated and filled with a very small amount of background gas. One plate is heated (by passing a current through it) and “particles” boil off of the cathode and accelerate towards the othe ...
... ray tube in 1897. A cathode ray tube basically consists of two metallic plates in a glass tube which has been evacuated and filled with a very small amount of background gas. One plate is heated (by passing a current through it) and “particles” boil off of the cathode and accelerate towards the othe ...
P6.3.1.1 - LD Didactic
... researchers were quick to apply the fact that x-rays can be “observed” on a luminous screen in medical examinations. At that time, the most common type of luminous screen was barium-platinum-cyanide, which fluoresces bright green; today, yellow-green zinc-cadmium-sulfide is used almost exclusively. ...
... researchers were quick to apply the fact that x-rays can be “observed” on a luminous screen in medical examinations. At that time, the most common type of luminous screen was barium-platinum-cyanide, which fluoresces bright green; today, yellow-green zinc-cadmium-sulfide is used almost exclusively. ...
0NesamostStvrtaci
... the drift chamber. This is used to measure the time taken for liberated electrons to drift to the anode. In this way precision was further improved. The multiwire chamber – both the proportional chamber and the drift chamber – is now in use in practically every experiment in particle physics laborat ...
... the drift chamber. This is used to measure the time taken for liberated electrons to drift to the anode. In this way precision was further improved. The multiwire chamber – both the proportional chamber and the drift chamber – is now in use in practically every experiment in particle physics laborat ...
x-rays
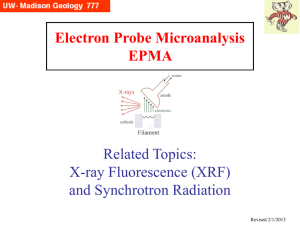
... used to produce x-rays by secondary fluorescence in samples of interest (traditionally a macro-technique) • Synchrotron Radiation, where electrons are accelerated in ~10s100s meters diameter rings, and then made to produce highly focused beams of extremely intense x-rays or light, which are then fed ...
... used to produce x-rays by secondary fluorescence in samples of interest (traditionally a macro-technique) • Synchrotron Radiation, where electrons are accelerated in ~10s100s meters diameter rings, and then made to produce highly focused beams of extremely intense x-rays or light, which are then fed ...
x-rays
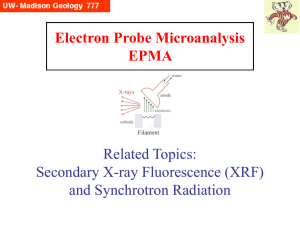
... used to produce x-rays by secondary fluorescence in samples of interest (traditionally a macro-technique) • Synchrotron Radiation, where electrons are accelerated in ~10s100s meters diameter rings, and then made to produce highly focused beams of extremely intense x-rays or light, which are then fed ...
... used to produce x-rays by secondary fluorescence in samples of interest (traditionally a macro-technique) • Synchrotron Radiation, where electrons are accelerated in ~10s100s meters diameter rings, and then made to produce highly focused beams of extremely intense x-rays or light, which are then fed ...
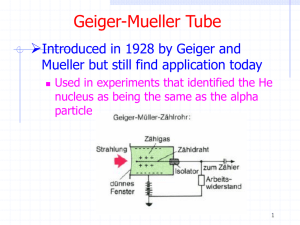
6 Geiger-Müller Tube - Ioniserende Stralen Practicum
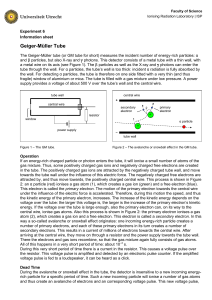
... If an energy-rich charged particle or photon enters the tube, it will ionise a small number of atoms of the gas mixture. Thus, some positively charged gas ions and negatively charged free electrons are created in the tube. The positively charged gas ions are attracted by the negatively charged tube ...
... If an energy-rich charged particle or photon enters the tube, it will ionise a small number of atoms of the gas mixture. Thus, some positively charged gas ions and negatively charged free electrons are created in the tube. The positively charged gas ions are attracted by the negatively charged tube ...
geiger-muller counter
... tubes, mechanical registers are also used. Typically, the counting rate of a G.M. counter depends on the applied voltage. Below a minimum voltage, the threshold voltage, no counts will be registered. This minimum voltage is a function of the gas pressure and the anode diameter, and may be between 30 ...
... tubes, mechanical registers are also used. Typically, the counting rate of a G.M. counter depends on the applied voltage. Below a minimum voltage, the threshold voltage, no counts will be registered. This minimum voltage is a function of the gas pressure and the anode diameter, and may be between 30 ...
Geiger Counter
... the window must be extremely thin. Thus, the windows are difficult to manufacture and are fragile. Geiger tubes constructed to detect only beta and gamma radiations do not have an end window, otherwise construction is similar. In the centre of the tube is a wire ANODE. The metal cylinder itself serv ...
... the window must be extremely thin. Thus, the windows are difficult to manufacture and are fragile. Geiger tubes constructed to detect only beta and gamma radiations do not have an end window, otherwise construction is similar. In the centre of the tube is a wire ANODE. The metal cylinder itself serv ...
Wideroe accelerator Concept Analysis
... Due to this, it can be seen that at high frequencies the material doesn’t have enough time to fully charge to the given voltage. ...
... Due to this, it can be seen that at high frequencies the material doesn’t have enough time to fully charge to the given voltage. ...
X-ray tube

An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that produces X-rays. X-ray tubes evolved from experimental Crookes tubes with which X-rays were first discovered in the late 19th century, by Wilhelm Röntgen and the availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of opaque objects with penetrating radiation. X-ray tubes are also used in CAT scanners, airport luggage scanners, X-ray crystallography, and for industrial inspection.